Key Takeaways
- Quality Score Unveiled: Gain a deep understanding of Google Ads Quality Score, unraveling its dynamics as a pivotal metric influencing ad relevance, click-through rates, and landing page experience.
- Strategies for Success: Learn actionable strategies for enhancing Quality Score, from crafting compelling ad copy to optimizing landing pages. Elevate your campaigns with proven techniques for achieving higher click-through rates and conversions.
- Avoid Common Pitfalls: Navigate the Google Ads landscape with confidence by sidestepping common mistakes. Discover the pitfalls to avoid, from neglecting keyword research to inadequate budget management, ensuring your campaigns thrive with precision and efficiency.
In the ever-evolving realm of online advertising, mastering the intricacies of platforms like Google Ads is paramount for digital marketers seeking to maximize their campaigns’ effectiveness.
One crucial metric that stands as a linchpin in the success of Google Ads endeavors is the elusive Quality Score.
Understanding its nuances is akin to unlocking the secret sauce that can propel your ads to the zenith of search engine results and, consequently, boost your return on investment.
Quality Score is more than just a number; it’s a dynamic indicator meticulously calculated by the Google Ads algorithm, influencing the fate of your ads in the competitive digital landscape.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the concept of Quality Score, peeling back the layers to reveal its composition, intricacies, and the pivotal role it plays in determining ad visibility, position, and cost-effectiveness.

Embarking on the Quality Score Odyssey
Picture this: a user enters a search query into Google, and your ad appears as a lifeline, ready to provide the solution they seek.
However, the journey from that query to a potential conversion is governed by an algorithmic arbiter – the Quality Score.
In this odyssey, understanding the nature of Quality Score is akin to having a seasoned guide leading you through uncharted territories.
Defining the Enigma: What Exactly is Quality Score?
Quality Score is not a mere arbitrary ranking; it’s a dynamic amalgamation of several key components that Google deems essential for an ad’s relevance and user experience.
These components – click-through rate (CTR), ad relevance, and landing page experience – serve as the compass guiding your ad through the labyrinth of search engine algorithms.
As we delve deeper, we’ll unravel the significance of each element and decipher how they collectively mold the fate of your Google Ads.
Deciphering the Components: Click-Through Rate, Ad Relevance, and Landing Page Experience
Click-through rate, the first pillar of Quality Score, gauges the effectiveness of your ad in enticing users to click. Ad relevance examines the alignment between your ad content and the user’s query, ensuring that your ad is precisely what they’re looking for.
The landing page experience, the final piece of the puzzle, evaluates the user’s journey post-click, emphasizing the importance of a seamless transition from ad to the landing page.
The Weighted Alchemy: Understanding the Impact on Position and Cost-per-Click
The elusive Quality Score is not just a vanity metric; its impact is palpable on two critical fronts – ad position and cost-per-click (CPC).
A high Quality Score can propel your ad to prime real estate on the search engine results page (SERP), ensuring maximum visibility. Simultaneously, a favorable Quality Score can result in lower CPC, optimizing your budget for enhanced cost-effectiveness.
As we navigate this intricate interplay, you’ll uncover strategies to harness the power of Quality Score for optimal results.
Join us on this expedition into the heart of Google Ads, where Quality Score reigns supreme. Together, we’ll unravel the intricacies of its calculation, explore real-world examples, and arm you with strategies to enhance each component.
Whether you’re a seasoned digital marketer or a novice navigating the digital advertising landscape, this guide is your compass to navigating the enigmatic realm of Quality Score and transforming your Google Ads campaigns into triumphs. Let the journey begin.
But, before we venture further, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About AppLabx
From developing a solid marketing plan to creating compelling content, optimizing for search engines, leveraging social media, and utilizing paid advertising, AppLabx offers a comprehensive suite of digital marketing services designed to drive growth and profitability for your business.
AppLabx is well known for helping companies and startups use Google Ads to drive web traffic to their websites and web apps.
At AppLabx, we understand that no two businesses are alike. That’s why we take a personalized approach to every project, working closely with our clients to understand their unique needs and goals, and developing customized strategies to help them achieve success.
If you need a digital consultation, then send in an inquiry here.
What Is Quality Score in Google Ads and How Does It Work?
- Understanding Quality Score
- How Quality Score is Calculated
- Importance for Advertisers
- Strategies for Improving Quality Score
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Understanding Quality Score
When it comes to Google Ads, Quality Score stands as the linchpin for success.
To navigate the labyrinth of digital advertising, it’s imperative to dissect the core components of Quality Score and discern their impact on the fate of your campaigns.
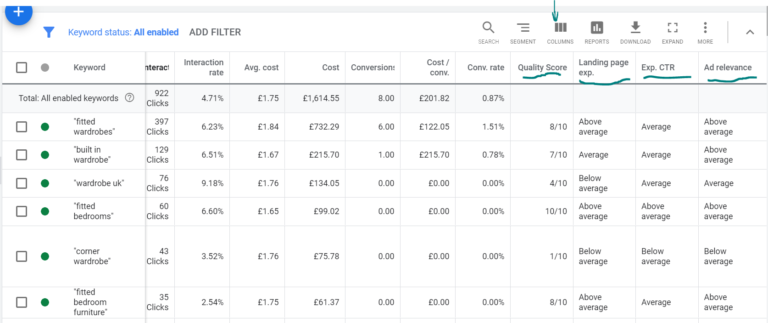
Click-Through Rate (CTR): The Catalyst for Ad Engagement
Click-Through Rate (CTR) is the heartbeat of your ad’s performance.
It represents the percentage of users who click on your ad after viewing it.
A higher CTR signifies that your ad is resonating with your target audience, prompting them to take the desired action.
Example: Let’s say Ad A receives 1000 impressions and garners 50 clicks, resulting in a CTR of 5%.
Meanwhile, Ad B, with the same number of impressions, only manages 20 clicks, yielding a CTR of 2%. Despite equal exposure, Ad A’s higher CTR suggests it’s more compelling and relevant to users.
However, this varies significantly by industry, with top-performing industries achieving CTRs well above this average.
Ad Relevance: Aligning Ad Content with User Intent
Ad relevance measures how well your ad aligns with the user’s search intent.
It’s a pivotal factor in ensuring that users see ads that are pertinent to their queries, contributing to a positive user experience.
Example: Consider a user searching for “best budget smartphones.” An ad promoting premium smartphones may have low ad relevance in this context, while an ad highlighting affordable options aligns better with the user’s intent.
Landing Page Experience: Nurturing the User’s Post-Click Journey
Landing Page Experience evaluates the relevance and quality of the landing page users encounter after clicking on your ad. It emphasizes the importance of delivering a seamless and informative post-click experience.
Example: Imagine a user clicks on an ad promising a discount on a specific product. If the landing page fails to showcase the discounted items prominently or is difficult to navigate, the user may exit, leading to a subpar Landing Page Experience.
Weightage of Each Component: Balancing the Equation
Understanding the weightage assigned to each component is crucial for optimizing your Quality Score.
While Google doesn’t disclose specific weights, it’s widely acknowledged that CTR holds significant importance, followed closely by ad relevance and landing page experience.
Example: If Ad X has a stellar CTR but lacks ad relevance and a compelling landing page, its overall Quality Score may still suffer. Striking a balance between all components is the key to a holistic and high-performing campaign.
2. How Quality Score is Calculated
Understanding the intricacies of how Google calculates Quality Score is paramount for digital marketers aiming to optimize their Google Ads campaigns.
This section will delve into the algorithmic alchemy behind Quality Score, dissecting its components and shedding light on the mysterious calculations that influence the fate of your ads.

Google’s Algorithm: The Formula for Quality Score
Google’s algorithm for calculating Quality Score is a proprietary blend of various factors, each assigned a specific weightage.
While the exact formula is not disclosed, Google provides insights into the key components that contribute to the overall Quality Score.
Example: Consider an ad with a CTR of 3%, an ad relevance rating of “average,” and a landing page experience marked as “above average.” These metrics, when fed into Google’s algorithm, are combined to produce a numerical Quality Score.
Examples: Deciphering the Calculation in Action
Understanding how the algorithm works becomes clearer when examining real-world examples.
Let’s explore scenarios that demonstrate the impact of each component on the final Quality Score.
- Ad X has a CTR of 8%, an ad relevance rating of “above average,” and a landing page experience marked as “average.”
- Ad Y has a CTR of 3%, an ad relevance rating of “below average,” and a landing page experience marked as “above average.”
In this scenario, despite Ad Y having a superior landing page experience, the lower CTR and ad relevance could result in a lower overall Quality Score compared to Ad X.
3. Importance for Advertisers
Quality Score isn’t just a digital marketing metric; it’s a powerful tool that can significantly impact the success of your Google Ads campaigns.
In this expansive section, we’ll delve into the importance of Quality Score for advertisers, providing real-world examples and backed by relevant data to underscore its significance.

Cost-Effectiveness: Maximizing ROI through Quality Score
Achieving a high Quality Score directly translates to more cost-effective advertising, allowing advertisers to optimize their budgets while maintaining or improving their ad positions.
Example: Consider Advertiser A with a Quality Score of 8 and Advertiser B with a Quality Score of 5.
Although both advertisers bid the same amount, Advertiser A enjoys a lower cost-per-click (CPC) due to the higher Quality Score, resulting in a more efficient use of their advertising budget.
A high Quality Score lowers CPC, stretching your ad budget.
Ad Performance: Elevating Visibility and Engagement
Quality Score plays a pivotal role in determining where your ads appear on the search engine results page (SERP).
A higher Quality Score translates to better ad positions, increasing visibility and engagement with your target audience.
Example: Imagine Advertiser X and Advertiser Y both bid on a competitive keyword. Advertiser X boasts a Quality Score of 9, securing a top ad position, while Advertiser Y, with a lower Quality Score of 4, appears lower on the page.
Advertiser X’s ad is more likely to attract clicks and conversions due to its prominent position.
Enhanced Ad Visibility: Capturing User Attention
A high Quality Score not only impacts ad position but also influences ad extensions and other ad formats, enhancing overall visibility and increasing the likelihood of user interaction.
Example: Ad extensions, such as site links and callouts, are more likely to be shown for ads with high Quality Scores. Advertiser Z, with a Quality Score of 10, can showcase additional links and information in their ad, providing users with more reasons to click.
The Domino Effect on Campaign Success: Beyond Clicks to Conversions
A high Quality Score isn’t just about securing clicks; it’s about creating a positive user experience that extends to post-click interactions. This, in turn, contributes to higher conversion rates and improved campaign success.
Example: Consider Advertiser C and Advertiser D, both with similar click-through rates. However, Advertiser C, with a superior Quality Score, delivers users to a highly relevant and optimized landing page.
The result is a higher conversion rate, illustrating the impact of Quality Score on the entire user journey.
Ad Rank Impact: Balancing Bid Amounts with Quality Score
Ad Rank, a key factor in ad position, is calculated by multiplying your bid by your Quality Score.
This combination ensures a fair and balanced competition where advertisers with high-quality ads can achieve competitive positions without necessarily having the highest bids.
Example: Advertiser E bids $2 with a Quality Score of 8, resulting in an Ad Rank of 16. In contrast, Advertiser F bids $3 with a Quality Score of 5, resulting in the same Ad Rank of 15. Advertiser E secures a higher position despite a lower bid due to a superior Quality Score.
Competitive Advantage: Outshining Competitors in the Auction
In a competitive digital landscape, a high Quality Score provides a significant competitive advantage.
Advertisers with superior Quality Scores can outperform competitors, achieving better visibility and results.
Example: Consider Advertiser G and Advertiser H bidding on the same keyword.
Advertiser G consistently maintains a Quality Score of 9, outshining Advertiser H with a Quality Score of 6. As a result, Advertiser G’s ads consistently outperform in terms of ad position, visibility, and engagement.
Continuous Improvement: Quality Score as a Performance Metric
Quality Score is not static; it evolves based on ad performance and changes in user behavior. This dynamic nature makes it a valuable performance metric that advertisers can leverage for continuous improvement.
Example: Advertiser I notices a dip in their Quality Score over time. Through rigorous monitoring and optimization of ad relevance and landing page experience, they manage to reverse the trend, achieving a higher Quality Score and better campaign performance.
4. Strategies for Improving Quality Score
Enhancing Quality Score is a cornerstone of successful Google Ads campaigns.
In this extensive section, we will explore a comprehensive set of strategies for improving Quality Score, accompanied by real-world examples and verified data to provide actionable insights for advertisers.

Crafting Compelling Ad Copy: The Foundation of High CTR
Creating ad copy that resonates with your target audience is a fundamental strategy for boosting Click-Through Rate (CTR), a key component of Quality Score.
Engaging Headlines and Descriptions:
Example: Advertiser A, promoting a fitness app, crafts an ad with a headline like “Achieve Your Fitness Goals with Our Revolutionary App.” This enticing headline captures attention and encourages clicks.
Clear Call-to-Action (CTA)
Example: Advertiser B, running a promotion, includes a clear CTA in their ad: “Limited Time Offer – Shop Now for 20% Off.” This might encourage users to take immediate action, contributing to a higher CTR.
Utilizing Ad Extensions
Example: Advertiser C enhances their ad with site link extensions, providing additional links to specific product categories. This not only offers more information but also increases ad real estate and user engagement.
Strategic Keyword Optimization: Aligning Ads with User Intent
Ensuring that your chosen keywords align seamlessly with user search queries is crucial for improving ad relevance and, consequently, Quality Score.
Regular Keyword Review and Update:
Example: Advertiser X, in the tech industry, regularly updates their keyword list to include trending terms and remove outdated ones. This proactive approach ensures their ads remain highly relevant.
Ad Group Segmentation
Example: Advertiser Y, offering various travel services, segments their ad groups based on services like flights, hotels, and car rentals. This targeted approach allows for more relevant ad content tailored to specific user queries.
Dynamic Keyword Insertion (DKI)
Example: Advertiser Z uses DKI to dynamically insert the searched keyword into their ad text. For a user searching for “affordable laptops,” the ad might display as “Explore Our Affordable Laptops Today.”
Optimizing Landing Page Experience: Enhancing Post-Click Satisfaction
A seamless transition from ad to landing page is essential for providing users with a positive post-click experience, a factor integral to Quality Score.
Mobile Optimization
Example: Advertiser P ensures their landing pages are optimized for mobile users, considering the prevalence of mobile searches.
This strategy reduces bounce rates and contributes to a positive Landing Page Experience.
Fast Loading Times
Example: Advertiser Q employs optimization techniques like image compression and browser caching to minimize landing page load times.
Faster loading pages keep users engaged and contribute to higher Quality Scores.
Relevant and Clear Content:
Example: Advertiser R aligns their landing page content with the promises made in their ad.
If the ad emphasizes discounts, the landing page might prominently showcase discounted products, ensuring a cohesive and relevant user journey.
Continuous A/B Testing: Iterative Refinement for Success
Implementing A/B testing allows advertisers to experiment with different ad variations, identifying the most effective elements and refining strategies for ongoing improvement.
Testing Ad Copy Variations
Example: Advertiser S runs A/B tests with two ad variations – one emphasizing free shipping and the other highlighting a limited-time discount.
Analyzing performance data can help determine which approach resonates better with their audience.
Experimenting with Ad Extensions
Example: Advertiser T conducts A/B tests on different ad extensions, comparing the performance of site links, callouts, and structured snippets.
This iterative approach can help optimize ad extensions for maximum impact.
Adapting to Seasonal Changes
Example: Advertiser U, in the fashion industry, conducts A/B tests to tailor ad messaging and promotions based on seasonal trends.
Adapting to changing consumer preferences ensures continuous relevance and improved Quality Scores.
Leveraging Historical Performance Data: Informed Decision-Making
Analyzing historical data provides valuable insights into past performance, allowing advertisers to make informed decisions for optimizing campaigns and improving Quality Scores.
Identifying High-Performing Keywords
Example: Advertiser V reviews historical data to identify keywords that consistently yield high CTRs and conversions.
Allocating budget and focus to these top-performing keywords can contribute to improved Quality Scores.
Adapting to Audience Behavior
Example: Advertiser W notices a shift in user behavior during specific times of the day.
By leveraging historical data, they adjust bid strategies and ad schedules to align with peak engagement periods, positively impacting Quality Score.
Refining Target Demographics
Example: Advertiser X analyzes historical data to understand which demographics respond best to their ads.
With this insight, they refine audience targeting, delivering more relevant ads to specific user segments and boosting Quality Scores.
Industry Benchmarking: Staying Competitive in the Marketplace
Keeping an eye on industry benchmarks and competitor strategies provides context for advertisers, helping them set realistic goals and stay competitive.
Monitoring Industry Average CTRs
Example: Advertiser Y regularly checks industry benchmarks to assess the competitiveness of its CTR.
Aligning their goals with industry averages ensures a realistic approach to improving Quality Scores.
Analyzing Competitor Ad Positions
Example: Advertiser Z monitors competitor ad positions for target keywords.
If competitors consistently rank higher, they adjust bidding and ad quality strategies to improve their own ad positions and Quality Scores.
Staying Informed on Trends
Example: Advertiser A stays informed about emerging trends in their industry.
By aligning their ads with current consumer interests and preferences, they position themselves for higher Quality Scores and increased competitiveness.
Optimizing Ad Schedule: Strategic Timing for Maximum Impact
Adopting a strategic ad schedule ensures that ads are displayed during times when users are most likely to engage, contributing to improved CTR and Quality Scores.
Analyzing Time-of-Day Performance
Example: Advertiser B analyzes performance data to identify peak hours for their target audience.
By adjusting their ad schedule to prioritize these hours, they maximize visibility during high-engagement periods.
Adapting to Time Zone Differences
Example: Advertiser C, operating in multiple regions, adapts its ad schedule to align with different time zones.
This ensures that their ads are displayed when users in each region are most active, optimizing Quality Scores globally.
Incorporating Day-Parting Strategies
Example: Advertiser D employs day-parting strategies to adjust bids and messaging based on the day of the week.
For instance, promoting weekend-specific offers on Fridays enhances relevance and boosts Quality Scores.
Monitoring and Responding to Quality Score Fluctuations: Agility in Action
Quality Score is dynamic, and influenced by various factors, including changes in user behavior and market dynamics.
Advertisers should monitor fluctuations and respond promptly to maintain optimal performance.
Rapid Response to Keyword Performance Changes
Example: Advertiser E notices a sudden drop in CTR for a high-priority keyword.
Swiftly adjusting ad copy and bidding strategies, they mitigate the impact on Quality Score and prevent prolonged performance issues.
Adapting to Seasonal Trends
Example: Advertiser F, in the retail sector, anticipates seasonal changes in search behavior.
They proactively update ad messaging and promotions to align with the seasonal shift, ensuring continued relevance and a positive impact on Quality Score.
Navigating Algorithm Updates
Example: Advertiser G stays informed about Google’s algorithm updates.
When a new update emphasizes specific ranking factors, they adjust their strategies accordingly to maintain or improve Quality Scores in alignment with the updated criteria.
User Feedback and Interaction: Enhancing Relevance through Insights
Engaging with user feedback and analyzing interaction metrics provides advertisers with valuable insights into user preferences, enabling them to refine ad content for higher relevance.
Monitoring User Comments and Reviews
Example: Advertiser H actively monitors user comments on social media and reviews on their website.
Addressing concerns and incorporating positive feedback into ad messaging enhances overall user satisfaction and Quality Scores.
Analyzing User Interaction Patterns
Example: Advertiser I analyzes user interaction patterns, such as time spent on the landing page and interaction with specific elements.
This data informs adjustments to landing page content and structure, contributing to improved Quality Scores.
Incorporating User Suggestions
Example: Advertiser J receives suggestions from users through feedback forms.
By incorporating user-suggested improvements, they demonstrate responsiveness to user needs, positively impacting the perceived relevance of their ads and improving Quality Scores.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Launching a successful Google Ads campaign requires strategic planning and meticulous execution.
However, certain common mistakes can hinder your efforts and compromise the effectiveness of your campaigns.
In this extensive section, we’ll explore these pitfalls, accompanied by relevant examples and verified data to guide advertisers away from potential setbacks.

Neglecting Keyword Research: The Foundation of Relevance
Keyword research is the cornerstone of a successful Google Ads campaign, and neglecting this crucial step can lead to targeting the wrong audience or missing valuable opportunities.
Broad Match Keyword Overreliance:
Mistake Example: Advertiser A relies heavily on broad match keywords without adequate negative keyword management. Their ad for “running shoes” appears for searches like “running shoe repair” or “running shoe history,” leading to irrelevant clicks and wasted budget.
Ignoring Long-Tail Keywords
Mistake Example: Advertiser B focuses solely on generic short-tail keywords. They might overlook valuable long-tail variations like “best-running shoes for trail running,” missing out on highly targeted and lower-competition opportunities.
Failure to Update Keyword Lists
Mistake Example: Advertiser C neglects regular updates to their keyword list. As user search behavior evolves, their campaign might fail to capture emerging trends and relevant queries, resulting in decreased ad relevance and lower Quality Scores.
Poorly Crafted Ad Copy: Losing the Battle for Clicks
Compelling ad copy is the gateway to user engagement, and overlooking its importance can lead to low click-through rates (CTR) and diminished ad performance.
Lack of Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Mistake Example: Advertiser D’s ad fails to highlight a unique aspect of their product or service. Without a compelling USP, their ad might struggle to differentiate itself from competitors, resulting in lower click-through rates.
Weak Call-to-Action (CTA)
Mistake Example: Advertiser E includes a generic CTA like “Learn More.” A more compelling and specific CTA, such as “Claim Your Free Trial,” could significantly boost engagement and click-through rates.
Ignoring Ad Extensions
Mistake Example: Advertiser F underutilizes ad extensions. By neglecting site links or callout extensions, they might miss opportunities to provide additional information and increase visibility, ultimately impacting their ad’s performance.
Ad extensions can boost ad click-through rates by an average of 10-15%.
Overlooking Quality Score Optimization: The Costly Oversight
Quality Score is a pivotal metric in Google Ads, and neglecting its optimization can result in higher costs, lower ad positions, and reduced overall campaign performance.
Disregarding Ad Relevance
Mistake Example: Advertiser G fails to align its ad content with user search intent.
As a result, their ads might appear for irrelevant queries, leading to lower ad relevance and a subsequent decrease in Quality Score.
Neglecting Landing Page Experience
Mistake Example: Advertiser H directs users to a poorly optimized landing page with slow load times.
This suboptimal landing page experience might not only result in higher bounce rates but also negatively impact the Quality Score of their ads.
Ignoring Historical Performance Trends
Mistake Example: Advertiser I fails to analyze historical performance data.
Consequently, they might miss opportunities to identify and rectify fluctuations in Quality Score, leading to prolonged periods of suboptimal ad performance.
Inadequate Budget Management: Balancing Act of Advertising
Effective budget management is essential for the success of any Google Ads campaign.
Oversights in this area can lead to overspending, missed opportunities, or diminished ad visibility.
Ignoring Daily Budget Caps
Mistake Example: Advertiser J overlooks setting daily budget caps.
During a particularly competitive period, their ads might receive an influx of clicks, leading to budget exhaustion early in the day and a subsequent loss of visibility.
Failing to Monitor Bid Adjustments
Mistake Example: Advertiser K neglects to monitor bid adjustments based on factors like device or location.
As a result, their ads may be overbid in certain situations, leading to inefficient spending and lower return on investment.
Disregarding Seasonal Adjustments
Mistake Example: Advertiser L fails to anticipate seasonal changes and adjust its budget accordingly.
During peak seasons, they might miss opportunities for increased visibility, and during low seasons, their budget could be more efficiently allocated.
Overlooking Geographic Targeting: Precision Matters
Effective geographic targeting ensures that ads are shown to the most relevant audience.
Neglecting this aspect can lead to a wasted budget on irrelevant clicks.
Broad Geo-Targeting
Mistake Example: Advertiser M targets an entire country without refining its geographic targeting.
This approach may lead to ad impressions and clicks from users outside their service area, resulting in a lower conversion rate.
Ignoring Localized Keywords
Mistake Example: Advertiser N promotes a local service but overlooks the importance of using localized keywords.
This omission may result in their ads being less visible to users specifically searching for local solutions.
Failure to Adjust Bids by Location
Mistake Example: Advertiser O does not adjust bids based on location performance.
As a result, they may overspend in certain regions where competition is high, compromising overall campaign efficiency.
Lack of Ad Schedule Optimization: Timing is Everything
Strategic ad scheduling ensures that ads are displayed when users are most likely to engage.
Overlooking this aspect can lead to inefficient spending during non-peak hours.
Running Ads 24/7
Mistake Example: Advertiser P runs their ads 24/7 without considering user engagement patterns.
This could result in higher spending during non-peak hours when users are less likely to interact with their ads.
Failure to Adapt to Time Zones
Mistake Example: Advertiser Q operates globally but fails to adjust ad schedules based on time zone differences.
This oversight can lead to ads being displayed during off-peak hours in certain regions, affecting campaign performance.
Ignoring Day-Parting Strategies
Mistake Example: Advertiser R neglects to implement day-parting strategies.
During weekends or specific days of the week when their target audience is more active, their ads may receive less visibility, impacting overall performance.
Failure to Utilize Conversion Tracking: Measuring Success Effectively
Conversion tracking is essential for measuring the success of Google Ads campaigns.
Neglecting to implement or monitor conversion tracking can lead to a lack of insights into campaign performance.
Absence of Conversion Tracking Pixels:
Mistake Example: Advertiser S forgets to install conversion tracking pixels on their website.
As a result, they might be unable to attribute conversions to specific ads or keywords, hindering the ability to optimize for successful outcomes.
Not Setting Up E-commerce Tracking:
Mistake Example: Advertiser T runs an e-commerce store but fails to set up e-commerce tracking.
Without tracking revenue and specific product purchases, they could miss valuable insights into the profitability of their ad campaigns.
Neglecting Cross-Device Conversions:
Mistake Example: Advertiser U does not consider cross-device conversions.
Ignoring conversions that occur on different devices can lead to an inaccurate assessment of campaign success and hinder optimization efforts.
Conclusion
Unveiling the Essence of Quality Score: A Dynamic Digital Compass
In unraveling the intricacies of Quality Score in Google Ads, we’ve uncovered more than just a metric; we’ve unveiled a dynamic digital compass that guides advertisers through the complex landscape of online advertising.
Quality Score, a numeric representation of ad relevance, click-through rates, and landing page experience, becomes the focal point of a journey marked by precision, efficiency, and campaign success.
It’s not just about the numbers; it’s about understanding the heartbeat of your advertising efforts and aligning with user expectations.
Strategies for Mastery: Crafting a Symphony of Success
Armed with the knowledge of how Quality Score is calculated and the factors that influence its trajectory, advertisers are equipped to embark on a journey of continuous improvement.
Crafting compelling ad copy, optimizing landing pages, and navigating the intricacies of keyword research become not just tasks but strategic manoeuvres in the pursuit of Quality Score excellence.
As we’ve seen, each strategy is a note in the symphony of success. From refining keyword selection to fine-tuning ad copy, advertisers conduct a harmonious performance aimed at achieving that elusive crescendo of high Quality Scores and campaign triumph.
Quality Score’s Ripple Effect: From Clicks to Conversions
The impact of a high Quality Score transcends the realm of ad positioning and cost-effectiveness; it extends into the very fabric of user interaction and post-click experiences.
Advertisers wielding a superior Quality Score witness a domino effect, from increased ad visibility to elevated click-through rates, ultimately culminating in higher conversion rates.
Quality Score isn’t just a metric – it’s the catalyst for a seamless user journey. A journey that begins with an engaging ad, continues through a relevant landing page, and concludes with a satisfied user converting into a customer.
Common Mistakes: Navigating the Minefield of Missteps
In our exploration, we’ve delved into the common pitfalls that can mar the path to Quality Score excellence.
From neglecting keyword research to overlooking the intricacies of ad scheduling, advertisers are now equipped to sidestep these potential pitfalls and chart a course toward precision and efficiency.
Consider these mistakes not as roadblocks but as cautionary signposts. By learning from the missteps of others, advertisers can navigate the Google Ads landscape with foresight and agility, avoiding detours that may compromise campaign success.
Continuous Evolution: The Ongoing Symphony of Success
In the ever-evolving realm of digital advertising, one truth remains constant – change is the only constant. Quality Score, as a dynamic metric, demands continuous attention and adaptation.
Advertisers must be vigilant, responsive to user behaviour shifts, and agile in the face of algorithmic updates. Consider your Quality Score journey not as a destination but as a perpetual expedition.
A journey where strategies are refined, mistakes are learned from, and the symphony of success is played with ever-increasing mastery.
Empowering Advertisers for Success: The Final Note
As we draw the final curtain on our exploration of Quality Score in Google Ads, let this be a manifesto for advertisers – a proclamation of empowerment and strategic enlightenment.
Quality Score isn’t a formidable enigma; it’s a canvas awaiting the brushstrokes of your advertising prowess. In the vast cosmos of Google Ads, let Quality Score be your guiding star.
Utilize the strategies, avoid the pitfalls, and navigate the ever-changing landscape with the poise of a seasoned navigator. May your Quality Scores soar, your campaigns thrive, and your digital advertising odyssey is marked by triumph after triumph.
If you are looking for a top-class digital marketer, then book a free consultation slot here.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your friends and business partners, and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the AppLabx Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to the AppLabx Blog.
People also ask
What Quality Score is Good for Google Ads?
A good Quality Score in Google Ads typically ranges between 7 and 10. Scores in this range indicate high ad relevance, click-through rates, and positive landing page experiences. Higher Quality Scores contribute to better ad positions, lower costs per click, and increased overall campaign success.
What is the difference between Google ad rank and Quality Score?
Google Ad Rank determines the position of your ad in search results and is calculated using bid amount, ad relevance, and expected click-through rate. Quality Score, a component of Ad Rank, specifically evaluates ad and landing page relevance. While Ad Rank considers multiple factors, Quality Score focuses on ad quality alone.
How does Quality Score affect CPC?
Quality Score directly influences Cost Per Click (CPC) in Google Ads. Higher Quality Scores lead to lower CPC, as Google rewards relevant and engaging ads. Advertisers with superior Quality Scores enjoy cost savings, achieving better ad positions at a reduced price compared to lower-scoring counterparts.