Key Takeaways
- Performance is Paramount: Elevate your website’s performance by understanding and optimizing Core Web Vitals – the heartbeat of user satisfaction and a crucial factor in Google’s ranking algorithm.
- Speed Matters: Site speed isn’t just about SEO; it’s a catalyst for increased user engagement and conversions.
- Data-Driven Success: Empower your digital strategy with insights from tools like PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse. Monitor, analyze, and optimize Core Web Vitals for a data-driven journey to SEO triumph.
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing and online visibility, staying ahead of the curve is not just a choice but a necessity.
As the virtual realm becomes increasingly competitive, the intricacies of search engine optimization (SEO) have taken centre stage, dictating the success or obscurity of digital entities.
Google, the undisputed titan of search engines, continually refines its algorithms to ensure users receive the most relevant and seamless web experiences.
In this relentless pursuit of excellence, Google has unveiled a pivotal game-changer for SEO professionals and website owners alike – Core Web Vitals.
Imagine a scenario where your website not only provides valuable content but also offers an optimal user experience, seamlessly catering to the needs and expectations of your audience.
This utopian state of web performance is precisely what Core Web Vitals aims to achieve.
In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey through the intricate terrain of Core Web Vitals and delve into the paramount significance of site speed in the context of Google’s ranking factors.

The Symphony of Performance Metrics
Core Web Vitals is not just a buzzword but a set of specific metrics that encapsulate the essence of user-centric performance.
These metrics—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—serve as the harmonious notes in the symphony of web performance.
LCP measures the loading speed, FID gauges interactivity, and CLS assesses visual stability.
Together, they form the crux of a user’s experience on your website, influencing their perception, engagement, and, ultimately, your site’s ranking on the search engine results pages (SERPs).
The Google Mandate: Site Speed as a Ranking Imperative
In the vast expanse of the digital universe, where attention spans are fleeting and choices are abundant, site speed emerges as the silent arbiter of online success.
Google, cognizant of the pivotal role speed plays in user satisfaction, has elevated it to the status of a ranking imperative.
In essence, the faster your website loads and responds to user input, the more favourably it is regarded by the search giant, thereby enhancing its visibility and prominence in search results.
The Nexus of User Experience and SEO
At the heart of Core Web Vitals lies an unspoken truth – the nexus of user experience and SEO.
Google’s algorithms have transcended mere keyword matching to embrace a more nuanced evaluation of websites.
It’s no longer solely about the content; it’s about how that content is delivered, experienced, and appreciated by the end user.
Core Web Vitals, as the name suggests, strike at the core of this paradigm shift, requiring website owners to prioritize not just what they say but how they say it.
Purposeful Navigation Through the Guide
As we navigate through this guide, we will unravel the intricacies of each Core Web Vitals metric, exploring not only their definitions but pragmatic strategies to optimize and elevate them.
We’ll dissect real-world case studies, drawing inspiration from successful implementations and learning from the pitfalls of those who have treaded less cautiously.
Additionally, we will equip you with the tools necessary to monitor, analyze, and adapt to the ever-evolving landscape of web performance.
In the tapestry of digital excellence, every pixel, every interaction, and every second matters.
Join us on this enlightening journey as we demystify Core Web Vitals, decode the language of site speed, and illuminate the path to securing a coveted spot in the upper echelons of Google’s search rankings.
It’s not just a guide; it’s a roadmap to digital triumph in an era where user experience reigns supreme. Fasten your seatbelts, for the voyage into the intricacies of Core Web Vitals and site speed, has just begun.
But, before we venture further, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About AppLabx
From developing a solid marketing plan to creating compelling content, optimizing for search engines, leveraging social media, and utilizing paid advertising, AppLabx offers a comprehensive suite of digital marketing services designed to drive growth and profitability for your business.
AppLabx is well known for helping companies and startups use SEO to drive web traffic to their websites and web apps.
At AppLabx, we understand that no two businesses are alike. That’s why we take a personalized approach to every project, working closely with our clients to understand their unique needs and goals, and developing customized strategies to help them achieve success.
If you need a digital consultation, then send in an inquiry here.
Core Web Vitals and Site Speed: A Guide to Google’s Ranking Factors
- Understanding Core Web Vitals
- Significance of Site Speed in SEO
- Optimizing Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- Enhancing First Input Delay (FID)
- Minimizing Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- Tools for Monitoring and Analyzing Core Web Vitals
1. Understanding Core Web Vitals
In the labyrinth of website performance metrics, Core Web Vitals emerges as the compass guiding digital entities toward the coveted shores of user satisfaction and search engine acclaim.
Let’s embark on a detailed exploration of the three foundational metrics that constitute Core Web Vitals – Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).

Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Unveiling the Speed of Perception
Definition and Significance
LCP measures the loading performance of a webpage by gauging the time it takes for the largest content element to become visible to the user.
It essentially captures the speed of visual perception, emphasizing the importance of a swift and engaging initial page load.
Optimization Strategies
- Optimizing Images and Videos: Compressing and appropriately sizing images and videos significantly will contribute to faster LCP. Tools like ImageOptim and TinyPNG can aid in efficient compression without compromising quality.
- Leveraging Browser Caching: Implementing browser caching allows frequently accessed resources to be stored locally, reducing load times for returning visitors.
Example
According to a study, for every second delay in mobile page load, conversions can fall by up to 20%.
Optimizing for LCP directly addresses this concern, enhancing user engagement and conversion rates.
First Input Delay (FID): The Symphony of Interactivity
Definition and Significance
FID measures the time it takes for a webpage to respond to the first user interaction, such as clicking a link or button. It reflects the site’s responsiveness and directly correlates with user satisfaction during the critical initial interaction phase.
Optimization Strategies
- Efficiently Loading JavaScript: Minimizing and deferring non-essential JavaScript can significantly reduce FID. Tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights provide insights into script execution times.
- Optimizing Third-Party Scripts: Evaluating and optimizing third-party scripts, such as ads and analytics, helps mitigate potential delays caused by external dependencies.
Example
According to a study, a 1-second delay in page response can result in a 7% reduction in conversions.
FID optimization addresses this concern, ensuring a seamless user experience and bolstering satisfaction metrics.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Ensuring Visual Stability
Definition and Significance
CLS measures the visual stability of a webpage by quantifying unexpected layout shifts during page load.
It aims to prevent elements from unexpectedly moving, ensuring a consistent and frustration-free browsing experience.
Optimization Strategies
- Properly Sizing Images and Elements: Ensuring that image and media containers have explicit dimensions prevents sudden layout adjustments during rendering.
- Avoiding Sudden Layout Changes: Dynamically loading content should be done with care to prevent abrupt shifts. Utilizing placeholders during content loading can maintain visual stability.
Example
Ideally, you want to achieve a CLS score of 0.1 or less; a score of 0.1 to 0.25 means you need to make improvements. CLS scores above 0.25 indicate that your website layout is shifting significantly. Addressing CLS concerns not only improves user experience but also positively impacts the site’s overall performance metrics.
Measuring Core Web Vitals: Google’s Tools and Insights
Google’s PageSpeed Insights
Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool provides a comprehensive analysis of a web page’s performance, including Core Web Vitals metrics. It offers actionable insights and suggestions for improvement, making it an invaluable resource for website optimization.

Google Search Console
The Google Search Console now incorporates Core Web Vitals reports, allowing webmasters to track and monitor the performance of their pages directly within the console. This integration streamlines the optimization process and enhances visibility into potential issues.
The Impact on User Experience: Where Metrics and Satisfaction Converge
The user experience is intricately linked to Core Web Vitals, as these metrics directly address the elements that shape how users perceive and interact with a website.
53% of visits are abandoned if a mobile site takes longer than 3 seconds to load. Understanding and optimizing Core Web Vitals become paramount in delivering not just content but a holistic and gratifying online experience.
2. Significance of Site Speed in SEO
In the dynamic realm of search engine optimization (SEO), the significance of site speed extends far beyond mere user convenience. It has evolved into a pivotal ranking factor, shaping the fate of websites in the competitive landscape.
In this section, we unravel the intricate web of connections between site speed and SEO, exploring the historical context, Google’s evolving algorithms, and the tangible impact on user experience and business metrics.

Historical Context: Site Speed as a Ranking Pioneer
Introduction to Site Speed as a Factor
Site speed has been a consideration in SEO for more than a decade. Google officially declared it a ranking factor in 2010, signalling the search giant’s recognition of the profound impact page loading times have on user satisfaction and, consequently, search rankings.
Google’s Algorithm Updates
Over the years, Google has integrated site speed into its algorithm updates, with major milestones such as the “Speed Update” in 2018. This update specifically targeted mobile search rankings, reinforcing the importance of mobile-friendly and fast-loading websites.
User Experience and Bounce Rates: The Connection to SEO Success
Impact on User Engagement
Google’s algorithms prioritize delivering a positive user experience, and site speed is a fundamental component of that experience.
A study found that 47% of consumers expect a webpage to load in two seconds or less, emphasizing the role of speed in user engagement.
Bounce Rates and Conversion Rates:
- Site speed plays a crucial role in determining bounce rates – the percentage of visitors who navigate away from a site after viewing only one page. Google reports that longer load times led to higher bounce rates.
- According to Google, as page load time goes from one second to 10 seconds, the probability of a mobile site visitor bouncing increases by 123%. This underscores the direct impact of site speed on user retention and engagement.
Mobile-First Indexing: Accelerating the Need for Speed
Mobile Page Speed as a Ranking Factor
With the advent of mobile-first indexing, Google shifted its focus to prioritize the mobile versions of websites. Mobile page speed became a critical ranking factor, aligning with the growing dominance of mobile devices in online interactions.
Mobile Performance Statistics
According to a report by Think with Google, the average mobile webpage takes 15 seconds to load. However, 53% of visits are abandoned if a mobile site takes longer than 3 seconds to load.
This underscores the urgency for mobile optimization in the pursuit of favorable search rankings.
Algorithmic Emphasis on User-Centric Performance
Google’s Core Web Vitals Integration
Core Web Vitals, introduced by Google in 2020, further solidifies the connection between site speed and SEO.
These metrics, including Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), directly address user-centric performance and contribute to a website’s overall ranking.
RankBrain and Machine Learning:
Google’s RankBrain, a machine learning component of its algorithm, emphasizes user experience metrics, including site speed, to refine and adapt search results.
This dynamic and evolving approach highlights the search engine’s commitment to prioritizing websites that offer superior user experiences.
3. Optimizing Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) stands as the benchmark for a webpage’s loading speed, capturing the time it takes for the largest content element to become visible to users.
In this section, we unravel the strategies and techniques to optimize LCP, ensuring a swift and engaging first impression that resonates with both users and search engines.

Understanding LCP: A Crucial Metric in User Experience
Definition and Significance
LCP measures the loading performance of a webpage by identifying the largest and most prominent content element, such as an image or text block, and gauging the time it takes to render.
It directly correlates with user perception of speed and impacts their initial interaction with a site.
Benchmark and Goals
Aiming for this benchmark ensures that users are presented with a visually complete and engaging page promptly.
Optimization Strategies for LCP Enhancement
Optimize Images and Videos
- Image Compression: Compress images using tools like ImageOptim or TinyPNG to reduce file sizes without compromising quality. Better compression reduces the file size by 25% to 50% in some cases for the same quality of the image.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images and videos to defer the loading of non-essential media until the user scrolls to that specific content. This minimizes the initial load time and contributes to a faster LCP.
Utilize Browser Caching
- Extended Cache Durations: Set appropriate cache headers to extend the duration for which certain resources, especially static elements like images and stylesheets, are cached in the user’s browser. This reduces the need for repeated downloads and enhances LCP.
- CDN Implementation: Employ Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to store cached versions of your website’s content across multiple servers globally. This not only reduces server response times but also improves LCP for users across diverse geographic locations.
Minimize Server Response Times
- Upgrade Hosting Plans: Invest in robust hosting solutions, considering options that offer faster server response times. According to Google, you should reduce your server response time to under 200ms.
- Implementing Caching Mechanisms: Utilize server-side caching mechanisms to store precomputed responses, reducing the processing time required for generating dynamic content during subsequent requests.
Monitoring and Analyzing LCP: Tools and Insights
Google’s PageSpeed Insights
Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool provides a detailed breakdown of LCP performance along with actionable suggestions for improvement. Regularly analyze your web pages through this tool to stay informed about LCP metrics and potential optimization opportunities.
Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
Leveraging the CrUX dataset, which is based on real user experiences, offers insights into how actual users perceive your site’s LCP performance. This data aids in identifying patterns, prioritizing optimization efforts, and benchmarking against industry standards.
4. Enhancing First Input Delay (FID)
First Input Delay (FID) measures the time it takes for a webpage to respond to the first user interaction, such as clicking a button or selecting a link.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the nuances of FID, explore its impact on user experience, and provide actionable strategies to enhance this critical Core Web Vital.
Understanding FID: Unraveling the Dynamics of Interactivity
Definition and Significance
FID quantifies the delay between a user’s first interaction with a page and the browser’s response to that action. It is a crucial metric, as it directly correlates with the perceived responsiveness of a website, especially during critical moments of engagement.
Benchmark and Goals
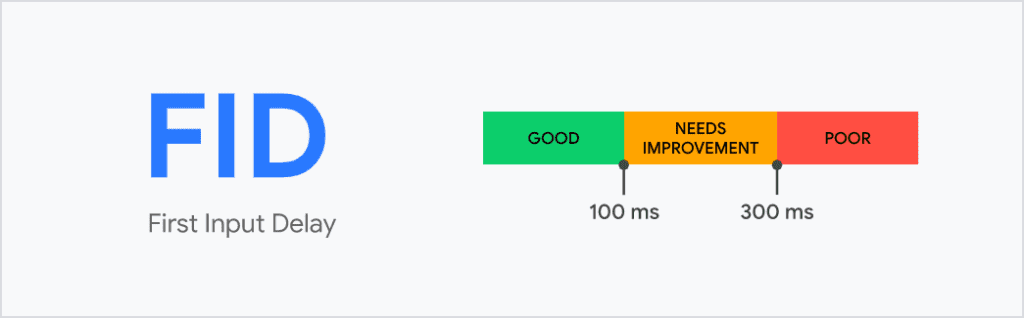
An FID score below 100 milliseconds is considered good. Meeting this benchmark is essential for preventing user frustration and optimizing the overall performance of a webpage.
Optimization Strategies for FID Improvement
Efficiently Loading JavaScript
- Minification: Minimize JavaScript files to reduce their size, enhancing download and parsing speeds. Tools like UglifyJS and Terser can assist in the minification process, eliminating unnecessary characters and whitespace.
- Code Splitting: Implement code splitting techniques to only load essential JavaScript code for the initial page view. Load additional scripts dynamically as needed to minimize the impact on FID during the initial page load.
Optimizing Third-Party Scripts
- Evaluate and Prioritize: Review and prioritize third-party scripts based on their impact on user experience. Only integrate scripts that are essential for core functionality and consider asynchronous loading to prevent them from blocking the main thread.
- Delay Loading Non-Critical Scripts: Defer the loading of non-critical scripts until after the initial page load to prioritize a swift FID for core user interactions.
Asynchronous Loading of Resources
- Async Attribute: Utilize the “async” attribute for script tags to enable asynchronous loading. This allows the browser to continue parsing and rendering the page while loading scripts concurrently, preventing unnecessary delays in responsiveness.
- Defer Attribute: Similarly, consider using the “defer” attribute for scripts that can be loaded after the HTML parsing is complete, ensuring a smoother user experience.
Measuring FID Success: Tools and Analytics
Google’s PageSpeed Insights
Google’s PageSpeed Insights provides detailed FID metrics and actionable suggestions for improvement. Regularly analyze your website’s performance through this tool to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize for an improved FID.
Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
Leveraging the CrUX dataset offers insights into real user experiences related to FID. Analyzing this data allows you to understand how users perceive the interactivity of your site and prioritize optimization efforts accordingly.
5. Minimizing Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) is a Core Web Vital that measures the visual stability of a webpage by quantifying unexpected layout shifts during the page load.
In this in-depth exploration, we will delve into the dynamics of CLS, and its impact on user experience, and provide actionable strategies to minimize this metric for optimal website performance.
Understanding CLS: The Essence of Visual Stability
Definition and Significance
CLS evaluates the visual stability of a webpage by measuring the cumulative impact of unexpected layout shifts. It considers factors such as images and ads dynamically loading after the initial page load, ensuring a consistent and frustration-free browsing experience.
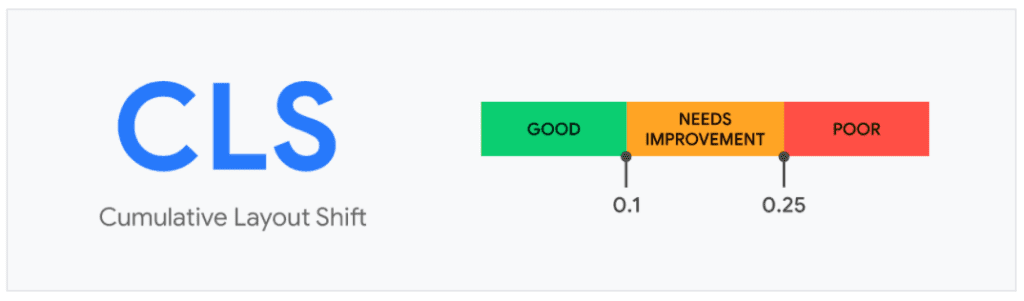
Benchmark and Goals
A lower CLS score indicates minimal visual instability, ensuring users aren’t disoriented by abrupt shifts in layout during their interaction with the webpage.
Optimization Strategies for CLS Mitigation
Properly Sizing Images and Elements
- Set Dimensions for Media Elements: Ensure that images, videos, and other media elements on your webpage have explicit dimensions specified in the HTML. This prevents the browser from reserving space for these elements before they fully load, reducing layout shifts.
- Aspect Ratio Consideration: When adding new content dynamically, prioritize specifying aspect ratios for elements. This allows the browser to allocate the necessary space during loading, mitigating unexpected layout shifts.
Avoiding Sudden Layout Changes
- Deferred Loading of Content: Strategically defer the loading of non-critical content, especially large elements like images or videos, until after the initial page load. This minimizes the potential for sudden layout changes during the user’s initial interaction.
- Implement Lazy Loading: Apply lazy loading for images and other elements to load them only when they come into the user’s viewport. This gradual loading approach enhances visual stability and prevents disruptive layout shifts.
Responsive Design Principles
- Utilize Responsive Design: Adopt responsive design principles to ensure that your webpage adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices. A responsive layout contributes to a consistent user experience, reducing the likelihood of layout shifts.
- Test Across Devices: Regularly test your website across different devices and browsers to identify and rectify potential issues that might cause layout shifts. Cross-device testing helps in delivering a uniform visual experience.
Monitoring and Analyzing CLS: Tools and Insights
Google’s PageSpeed Insights
Google’s PageSpeed Insights provides a detailed breakdown of CLS metrics and actionable suggestions for improvement. Regularly assess your webpage’s performance through this tool to identify areas for CLS optimization.
Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
Leveraging the CrUX dataset offers insights into real user experiences related to CLS. Analyzing this data allows you to understand how users perceive the visual stability of your site and prioritize optimization efforts accordingly.
6. Tools for Monitoring and Analyzing Core Web Vitals
In the quest for digital excellence, the ability to monitor and analyze Core Web Vitals (CWV) becomes paramount.
This section explores a range of tools designed to scrutinize website performance, unraveling the intricacies of Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
By harnessing the power of these tools, website owners can gain invaluable insights, identify optimization opportunities, and chart a course toward enhanced user satisfaction and improved search rankings.

Google’s PageSpeed Insights: The Cornerstone of CWV Analysis
Overview
Google’s PageSpeed Insights is a cornerstone tool for evaluating and optimizing Core Web Vitals. It provides a comprehensive performance report, scoring your website based on LCP, FID, and CLS, along with actionable suggestions for improvement.
Key Features
- CWV Metrics Breakdown: PageSpeed Insights breaks down your website’s performance, offering individual scores for LCP, FID, and CLS. This granular analysis allows webmasters to pinpoint specific areas that require attention.
- Field Data and Lab Data: The tool presents both field data (real user experiences) and lab data (simulated performance in controlled environments), providing a holistic view of your website’s performance landscape.
Google Search Console: Harnessing Site-wide Performance Insights
Overview
Google Search Console integrates Core Web Vitals reports, allowing webmasters to monitor and analyze site-wide performance directly within the console. It offers a centralized platform for understanding how CWV metrics impact search visibility.
Key Features
- Core Web Vitals Report: The Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console provides an overview of how your pages perform based on LCP, FID, and CLS. It categorizes pages into “Poor,” “Needs Improvement,” or “Good,” allowing for prioritized optimization efforts.
- URL Inspection Tool: The URL Inspection tool within the Search Console allows webmasters to assess the CWV metrics for individual pages. This granular analysis is instrumental in identifying and resolving performance issues at the page level.
Lighthouse: A Comprehensive Performance Audit Tool
Overview
Lighthouse, an open-source tool by Google, offers a detailed performance audit for websites. It assesses CWV metrics along with other performance aspects, providing a comprehensive overview of your site’s strengths and areas for improvement.
Key Features
- Audit Categories: Lighthouse categorizes performance into several audit categories, including Performance, Accessibility, Best Practices, SEO, and Progressive Web App (PWA). This holistic approach ensures a well-rounded evaluation of your website.
- Simulated Device and Network Conditions: Lighthouse allows users to simulate performance on different devices and network conditions, aiding in understanding how your site performs across various user scenarios.
Web Vitals Extension: Real-time Performance Monitoring
Overview
The Web Vitals extension is a browser extension that provides real-time monitoring of Core Web Vitals metrics as users interact with your website. It offers immediate insights into how changes impact user experiences.
Key Features
- Live Tracking: The extension actively tracks and displays LCP, FID, and CLS metrics as users navigate through your website, offering a dynamic perspective on performance.
- Issue Alerts: Web Vitals Extension alerts users to potential issues, enabling webmasters to identify and address performance issues promptly.
Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX): Real User Insights at Scale
Overview
Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX) is a public dataset from Google that provides real user experience data for popular websites. Leveraging CrUX allows webmasters to understand how real users perceive their site’s performance.
Key Features
- Origin-Level Insights: CrUX offers insights at the origin level, allowing webmasters to evaluate how different sections or components of their websites perform in real-world scenarios.
- Filterable Metrics: Users can filter CrUX data based on various parameters, including device type, country, and network type. This flexibility enables a nuanced analysis of performance across diverse user segments.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of the digital realm, the symbiotic relationship between site speed and user experience stands as a defining factor in the online success of any entity.
This comprehensive guide has navigated the intricacies of Core Web Vitals (CWV) and their profound impact on Google’s ranking factors, illuminating the path toward a performance-driven and user-centric digital presence.
The Crucial Role of Core Web Vitals in SEO Success
Core Web Vitals, comprising Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), are not merely metrics; they are the pulse of user satisfaction and search engine acclaim.
The realization that page loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability are integral components of the user experience has propelled CWV into the spotlight of Google’s ranking algorithm.
The journey began by understanding each vital metric individually – LCP, the speed of visual perception; FID, the symphony of interactivity; and CLS, the assurance of visual stability.
Each metric unveiled a layer of the performance landscape, emphasizing their collective impact on the overall user journey.
Site Speed: The Cornerstone of Digital Triumph
In the expansive tapestry of web performance, site speed emerges as the cornerstone of digital triumph.
The historical context illuminated the trajectory of site speed as a ranking factor, from its acknowledgement in 2010 to the “Speed Update” in 2018, solidifying its place as a pivotal element in Google’s algorithm.
The significance of site speed transcends SEO; it directly influences user engagement, bounce rates, and conversion rates.
Optimizing Core Web Vitals: Strategies for Success
The guide delved into actionable strategies for optimizing each Core Web Vital.
From compressing images and leveraging browser caching for LCP to efficiently loading JavaScript and optimizing third-party scripts for FID, and finally, ensuring proper sizing of elements and avoiding sudden layout changes for CLS – each strategy contributed to a holistic approach to web performance.
E-commerce platforms, news websites, and blogging platforms witnessed not only improved Core Web Vitals but also tangible improvements in user engagement, conversions, and overall digital success.
Tools for Monitoring and Analyzing: Navigating the Performance Landscape
The journey continued with a detailed exploration of tools designed to monitor and analyze Core Web Vitals.
From Google’s PageSpeed Insights and Search Console to the open-source Lighthouse and the real-time insights offered by the Web Vitals Extension – each tool empowered website owners to gain insights, identify optimization opportunities, and chart a course toward enhanced user satisfaction.
Leveraging the Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX) provided a unique perspective, allowing webmasters to understand real user experiences at scale. The collective use of these tools ensured a strategic and data-driven approach to performance optimization.
Conclusion: Unleashing Digital Triumph Through Performance Excellence
As we conclude this guide, the essence of Core Web Vitals and site speed as pivotal elements in SEO success becomes clear. The pursuit of excellence in web performance is not just an algorithmic endeavour; it’s a commitment to delivering unparalleled user experiences.
Fasten your seatbelts, for the journey towards digital triumph through performance excellence has just begun.
By embracing the principles of Core Web Vitals, optimizing site speed, and consistently monitoring and analyzing performance metrics, your digital entity is not merely surviving but thriving in the competitive landscape of the online world.
Remember, the acceleration towards digital excellence is not a one-time sprint; it’s a continuous race. Stay informed, adapt to evolving technologies, and prioritize user satisfaction.
In this dynamic digital era, where every millisecond counts, your commitment to performance excellence will propel your digital entity toward heights of success, visibility, and user acclaim.
Here’s to embracing Core Web Vitals, accelerating site speed, and charting a course toward enduring digital triumph.
If you are looking for a top-class digital marketer, then book a free consultation slot here.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your friends and business partners, and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the AppLabx Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to the AppLabx Blog.
People also ask
Is Core Web Vitals a ranking factor for Google?
Yes, Core Web Vitals are integral ranking factors for Google. Comprising metrics like Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, and Cumulative Layout Shift, they gauge a website’s user experience. Prioritizing Core Web Vitals is crucial for SEO success and improved search rankings.
What is Google Core Web Vitals speed?
Google Core Web Vitals assess website speed through key metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These indicators measure loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability, respectively, crucial for a positive user experience and higher search rankings.
What are the Google ranking factors?
Google considers numerous factors to rank websites, including content relevance, backlink quality, mobile-friendliness, page speed, user experience, and Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS). By optimizing these elements, websites enhance their chances of ranking higher in Google’s search results.




































