Key Takeaways
- Shared Hosting Essentials: Learn the fundamentals of shared hosting, where multiple websites coexist on a single server, sharing resources like CPU, RAM, and storage.
- Navigating Components: Understand the integral components of shared hosting, from user-friendly control panels to the choice between Linux and Windows operating systems.
- Optimizing Performance and Security: Explore strategies for enhancing website speed and efficiency in a shared hosting environment while fortifying your digital fortress with robust security measures.
Welcome to the dynamic world of web hosting, where the choice of the right hosting service can significantly impact the performance, reliability, and success of your online presence.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of one of the most popular and cost-effective hosting solutions – Shared Hosting.
Brace yourself for a journey into the heart of web hosting architecture as we unravel the mysteries behind “What Is Shared Hosting And How Does It Work?”
In the vast landscape of hosting options, Shared Hosting stands out as a compelling choice for individuals, small businesses, and startups looking to establish an online foothold without breaking the bank.
Whether you’re a seasoned website owner or a budding entrepreneur entering the digital realm, understanding the nuances of Shared Hosting is paramount.
The Hosting Tapestry Unraveled
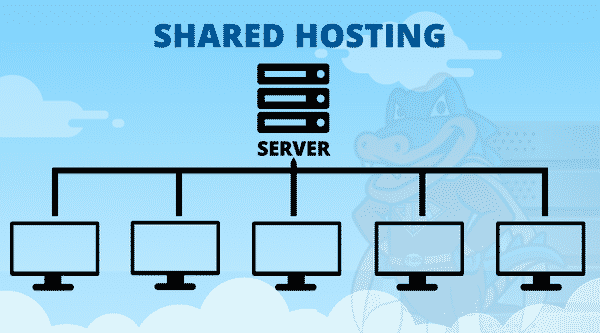
Shared Hosting, at its core, is a hosting arrangement where multiple websites share resources on a single server.
Imagine this server as a bustling apartment building, and each website as a tenant residing in one of the units.
These websites share common resources, such as CPU, RAM, and storage, akin to residents sharing communal amenities.
Unlike its counterparts, such as Virtual Private Servers (VPS) or dedicated hosting, Shared Hosting optimizes resource usage by hosting numerous websites on the same server.
This cost-effective model allows hosting providers to distribute operational expenses across multiple users, resulting in affordable hosting plans for individual website owners.
Peer into the Server Symphony
But how does this orchestration of shared resources actually work?
Picture the server as the central maestro coordinating a symphony of websites. Each website has its own sheet music, representing its code and content.
The server ensures that each website gets its turn to perform, distributing resources efficiently to prevent a cacophony of performance issues.
In this virtual symphony, the hosting provider plays a pivotal role as the conductor, managing server configurations, security protocols, and overall performance.
Through a user-friendly interface known as the control panel, website owners can tune their instruments, customize settings, and navigate the hosting landscape with ease.
Shared Hosting in the Spotlight
Now that we’ve scratched the surface, let’s spotlight the advantages and disadvantages that come with the Shared Hosting spotlight.
On one hand, cost-effectiveness and ease of use shine brightly, making Shared Hosting an attractive option for beginners and budget-conscious users.
On the other hand, resource limitations and potential security concerns cast a shadow that demands careful consideration.
While Shared Hosting undoubtedly offers a cost-effective entry point into the online world, its shared nature necessitates a keen understanding of the compromises involved.
Bandwidth limitations and the potential impact of neighbouring websites on performance are facets that require contemplation.
Choosing Your Shared Hosting Symphony
Selecting the right Shared Hosting provider is akin to choosing a conductor for your symphony.
Extensive research, an ear for features, and an understanding of your website’s needs are crucial elements in this decision-making process.
In this guide, we will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the hosting score.
From control panels like cPanel and Plesk to the intricacies of server operating systems such as Linux and Windows, we leave no stone unturned.
Your website’s performance is not just about the number of instruments; it’s about the harmony created when they all play in unison.
Embarking on an Informed Journey
As we embark on this journey through the shared corridors of hosting, our mission is to empower you with insights, best practices, and tips to make informed decisions.
From optimizing performance to fortifying your website’s security, we’re here to guide you through the symphony of Shared Hosting.
So, tighten your bowstrings, tune your instruments, and let’s dive into the multifaceted world of Shared Hosting – where your website’s performance takes center stage in the grand orchestration of the digital landscape.
But, before we venture further, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About AppLabx
From developing a solid marketing plan to creating compelling content, optimizing for search engines, leveraging social media, and utilizing paid advertising, AppLabx offers a comprehensive suite of digital marketing services designed to drive growth and profitability for your business.
AppLabx is well known for helping companies and startups use digital marketing to drive web traffic to their websites and web apps.
At AppLabx, we understand that no two businesses are alike. That’s why we take a personalized approach to every project, working closely with our clients to understand their unique needs and goals, and developing customized strategies to help them achieve success.
If you need a digital consultation, then send in an inquiry here.
What Is Shared Hosting And How Does It Work?
- Understanding Shared Hosting
- How Shared Hosting Works
- Shared Hosting Components
- Choosing the Right Shared Hosting Provider
- Tips for Optimizing Performance on Shared Hosting
- Security Measures for Shared Hosting
1. Understanding Shared Hosting
In the vast ecosystem of web hosting solutions, Shared Hosting emerges as a popular choice, particularly for those entering the online space with budget considerations.
Let’s embark on a detailed exploration to truly grasp the concept of Shared Hosting and its intricate workings.
Definition of Shared Hosting
Shared Hosting is a hosting arrangement where multiple websites share resources on a single server.
Think of it as a communal living space in the digital realm, where various websites coexist, sharing server space, CPU, RAM, and other resources.
This cost-effective model allows hosting providers to offer affordable plans by distributing operational costs among numerous users.
Key Features and Characteristics
- Cost-Efficiency: Shared Hosting is renowned for its affordability, making it an ideal choice for small businesses, bloggers, and individuals looking to establish an online presence without a hefty financial commitment.
According to a study, depending on where you go, you might find VPS hosting costing anywhere between twice as much to 10 times more than shared hosting. - Resource Sharing: The essence of Shared Hosting lies in the efficient sharing of resources among multiple websites.
While this results in a more economical solution, it also means that resources such as bandwidth and storage are distributed among all hosted websites, potentially impacting performance during traffic spikes.
Comparison with Other Hosting Types
To truly understand the merits of Shared Hosting, it’s essential to compare it with alternative hosting models, such as Virtual Private Servers (VPS) and dedicated hosting.
- Shared Hosting vs. VPS Hosting:
- Cost: Shared Hosting is generally more budget-friendly than VPS hosting.
- Isolation: VPS provides a higher level of isolation, as each virtual server operates independently, avoiding the potential impact of neighbouring websites.
- Shared Hosting vs. Dedicated Hosting:
- Resource Allocation: Dedicated hosting allocates an entire server to a single user, offering unparalleled resources. However, this comes at a significantly higher cost compared to Shared Hosting.
- Scalability: Shared Hosting is easily scalable, making it suitable for websites with varying levels of traffic. On the other hand, dedicated hosting may be more suitable for resource-intensive applications or websites with consistently high traffic.
2. How Shared Hosting Works
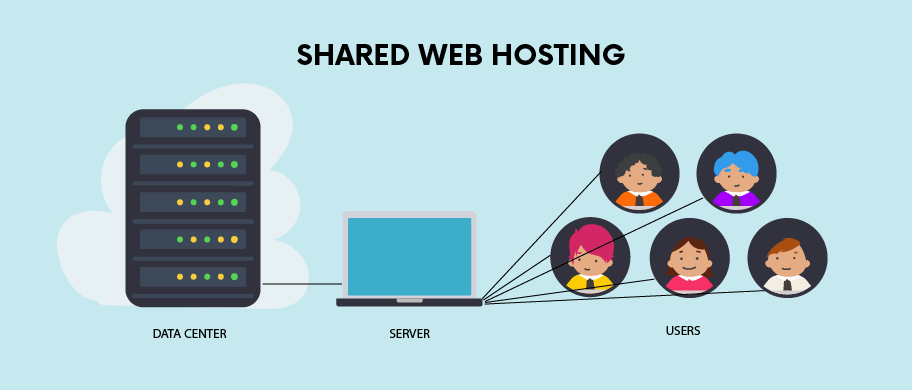
Shared Hosting, as a cost-effective and popular hosting solution, operates on a unique architecture where multiple websites coexist on a single server.
Let’s delve into the intricacies of how Shared Hosting works, exploring its server-sharing concept, resource distribution, and the role of hosting providers.

Server Sharing Concept
- Multiple Websites on a Single Server:
- Shared Hosting employs a communal living analogy, where multiple websites share the same server space. Visualize the server as a vast apartment building, with each website residing in its own “apartment” or hosting space.
- Just as residents share common areas like elevators and parking lots, websites on a shared server share essential resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage.
- Resource Sharing Among Websites:
- The shared nature of resources allows hosting providers to offer economical plans. However, it also means that the performance of one website can be influenced by the activities and traffic of others on the same server.
- Consider a scenario where one website experiences a sudden surge in traffic. This spike can impact the server’s overall performance, potentially affecting the loading times and responsiveness of other hosted sites.
Resource Distribution and Allocation
- Bandwidth Allocation:
- Bandwidth, the amount of data transferred between the server and visitors, is shared among all hosted websites. While hosting providers often allocate sufficient bandwidth, website owners need to monitor usage, especially during periods of increased traffic.
- Storage Sharing:
- Storage resources are distributed among websites, each having a designated amount for its files, databases, and other content.
Shared Hosting plans typically offer ample storage, but resource-hungry websites might encounter limitations, necessitating upgrades or alternative hosting solutions.
- Storage resources are distributed among websites, each having a designated amount for its files, databases, and other content.
The Role of Hosting Providers
- Server Management:
- Hosting providers play a pivotal role in managing and maintaining the shared server. Regular updates, security patches, and server optimizations fall under the purview of the hosting provider.
This ensures that the server environment remains secure, and stable, and performs optimally.
- Hosting providers play a pivotal role in managing and maintaining the shared server. Regular updates, security patches, and server optimizations fall under the purview of the hosting provider.
- Control Panel Functionality:
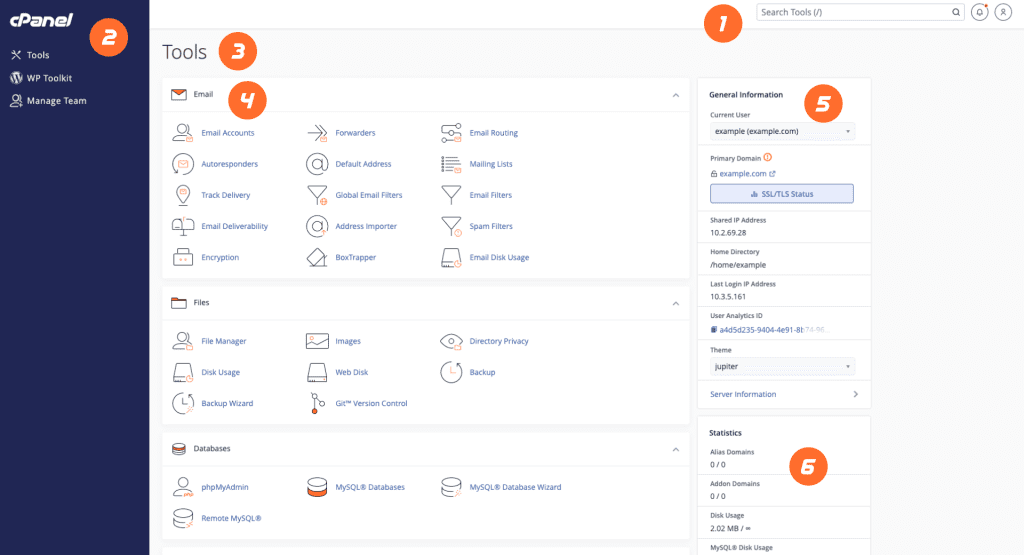
- Hosting providers equip users with control panels, such as cPanel or Plesk, offering an intuitive interface for managing various aspects of their websites.
From domain management to email configuration, control panels empower users to navigate and control their hosting environment effortlessly. - Example: Let’s consider cPanel, a widely used control panel. It provides a graphical interface and tools for tasks like managing files, creating databases, and installing applications. Its user-friendly nature makes it accessible even to those with limited technical expertise.
- Hosting providers equip users with control panels, such as cPanel or Plesk, offering an intuitive interface for managing various aspects of their websites.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages of Shared Hosting:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Shared Hosting is budget-friendly, making it an ideal choice for individuals and small businesses.
- Ease of Use: The simplicity of Shared Hosting makes it accessible to beginners. The user-friendly interfaces provided by control panels contribute to a seamless hosting experience.
- Maintenance Handled by Provider: Hosting providers take on the responsibility of server maintenance, security protocols, and updates, allowing website owners to focus on content creation and business development.
- Disadvantages of Shared Hosting:
- Resource Limitations: The shared nature of resources means that websites may face limitations during traffic spikes. While hosting providers allocate resources, excessive usage by one website can impact the performance of others.
- Security Concerns: Shared servers pose security challenges. A security vulnerability in one website may potentially affect others on the same server. However, hosting providers implement security measures to mitigate these risks.
- Example: In a shared hosting environment, if one website experiences a security breach, there’s a slim chance it could affect other websites on the same server.
This emphasizes the importance of implementing robust security measures, such as regular updates and secure coding practices.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
- Scalability in Shared Hosting:
- Shared Hosting offers scalability to accommodate the evolving needs of websites. As a website grows, hosting plans can be upgraded to VPS or dedicated hosting for increased resources and performance.
- Performance Optimization Tips:
- Website owners can optimize performance on a shared server by adopting efficient coding practices, utilizing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), and ensuring regular updates and maintenance.
- Example: Implementing a CDN can significantly enhance website performance by distributing content across multiple servers globally. This reduces latency and accelerates page loading times, providing an improved user experience.

3. Shared Hosting Components
Shared Hosting relies on a set of key components to facilitate the smooth operation of multiple websites on a single server. Understanding these components is essential for users navigating the shared hosting landscape.
In this section, we’ll delve into the integral elements, exploring control panels and server operating systems that contribute to the functionality of Shared Hosting.

Control Panel
- cPanel: A User-Friendly Powerhouse:
- Usage Statistics: cPanel stands out as a leading control panel in the shared hosting realm. cPanel has a market share of 93.59% in the web-hosting-control-panel market.
- User Interface and Functionalities: Known for its user-friendly interface, cPanel empowers website owners to manage various aspects of their hosting environment effortlessly.
Tasks such as domain management, file uploads, and email configuration are streamlined for a seamless user experience.
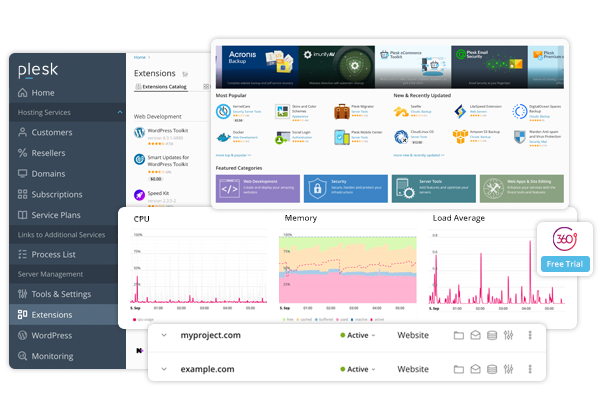
- Plesk: Versatility for Shared and VPS Hosting:
- Adoption Across Platforms: Plesk is another robust control panel with widespread adoption in both shared and VPS hosting environments. Its versatility caters to users with diverse hosting needs.
- Server and Website Management: Plesk offers a comprehensive suite of features, allowing users to manage servers and websites efficiently. From setting up domains to configuring databases, Plesk provides a centralized hub for hosting management.
- Example: Imagine a user leveraging cPanel to effortlessly upload files, manage domains, and configure email settings. The graphical interface simplifies complex tasks, making it accessible to both novice and experienced website owners.
Server Operating System
- Linux: Dominance in Stability and Security:
- Usage Dominance: Linux asserts its dominance in the shared hosting arena.
- Benefits of Linux: Renowned for stability, security, and open-source flexibility, Linux serves as a reliable foundation for shared hosting environments. Its compatibility with popular web technologies like PHP and MySQL contributes to its widespread adoption.
- Windows: Niche Applicability and Specific Technologies:
- Specialized Applications: While less common in shared hosting, Windows operating systems find favour for specific applications and technologies, such as ASP.NET.
- Considerations for Compatibility: Website owners opt for Windows hosting when their websites rely on technologies that align with the Windows environment. It’s a niche choice catering to specific compatibility requirements.
- Example: Consider a website running on a Linux server benefiting from the platform’s stability and security features. On the other hand, a website utilizing ASP.NET might find Windows hosting more suitable due to compatibility requirements.
Impact on Website Performance and Compatibility
- Linux: Open-Source Powerhouse:
- Community Support: The open-source nature of Linux fosters a robust community, ensuring continuous development, updates, and support. This communal strength contributes to the platform’s reliability.
- Compatibility with Popular Technologies: Linux’s compatibility with widely used web technologies, such as PHP and MySQL, makes it a preferred choice for websites built on these foundations.
- Windows: Niche Compatibility for Specialized Needs:
- Support for ASP.NET: Windows hosting becomes relevant when websites rely on technologies like ASP.NET, which is specifically designed for the Windows environment.
- Considerations for Proprietary Software: Some proprietary software applications are optimized for Windows, influencing the choice of hosting platform based on compatibility requirements.
- Example: A website running a content management system (CMS) developed in PHP and utilizing a MySQL database might seamlessly operate on a Linux server. Conversely, a website built with ASP.NET might require the Windows environment for optimal performance.
4. Choosing the Right Shared Hosting Provider
Selecting the ideal shared hosting provider is a critical decision that can significantly impact your website’s performance, security, and overall online presence.
In this guide, we’ll explore the key factors to consider when choosing a shared hosting provider, backed by relevant data and examples to aid in your decision-making process.

Researching Hosting Providers
- Market Share and Popularity:
- Explore market share statistics to gauge the popularity and trustworthiness of hosting providers.
- Example: Bluehost, powering over 2 million websites, is renowned for its reliability and user-friendly services.
- User Reviews and Testimonials:
- User reviews on platforms like Trustpilot, G2, and others offer insights into the real-world experiences of customers. Look for providers with positive reviews and consistent customer satisfaction.
- Example: SiteGround boasts a 4.8/5 rating on Trustpilot, emphasizing its commitment to customer satisfaction.
Important Features to Consider
Bandwidth and Storage
- Adequate Bandwidth Allocation:
- Ensure the hosting provider allocates sufficient bandwidth for your website’s needs. 99% of websites currently on the web use no more than 5 GB of bandwidth a month.
- Example: Bluehost provides unlimited bandwidth on its shared hosting plans, catering to the diverse needs of website owners.
- Sufficient Storage Space:
- Assess your website’s storage requirements and choose a provider that offers adequate storage.
- Example: HostGator’s shared hosting plans come with ample storage space, ensuring users have room to grow their online presence.
Uptime Guarantees
- Reliable Uptime Performance:
- Evaluate the uptime guarantees provided by hosting providers.
- Example: SiteGround boasts an impressive uptime guarantee of 99.99%.
Customer Support
- 24/7 Customer Support:
- Opt for a provider with reliable 24/7 customer support.
- Example: A2 Hosting is praised for its responsive 24/7 customer support, offering assistance through various channels, including live chat and ticketing.
Additional Considerations
- Scalability Options:
- Evaluate the scalability options offered by hosting providers. A provider that allows seamless upgrades to higher-tier plans or other hosting types accommodates the evolving needs of your website.
- Security Measures:
- Prioritize providers with robust security measures, such as SSL certificates and regular backups. Security breaches can have severe consequences, and proactive measures are crucial.
- Example: Bluehost includes a free SSL certificate with its shared hosting plans, enhancing website security and instilling trust among visitors.
Making an Informed Decision
Comparative Analysis
- Feature Comparison:
- Conduct a thorough feature-by-feature comparison of shortlisted hosting providers. Assess factors like control panel options, one-click installations, and additional perks offered.
- Pricing Considerations:
- Compare pricing structures and consider long-term affordability. The average price for shared web hosting is between $1.49 and $15 per month.
- Example: SiteGround’s pricing reflects a balance between quality services and affordability, making it a competitive choice in the shared hosting market.
5. Tips for Optimizing Performance on Shared Hosting
Optimizing performance on shared hosting is a crucial aspect of ensuring your website delivers a seamless experience to visitors.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective strategies, backed by relevant examples and verified data, to enhance the performance of your website within a shared hosting environment.
Efficient Coding Practices
- Minimize HTTP Requests:
- Around 80% of application response time is spent downloading elements such as images, stylesheets, scripts, etc.
- Example: Combine CSS and JavaScript files to reduce the number of HTTP requests. WordPress plugins like Autoptimize can automate this process, improving page load times.
- Optimize Images:
- Unoptimized images can significantly impact page load times.
- Example: Utilize image compression tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file sizes without compromising quality.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Usage
- Reduce Latency with CDNs:
- A CDN reduces latency, thus delivering content faster to end-users.
- Example: Cloudflare, a popular CDN provider, offers a free plan with basic performance optimizations, including global content distribution and caching.
- Distributed Servers for Global Reach:
- Example: Choose a CDN with a wide network of distributed servers. Amazon CloudFront, for instance, spans across numerous locations globally, ensuring fast content delivery.

Regular Updates and Maintenance
- Keep Software and Plugins Updated:
- Outdated software and plugins are common targets for security breaches. Regular updates are essential for maintaining website security and performance.
- Example: Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress provide automatic updates for core software and plugins, ensuring you have the latest features and security patches.
- Database Optimization:
- Inefficient queries can cause the database to become overloaded, leading to decreased performance and increased response times for users. Optimizing databases can lead to a significant speed boost.
- Example: Use plugins like WP-Optimize for WordPress or phpMyAdmin for manual database optimization. Regularly clean up unnecessary data and optimize database tables.
Server-Side Optimization
- Choose a Fast and Reliable Hosting Provider:
- Hosting performance directly impacts website speed. According to Google, for every second delay in mobile page load, conversions can fall by up to 20%.
- Example: SiteGround is renowned for its performance-focused shared hosting plans, utilizing technologies like SSD storage and server-side caching to enhance website speed.
- Utilize OpCode Caching:
- OpCode caching, such as through PHP’s OPcache extension, can significantly reduce server response times.
- Example: Most hosting providers enable OpCode caching by default. For example, Bluehost includes OpCode caching on its shared hosting plans, improving PHP script execution.
Content Optimization
- Leverage Browser Caching:
- Enabling browser caching allows returning visitors to load your site faster by storing static resources locally. Google recommends a minimum cache time of one week and preferably up to one year for static assets or assets that change infrequently.
- Example: In the website’s .htaccess file, you can specify caching rules. For WordPress users, plugins like W3 Total Cache simplify this process.
- Lazy Loading for Images:
- Lazy loading defers the loading of images until they are about to appear in the user’s viewport.
- Example: WordPress users can implement lazy loading using plugins like Lazy Load by WP Rocket or native support in recent WordPress versions.
Monitoring and Analytics
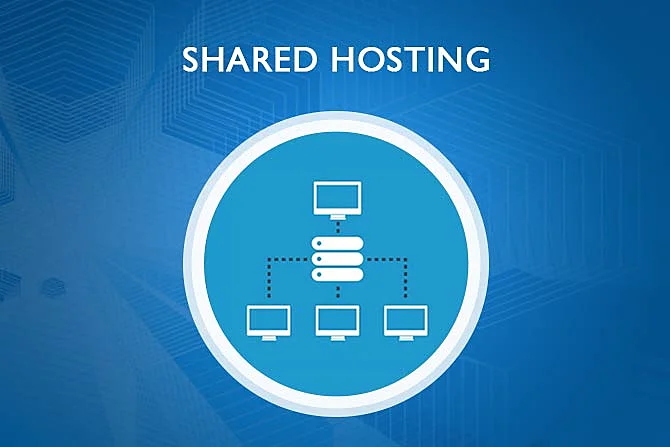
- Use Performance Monitoring Tools:
- Regular performance monitoring is crucial for identifying bottlenecks.
- Example: Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or New Relic provide valuable insights into website performance, helping you pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Google Analytics for User Insights:
- Google Analytics provides valuable user behavior insights.
- Example: Regularly analyze Google Analytics reports to identify high-traffic pages, user demographics, and user flow, helping you tailor your optimization efforts effectively.
6. Security Measures for Shared Hosting
Securing your website on shared hosting demands a robust strategy, as the shared environment introduces unique challenges.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into effective security measures, supported by relevant examples and verified data, to ensure the safety of your website within a shared hosting landscape.

SSL Encryption
- Importance of SSL Encryption:
- Google emphasizes the importance of SSL encryption, considering it a ranking factor. 85% of web users state they wouldn’t buy through a website where they weren’t certain their data was being transferred securely.
- Example: Bluehost includes a free SSL certificate with its shared hosting plans, encrypting data transmitted between users and the server.
- Types of SSL Certificates:
- Different SSL certificate types offer varying levels of security. Extended Validation (EV) certificates, for instance, provide the highest level of trust.
- Example: Namecheap offers a range of SSL certificates, allowing users to choose the level of validation that suits their website’s security requirements.
Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
- Role of Web Application Firewalls:
- WAFs protect websites from various online threats, including SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
- Example: SiteGround integrates a robust WAF into its shared hosting environment, shielding websites from common online threats.
- Cloud-Based WAF Solutions:
- Cloud-based WAF solutions offer scalability and real-time threat detection.
- Example: Sucuri, a leading website security platform, provides a cloud-based WAF that protects websites against DDoS attacks, malware, and other online threats.
Regular Software Updates
- Significance of Software Updates:
- Unpatched software is a common target for cyberattacks. Unpatched vulnerabilities are directly responsible for 60% of all data breaches.
- Example: Hosting providers like A2 Hosting prioritize server and software updates to ensure the latest security patches are applied promptly.
- Automated Update Features:
- Automated updates streamline the process of applying security patches.
- Example: Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress offer automated updates for core software and plugins, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities.
Account Isolation and Resource Monitoring
- Isolation of User Accounts:
- Isolating user accounts prevents the impact of security breaches on other accounts.
- Example: HostGator employs account isolation measures to contain security incidents and protect shared hosting accounts.
- Resource Monitoring for Anomalies:
- Monitoring resource usage helps detect abnormal activities, potentially indicating a security threat.
- Example: InMotion Hosting includes resource monitoring tools in its shared hosting plans, allowing users to track and address any unusual resource usage patterns.
Two-factor Authentication (2FA)
- Enhancing Login Security with 2FA:
- Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to account logins.
- Example: Namecheap offers 2FA as an optional security feature for its shared hosting account logins, enhancing overall account security.
- Implementation Across Control Panels:
- Two-factor authentication is supported by popular control panels. cPanel, for instance, provides documentation on enabling 2FA for enhanced security.
- Example: Users of cPanel-based hosting accounts, including those offered by Bluehost, can enable 2FA to secure their account access.
Conclusion
In our exploration of “What Is Shared Hosting And How Does It Work?” we’ve embarked on a journey through the intricacies of a hosting solution that serves as the foundation for countless websites across the digital realm.
From unraveling the core concept of shared hosting to delving into its mechanics and components, our comprehensive guide has aimed to empower you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions in the vast world of web hosting.
Shared Hosting Unveiled: A Recap
We commenced our journey by demystifying the concept of shared hosting. In this communal living arrangement of the digital world, multiple websites coexist on a single server, sharing essential resources like CPU, RAM, and storage.
This shared environment offers an accessible and budget-friendly entry point for individuals and small businesses venturing into the online landscape.
Understanding Shared Hosting Components
Diving into the components of shared hosting, we explored control panels like cPanel and Plesk, providing users with intuitive interfaces for managing their hosting environment.
The choice between Linux and Windows operating systems was dissected, considering factors like website technologies and community support.
We navigated through the importance of these components in shaping the hosting experience and how they contribute to website performance.
How Shared Hosting Works: Unveiling the Mechanics
Our exploration continued into the mechanics of how shared hosting operates.
We dissected the server-sharing concept, delving into the resource-sharing dynamics among websites.
Resource distribution, bandwidth allocation, and storage sharing were unraveled, shedding light on the nuances that website owners must navigate in a shared hosting environment.
The role of hosting providers, from server management to control panel functionalities, emerged as a critical factor in ensuring a stable and secure hosting experience.
Optimizing Performance on Shared Hosting
Recognizing the significance of website performance, we ventured into strategies for optimizing speed and efficiency on shared hosting.
From efficient coding practices and CDN utilization to regular updates and server-side optimizations, we provided a roadmap for website owners to enhance their online presence within the constraints of a shared hosting environment.
Choosing the Right Shared Hosting Provider
In the vast sea of hosting providers, selecting the right one is a pivotal decision.
We explored market share, user reviews, and essential features to consider when making this choice.
Security Measures for Shared Hosting: Fortifying Your Digital Fortress
As security is paramount in the online landscape, we delved into robust security measures tailored for shared hosting.
From SSL encryption and web application firewalls to regular software updates and two-factor authentication, we equipped website owners with a comprehensive security toolkit to protect their digital assets.
A Secure Haven in Shared Hosting: A Resilient Conclusion
In conclusion, shared hosting serves as a dynamic and cost-effective solution for individuals and small businesses venturing into the digital arena.
Armed with an understanding of its workings, components, performance optimization strategies, and security measures, you are well-prepared to navigate the shared hosting landscape with confidence.
Remember, the choice of a hosting solution is not one-size-fits-all. It should align with the unique needs and goals of your website.
Whether you’re launching a personal blog, a small business site, or an e-commerce platform, the insights gained from this guide empower you to make decisions that propel your online presence forward.
As you embark on your shared hosting journey, stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay curious. The digital landscape is ever-evolving, and with the right knowledge, you have the tools to not only navigate the shared hosting terrain but to thrive in it.
Here’s to a seamless and secure hosting experience, and may your digital endeavours reach new heights.
If you are looking for a top-class digital marketer, then book a free consultation slot here.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your friends and business partners, and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the AppLabx Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to the AppLabx Blog.
People also ask
How does shared hosting work?
Shared hosting works by hosting multiple websites on a single server. Websites share server resources like CPU, RAM, and storage. It’s cost-effective, making it ideal for small websites. However, resource sharing can impact performance if one site experiences high traffic or resource usage.
What is hosting and how does it work?
Hosting involves storing a website’s files on a server, making it accessible on the internet. Servers store data, and hosting providers manage these servers. When a user enters a website’s domain, the server delivers the website’s files to their browser, enabling access and interaction.
When should I use shared hosting?
Choose shared hosting for small to medium websites with moderate traffic. It’s cost-effective, making it ideal for beginners, bloggers, and small businesses. Shared hosting is user-friendly, but consider upgrading to a more robust solution as your website grows in size and traffic.