Key Takeaways
- Precision in Targeting: Geographic Segmentation allows businesses to precisely target local markets, enhancing relevance and boosting conversion rates by aligning products and messages with unique regional preferences.
- Future-Proof Strategies: Embrace the future with advanced technologies like AI and ML, ensuring your Geographic Segmentation strategies remain at the forefront of marketing innovation for hyper-personalization and individualized experiences.
- Balancing Global and Local Dynamics: Successfully navigate the globalization of markets while addressing privacy concerns by crafting nuanced Geographic Segmentation strategies that transcend borders, ensuring your campaigns resonate on both a global and local scale.
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of one of the cornerstones of modern marketing strategies – Geographic Segmentation.
In a world where consumers are diverse and markets span vast landscapes, understanding the intricacies of Geographic Segmentation is paramount for any business aiming to thrive in the competitive arena.
This comprehensive guide is your key to unraveling the mysteries of Geographic Segmentation, providing you with insights, strategies, and tools to navigate this dynamic facet of marketing successfully.
What is Geographic Segmentation?
Geographic Segmentation is not merely a marketing buzzword; it’s a powerful approach that allows businesses to tailor their marketing efforts based on the geographic locations of their target audience.
In essence, it involves dividing a broad market into distinct geographical units, such as countries, regions, cities, or even neighborhoods.
The goal?
To identify and understand the unique characteristics, preferences, and behaviors of consumers in specific locations, enabling businesses to craft highly targeted and effective marketing campaigns.
Why does Geographic Segmentation Matter?
Imagine trying to sell snow boots in a tropical paradise or promoting sunscreen in the Arctic Circle.
Geographic Segmentation is the compass that guides businesses away from such missteps.
By recognizing the diversity in consumer needs, cultural influences, and economic factors across different locations, businesses can align their products, services, and marketing messages with the specific demands of each geographic segment.
The result?
A more personalized and resonant approach that not only meets the needs of the local market but also establishes a deeper connection with consumers.
The Importance of Localized Marketing
Geographic Segmentation isn’t just about dividing markets; it’s about conquering them strategically.
Whether you’re a local business targeting a specific neighbourhood or a global brand expanding across continents, the ability to localize your marketing efforts can make or break your success.
This guide will delve into the intricacies of targeting local markets, understanding regional nuances, and tailoring marketing strategies that resonate on a hyper-local level.
Enhancing Relevance and Engagement
In an era where consumers are bombarded with information from all directions, relevance is the currency of attention.
Geographic Segmentation empowers businesses to cut through the noise by delivering messages that speak directly to the unique needs and interests of specific geographic segments.
We’ll explore how this enhanced relevance leads to increased customer engagement, loyalty, and, ultimately, a higher return on investment (ROI).
Buckle up as we embark on this enlightening journey through the world of Geographic Segmentation.
From the fundamentals to advanced strategies, this complete guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to harness the power of location-based marketing.
Let’s navigate the diverse landscapes of consumer behaviour and market dynamics together, ensuring your marketing efforts are not just seen but deeply felt by your target audience.
But, before we venture further, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About AppLabx
From developing a solid marketing plan to creating compelling content, optimizing for search engines, leveraging social media, and utilizing paid advertising, AppLabx offers a comprehensive suite of digital marketing services designed to drive growth and profitability for your business.
AppLabx is well known for helping companies and startups use SEO and Digital Marketing to drive web traffic to their websites and web apps.
At AppLabx, we understand that no two businesses are alike. That’s why we take a personalized approach to every project, working closely with our clients to understand their unique needs and goals, and developing customized strategies to help them achieve success.
If you need a digital consultation, then send in an inquiry here.
What is Geographic Segmentation: The Complete Guide
- Why Geographic Segmentation Matters
- Benefits of Geographic Segmentation
- How to Implement Geographic Segmentation
- Best Practices for Effective Geographic Segmentation
- Future of Geographic Segmentation
1. Why Geographic Segmentation Matters
Targeting Local Markets for Maximum Impact
Geographic Segmentation matters significantly as it enables businesses to focus their marketing efforts on specific localities, ensuring a more precise targeting strategy.
For instance, consider the success story of Starbucks.
The global coffee giant strategically adapts its menu to cater to local preferences, offering matcha lattes in Japan and masala chai in India, resulting in increased consumer engagement and brand loyalty.

Understanding Regional Preferences and Cultural Nuances
Geographic Segmentation is instrumental in unravelling the intricate tapestry of regional preferences and cultural nuances.
A notable example is McDonald’s, a global fast-food giant that tailors its menu to suit local tastes.
In India, where a large portion of the population follows a vegetarian diet, McDonald’s introduced the McAloo Tikki, a spicy vegetarian burger.

This localization strategy not only resonates with the cultural preferences but also significantly contributes to the company’s success in diverse markets.
Tailoring Marketing Strategies for Maximum Relevance
Geographic Segmentation empowers businesses to create highly targeted and relevant marketing strategies.
For instance, e-commerce giant Amazon utilizes this strategy effectively.
Amazon employs sophisticated algorithms that customize product recommendations based on the user’s geographic location, weather conditions, and local trends.
This level of personalization not only enhances user experience but also contributes significantly to Amazon’s unparalleled success in the e-commerce landscape.
Increasing ROI through Targeted Advertising
Geographic Segmentation is a key driver in optimizing advertising efforts for a higher return on investment (ROI).
According to a study by Statista, global digital advertising spending will reach 836 billion dollars by 2026.
By leveraging Geographic Segmentation, businesses can allocate their advertising budgets more effectively, targeting regions with higher potential for conversion. This not only maximizes ROI but also minimizes ad spend wastage in less responsive areas.
Enhanced Customer Engagement Through Localized Campaigns
Geographic Segmentation plays a crucial role in fostering a deeper connection with consumers through localized marketing campaigns.
According to a study, 63% of consumers will stop buying from brands that use poor personalization tactics.
By tailoring campaigns to specific geographic segments, businesses can create content that resonates with the local audience, leading to increased engagement and brand loyalty.
An exemplary case is Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign, where the brand replaced its logo with popular names, resulting in a surge of consumer engagement globally.

2. Benefits of Geographic Segmentation

Improved Relevance in Marketing Campaigns
Geographic Segmentation offers businesses the unique advantage of tailoring their marketing campaigns with unparalleled precision, resulting in improved relevance and resonance with the target audience.
Higher Conversion Rates with Targeted Messaging
Utilizing geographic data in marketing messages can significantly boost conversion rates.
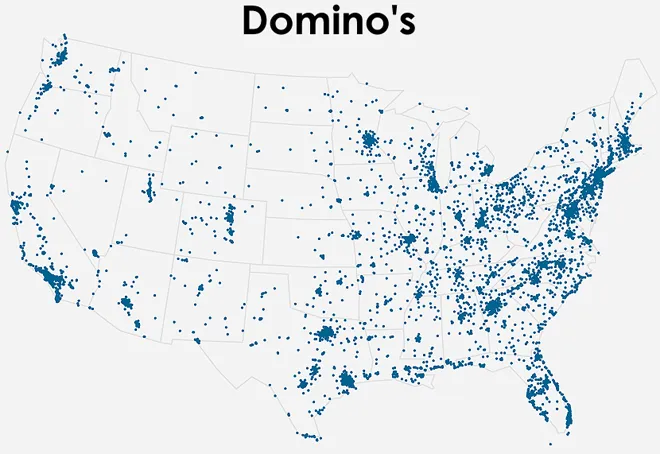
Domino’s Pizza Delivery Zones
Domino’s Pizza is a prime example of leveraging geographic segmentation for increased relevance.
By defining specific delivery zones based on geographic proximity to their outlets, Domino’s ensures timely deliveries and hot pizzas, creating a localized experience for customers.
This strategic use of geographic segmentation contributes significantly to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enhanced Customer Engagement
Beyond improved relevance, Geographic Segmentation fosters higher levels of customer engagement by aligning marketing efforts with the unique needs and preferences of specific geographic segments.
Personalized Offers and Promotions
Studies, such as the one by Epsilon, reveal that 80% of consumers are more likely to make a purchase when brands offer personalized experiences.
Geographic Segmentation enables businesses to craft personalized offers and promotions based on regional preferences, leading to increased engagement and a positive brand perception.
Starbucks Rewards Program
Starbucks, with its highly successful rewards program, exemplifies the impact of personalized promotions based on geographic data.
The coffee giant tailors its rewards and promotions to individual customer preferences, considering factors like location, purchase history, and local events. This approach not only enhances customer engagement but also drives repeat business.

Increased Return on Investment (ROI) through Targeted Advertising
One of the most compelling benefits of Geographic Segmentation is its ability to optimize advertising efforts, resulting in a higher return on investment (ROI).
Efficient Budget Allocation
According to a report, businesses that invest in targeted advertising witness an average revenue increase of 200%.
Geographic Segmentation allows businesses to allocate their advertising budgets more efficiently by focusing on regions with higher potential for conversion.
This ensures that marketing resources are invested where they are most likely to generate a positive return.
Airbnb’s Localized Ad Campaigns
Airbnb, a pioneer in the sharing economy, effectively utilizes geographic segmentation in its advertising strategy.
The platform tailors its ads to showcase unique and popular listings in specific cities or regions.
This localized approach not only attracts potential guests but also maximizes the impact of their advertising budget by targeting users interested in specific destinations.

Tailored Product and Service Offerings
Understanding the diverse needs of different geographic segments enables businesses to tailor their product and service offerings for maximum customer satisfaction.
McDonald’s Regional Menus
McDonald’s is a global brand that successfully implements geographic segmentation in its product offerings.
In different parts of the world, McDonald’s adapts its menu to cater to local tastes and cultural preferences.
For instance, in Japan, McDonald’s offers the “Teriyaki Burger,” showcasing an understanding of and respect for local culinary preferences.

Regional Variants in Automobiles
Automobile manufacturers often customize their product offerings based on regional preferences.
For example, SUVs may dominate the market in regions with rough terrains, while smaller and more fuel-efficient cars might be preferred in urban areas.
This approach not only meets local demands but also contributes to the long-term success of automotive brands in diverse markets.
3. How to Implement Geographic Segmentation

Data Collection and Analysis for Effective Geographic Segmentation
Implementing Geographic Segmentation begins with robust data collection and analysis, allowing businesses to gain valuable insights into the demographics, behaviors, and preferences of specific geographic segments.
Utilizing Location-Based Analytics Tools
Leverage advanced location-based analytics tools like Google Analytics, Heatmaps, and Geospatial Data Platforms to gather data on customer interactions, website visits, and purchasing patterns based on geographic locations.
These tools provide actionable insights that form the foundation of effective segmentation strategies.
Customer Surveys and Feedback
Conducting targeted customer surveys and feedback forms can provide direct input from your audience regarding their preferences and expectations in different regions.
Analyzing this qualitative data alongside quantitative metrics enhances the accuracy of geographic segmentation.
Spotify’s User Location Data
Spotify, the music streaming giant, utilizes user location data to curate personalized playlists.
By analyzing the listening habits of users in specific regions, Spotify tailors playlists to reflect local music trends.
This not only enhances user satisfaction but also showcases the power of leveraging location data for personalized content delivery.
Tools and Technologies for Geographic Segmentation Implementation
Implementation of Geographic Segmentation is greatly facilitated by the use of advanced tools and technologies designed to handle geographic data efficiently.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS tools like ArcGIS and MapInfo enable businesses to visualize and analyze geographic data effectively.
These tools provide spatial insights, allowing marketers to identify patterns, hotspots, and areas of high potential for targeted marketing campaigns.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Integrating CRM systems with geographic data allows businesses to create detailed customer profiles enriched with location-specific information.
This enables personalized communication and targeted marketing strategies based on the geographic preferences of individual customers.
Airbnb’s Dynamic Pricing Algorithm
Airbnb utilizes a sophisticated dynamic pricing algorithm that considers various factors, including location, to adjust rental prices in real-time.
By incorporating geographic data into their pricing strategy, Airbnb maximizes revenue by aligning prices with the demand and supply dynamics of specific regions.
Segmentation Criteria: Demographics, Psychographics, and Behavior
Effective Geographic Segmentation involves the identification of specific criteria to categorize and target different geographic segments accurately.
Demographic Segmentation
Consider demographic factors such as age, gender, income levels, and population density when defining geographic segments.
For example, a luxury fashion brand may target affluent neighborhoods in urban areas, tailoring marketing messages to match the demographic profile of the residents.

Psychographic Segmentation
Understanding the psychographics of different geographic segments involves analyzing lifestyle choices, values, and interests.
For instance, an outdoor adventure brand might focus on regions with a high concentration of nature enthusiasts, tailoring campaigns to resonate with the adventurous spirit of the local population.
Behavioral Segmentation
Examine the purchasing behavior and patterns of consumers in different geographic segments.
This could include the frequency of purchases, preferred channels, and brand loyalty.
For instance, an e-commerce platform might offer location-based promotions to encourage repeat purchases from specific regions.
Real-Time Monitoring and Adjustment Strategies
Geographic Segmentation is not a static process; continuous monitoring and adjustment are crucial for adapting to dynamic market changes.
Utilizing Analytics Dashboards
Implement real-time analytics dashboards that provide insights into the performance of marketing campaigns across different geographic segments.
This enables marketers to identify trends, assess campaign effectiveness, and make data-driven adjustments on the fly.
Social Media Listening Tools
Employ social media listening tools like Hootsuite or Brandwatch to monitor conversations and sentiment in specific geographic areas.
This real-time feedback allows businesses to adjust their messaging and engagement strategies based on the evolving preferences and opinions of local communities.
Netflix’s Content Localization Strategy
Netflix employs a dynamic content localization strategy based on geographic preferences.
By analyzing viewer behaviour and preferences in different regions, Netflix tailors its content library to include locally relevant shows and movies. This adaptive approach has contributed significantly to Netflix’s global success.

Challenges in Geographic Segmentation and Mitigation Strategies
Implementing Geographic Segmentation comes with its set of challenges, and businesses must be prepared to address them effectively.
Data Privacy Concerns
With the increasing emphasis on data privacy, businesses must adopt robust data protection measures.
Clearly communicate privacy policies, obtain explicit consent for data collection, and ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR to build trust with customers.
Adapting to Dynamic Market Changes
The business landscape is dynamic, and geographic preferences can change rapidly. Regularly update data sources, conduct market research, and stay informed about local trends to adapt marketing strategies promptly.
Overcoming Communication Barriers
Language and cultural differences can pose challenges to effective communication. Implement localization strategies, including translated content and culturally sensitive messaging, to overcome communication barriers and resonate with diverse audiences.
4. Best Practices for Effective Geographic Segmentation

Utilizing Demographic Data for Precision Targeting
Effectively implementing Geographic Segmentation involves leveraging demographic data to tailor marketing efforts to the specific characteristics of different geographic segments.
Age, Gender, and Income Levels
- Example: Tailoring social media campaigns based on age demographics ensures maximum reach and engagement.
- Best Practice: Utilize demographic insights to create targeted campaigns; for instance, promoting retirement services in regions with a higher concentration of elderly residents.
Population Density and Urban vs. Rural Dynamics
- Example: Urban-centric products may benefit from targeting densely populated areas, while rural areas may require different marketing strategies.
- Best Practice: Adapt marketing messages to suit the lifestyle and preferences of residents in urban and rural settings.
Integrating Social and Cultural Factors into Segmentation Strategies
Understanding the social and cultural nuances of different geographic segments is vital for crafting resonant marketing messages.
Language Preferences
- Example: Canada, with its bilingual population, provides an excellent example of language-based segmentation. Tailoring marketing materials in English and French reflects an understanding of the linguistic diversity in different regions.

- Best Practice: Implement multilingual strategies where applicable, ensuring that language aligns with the preferences of specific geographic segments.
Cultural Sensitivity
- Example: McDonald’s adapts its menu to suit cultural preferences worldwide. In India, where the majority of the population follows Hinduism, McDonald’s offers a range of vegetarian options, showcasing cultural sensitivity.
- Best Practice: Prioritize cultural sensitivity in marketing materials, avoiding potentially offensive content and incorporating elements that resonate positively with local cultures.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment for Timely Adaptation
The dynamic nature of markets requires continuous monitoring and adjustment of Geographic Segmentation strategies to stay relevant and effective.
Real-Time Analytics and Dashboards
- Example: Marketing analytics platforms like Google Analytics provide real-time data on website traffic, allowing businesses to monitor the performance of location-specific campaigns promptly.

- Best Practice: Set up real-time analytics dashboards to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and adjust strategies based on emerging trends.
Consumer Behavior Analysis
- Example: E-commerce platforms often analyze consumer behaviour data to understand the purchasing patterns of different regions. This data informs inventory management and targeted promotions.
- Best Practice: Regularly analyze consumer behaviour data to identify shifts in preferences, allowing for agile adjustments in marketing strategies.
Holistic Integration of Geographic and Psychographic Data
Combining geographic and psychographic data enriches segmentation strategies, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the target audience.
Interests, Hobbies, and Values
- Example: Social media platforms gather data on user interests and hobbies. A business promoting outdoor gear may target regions with a high concentration of users interested in hiking and camping.
- Best Practice: Integrate psychographic data with geographic segmentation to create highly targeted campaigns that align with both location-based and interest-based preferences.
Aligning Products with Local Lifestyles
- Example: Tesla’s success in different markets is partly attributed to its understanding of local lifestyles. In crowded urban areas, compact electric vehicles may be promoted, while larger models may be emphasized in suburban regions.
- Best Practice: Tailor product offerings based on a holistic understanding of local lifestyles and preferences, integrating both geographic and psychographic insights.
Building Community Engagement through Localized Initiatives
Geographic Segmentation isn’t just about marketing products; it’s about engaging with communities on a personal level.
Supporting Local Causes
- Example: Many global brands engage in community support initiatives based on geographic segmentation. Supporting local charities or environmental causes creates a positive brand image.
- Best Practice: Identify and support causes that resonate with the values and concerns of specific geographic segments, showcasing a commitment to community well-being.
Localized Events and Sponsorships
- Example: Sports sponsorships are often tailored to suit the preferences of local audiences. A sports brand may sponsor different teams or events based on the popularity of specific sports in different regions.
- Best Practice: Participate in or sponsor events that are culturally significant or popular in specific geographic areas, fostering a sense of community engagement.
Adapting Digital Advertising Strategies for Geographic Reach
In the digital era, optimizing online advertising strategies based on geographic segmentation is essential for maximum impact.
Geo-Targeted Digital Ads
- Example: Platforms like Facebook and Google Ads offer geo-targeting options. An online clothing retailer can create targeted ads for regions with specific weather conditions, promoting relevant seasonal attire.
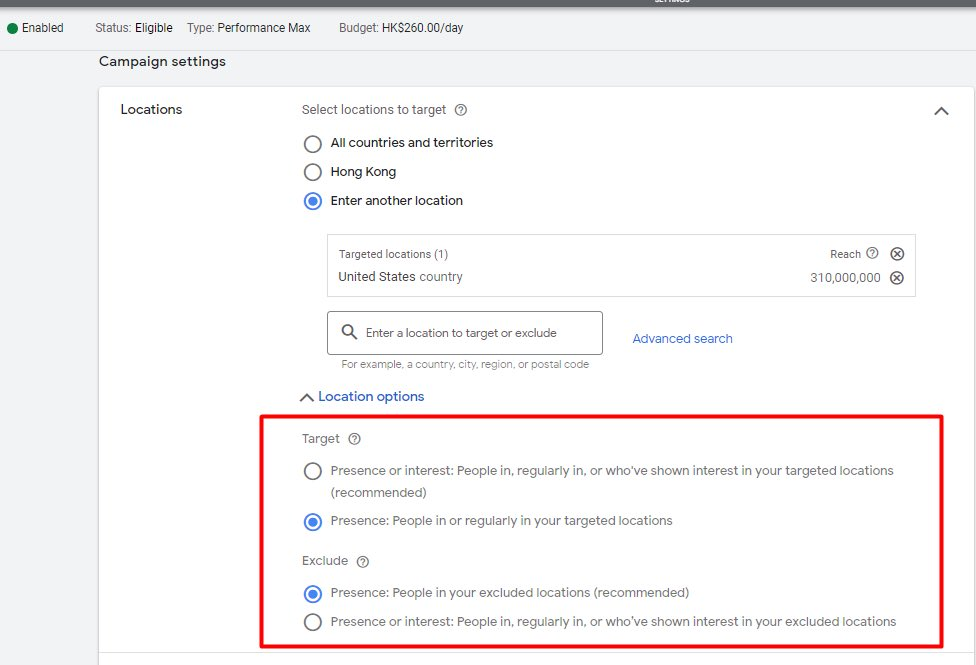
- Best Practice: Utilize geo-targeting features to create highly relevant digital ads based on the geographic and climate-specific needs of the audience.
Mobile Marketing and Location-Based Services
- Example: Mobile apps often use location-based services to provide users with personalized content or promotions. Retailers can send push notifications to users when they are in proximity to a physical store.
- Best Practice: Implement location-based services in mobile marketing strategies to deliver personalized and contextually relevant content to users based on their geographic location.
5. Future of Geographic Segmentation

Rise of Advanced Technologies in Geographic Segmentation
The future of Geographic Segmentation is tightly intertwined with advancements in technology, paving the way for more precise and sophisticated targeting strategies.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- AI and ML play a significant role in data analytics and decision-making, providing businesses with enhanced capabilities in segmentation and targeting.
- Example: Netflix’s recommendation algorithm, powered by machine learning, analyzes user behaviour, including geographic location, to deliver personalized content suggestions. This dynamic approach anticipates the future trend of more intelligent Geographic Segmentation.
Predictive Analytics for Location-Based Insights
- Data Source: The predictive analytics industry is projected to reach USD 28.1 billion by 2026.
- Example: Retailers are increasingly utilizing predictive analytics to forecast consumer behaviour based on location-specific data. By analyzing historical trends and external factors, businesses can proactively adapt their strategies for future geographic segmentation.
Hyper-Personalization and Individualized Experiences
The future of Geographic Segmentation emphasizes a shift towards hyper-personalization, offering consumers experiences tailored to their individual preferences and location-based needs.
Geo-fencing and Proximity Marketing
- Example: Retailers deploy geo-fencing to trigger targeted promotions when a consumer enters a predefined geographic area. This approach, often seen in mobile apps, enhances engagement by delivering real-time, location-specific offers.
- According to a study by MarketsandMarkets, the geo-marketing market size is expected to reach USD 32.5 billion by 2025.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Location-Based Experiences
- Example: Pokémon GO, a location-based augmented reality game, demonstrated the potential of combining geolocation with AR technology. Players engaged with the game in specific geographic locations, showcasing the future potential for location-based experiences.

- The global augmented reality market is projected to grow from $62.75 billion in 2023 to $1109.71 billion by 2030.
Evolution of Privacy-Centric Geographic Segmentation
As concerns around data privacy grow, the future of Geographic Segmentation will involve strategies that prioritize user consent, transparency, and compliance with evolving regulations.
Permission-Based Location Tracking
- Example: Mobile apps increasingly seek user consent for location tracking, emphasizing transparency about the purposes of data collection. Users can choose to share their location only when they perceive a clear benefit.
- Most (81%) believe they have very little or no control over their personal data once it’s shared with companies.
Blockchain for Secure Location Data
- Example: Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and secure nature, is explored for ensuring the integrity and security of location data. This approach aligns with the growing emphasis on data security in geographic segmentation.
- The global blockchain technology market size is expected to reach USD 1,431.54 billion by 2030.
Globalization and Cross-Border Geographic Segmentation
As businesses expand globally, the future of Geographic Segmentation will witness an increased focus on strategies that transcend traditional borders.
Localization Beyond Language
- Example: Companies like Amazon and Netflix are expanding their content libraries to cater to diverse global audiences. This goes beyond language localization, encompassing cultural preferences and regional content relevance.
- A study found that nearly 75% of consumers said they would be more likely to buy a product with information in their native language.
Cross-Border E-Commerce Trends
- Example: Cross-border e-commerce is on the rise, with platforms like Alibaba’s Tmall Global connecting international sellers with consumers worldwide. This trend necessitates nuanced geographic segmentation strategies that consider cultural and logistical differences.
- A report estimates that retail e-commerce sales worldwide will reach about 8.1 trillion dollars by 2026.
Emergence of Virtual and Augmented Reality in Geographic Marketing
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are poised to revolutionize the way businesses engage with consumers based on their geographic locations.
Virtual Storefronts and Spatial Computing
- Example: Spatial computing enables the creation of virtual storefronts that consumers can explore using augmented reality. This futuristic approach allows businesses to establish a digital presence in specific geographic locations without physical infrastructure.
- A report by Statista projects the global augmented and virtual reality market to grow at an annual rate of 10.77% (CAGR 2024-2028), resulting in a projected market volume of US$58.1 billion by 2028.
Location-Based AR Advertising
Example: Snapchat’s augmented reality ads are location-specific, allowing users to engage with branded content based on their geographic location. This form of advertising enhances user interaction and brand visibility.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this comprehensive guide has unravelled the intricate world of Geographic Segmentation, showcasing its pivotal role in modern marketing strategies.
From its foundational definition to advanced strategies and futuristic trends, we’ve delved into every aspect to provide you with a complete understanding of this powerful marketing tool.
Geographic Segmentation: A Strategic Imperative
Geographic Segmentation isn’t merely an option; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to thrive in an increasingly competitive and diverse marketplace.
The ability to dissect broad markets into specific geographic segments enables businesses to tailor their products, services, and marketing messages with surgical precision.
As we’ve explored, this strategic approach has far-reaching benefits, from improved relevance and enhanced customer engagement to increased return on investment through targeted advertising.
Realizing the Importance of Local Markets
The significance of targeting local markets cannot be overstated. Through Geographic Segmentation, businesses can resonate with the unique needs, preferences, and cultural nuances of specific regions.
Successful examples abound, such as Starbucks adapting its menu globally and McDonald’s tailoring offerings to suit local tastes.
These approaches not only boost customer satisfaction but also solidify brand loyalty, proving that understanding and catering to local markets are indispensable components of effective marketing.
Embracing the Future: Advanced Technologies and Personalization
As we gaze into the future of Geographic Segmentation, it’s evident that advanced technologies will play a pivotal role.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are poised to elevate segmentation strategies to new heights, providing businesses with unparalleled insights.
The rise of hyper-personalization, exemplified by geo-fencing, proximity marketing, and augmented reality experiences, signals a future where individualized customer interactions based on location become the norm.
Navigating Privacy Concerns and Globalization Dynamics
The future also brings forth challenges that demand careful consideration.
Privacy concerns surrounding data collection emphasize the need for transparent and permission-based approaches to Geographic Segmentation.
Simultaneously, the globalization of markets and the surge in cross-border e-commerce underscore the importance of nuanced strategies that transcend traditional borders.
Geographic Segmentation: A Balancing Act
In the dynamic landscape of Geographic Segmentation, finding the right balance is key.
It requires a harmonious integration of demographic, psychographic, and behavioural data, coupled with continuous monitoring and agile adjustment strategies.
The successful implementation of Geographic Segmentation necessitates a holistic understanding of not only the geographic landscape but also the cultural, social, and technological dynamics that shape consumer behaviour.
Looking Ahead: Crafting Impactful Campaigns
Armed with the insights from this guide, businesses can navigate the complexities of Geographic Segmentation with confidence.
Whether adapting to the latest technological trends, addressing privacy concerns, or crafting campaigns for diverse global audiences, the principles outlined here serve as a compass for strategic marketing endeavours.
Your Geographic Segmentation Journey Begins Now
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, it’s important to recognize that Geographic Segmentation isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s a dynamic journey that requires continual learning, adaptation, and innovation.
The landscape will evolve, consumer behaviours will shift, and technologies will advance, but the principles of Geographic Segmentation will remain at the forefront of successful marketing strategies.
If you are looking for a top-class digital marketer, then book a free consultation slot here.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your friends and business partners, and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the AppLabx Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to the AppLabx Blog.
People also ask
What is a geographic segmentation?
Geographic segmentation is a marketing strategy that divides a broad market into distinct segments based on geographic factors. By considering location-specific characteristics, businesses tailor products, services, and marketing messages to meet the unique preferences and needs of consumers in different regions, optimizing relevance and engagement.
What is a geographic business?
A geographic business refers to a company whose operations, focus, or market presence is defined by specific geographic locations. Whether local, regional, national, or global, a geographic business strategically aligns its activities and marketing efforts to suit the unique characteristics and demands of particular regions.
What is geographic segmentation in a level business?
In a level business, geographic segmentation involves dividing the market based on geographical factors such as location, climate, or population density. This strategic approach tailors products and marketing efforts to meet the distinct needs and preferences of consumers in different geographic areas, ensuring relevance and effectiveness.