Key Takeaways
- Consumer behaviours are evolving due to digital transformation, cultural shifts, and rising expectations for personalization and ethical engagement.
- Marketers must adopt data-driven, omnichannel, and emotionally resonant strategies to meet modern customer needs effectively.
- Brands that align with evolving behaviours through personalized experiences and purpose-driven messaging achieve higher loyalty and long-term success.
Evolving consumer behaviors are reshaping how brands attract, engage, and retain customers in every industry. As digital technologies, economic conditions, cultural values, and lifestyle expectations continue to shift, consumers no longer think, shop, or interact with brands in predictable ways. Traditional marketing approaches that once relied on mass messaging and static customer personas are becoming less effective in a market where buyers are more informed, selective, and experience-driven than ever before.

Today’s consumers expect convenience, personalization, transparency, and relevance at every touchpoint. They actively research products, compare alternatives across multiple platforms, rely on peer reviews and social proof, and demand seamless experiences across online and offline channels. At the same time, rising concerns around sustainability, ethical business practices, data privacy, and value for money are influencing purchasing decisions in ways that go far beyond price alone. These evolving expectations are forcing marketers to rethink how they understand audiences, design campaigns, and measure success.
Understanding evolving consumer behaviors is no longer optional for businesses that want to remain competitive. Consumer preferences are influenced by rapid digital adoption, mobile-first lifestyles, social media communities, and on-demand access to information. Shifts in demographics, such as the growing influence of digitally native generations, are accelerating changes in how trust is built and how brand loyalty is earned. Consumers now engage with brands through multiple channels simultaneously, expecting consistent messaging, personalized content, and real-time responsiveness regardless of where or how they interact.
For marketers, these changes present both challenges and opportunities. Brands that fail to adapt risk losing relevance, engagement, and market share, while those that successfully align their strategies with modern consumer behaviors can unlock stronger relationships, higher conversion rates, and long-term growth. Marketing to evolving consumer behaviors requires a deeper understanding of behavioral data, intent signals, and emotional drivers, as well as the ability to respond quickly to changing trends and expectations.
This topic explores what evolving consumer behaviors truly mean in today’s market and why they matter so much to modern marketing strategies. It also examines how businesses can adapt their marketing approaches to connect with today’s consumers more effectively, using insights, personalization, omnichannel experiences, and value-driven messaging. By understanding how and why consumer behaviors are changing, marketers can design smarter, more adaptive strategies that resonate with audiences, build trust, and drive sustainable business outcomes in an increasingly competitive landscape.
But, before we venture further, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About AppLabx
From developing a solid marketing plan to creating compelling content, optimizing for search engines, leveraging social media, and utilizing paid advertising, AppLabx offers a comprehensive suite of digital marketing services designed to drive growth and profitability for your business.
At AppLabx, we understand that no two businesses are alike. That’s why we take a personalized approach to every project, working closely with our clients to understand their unique needs and goals, and developing customized strategies to help them achieve success.
If you need a digital consultation, then send in an inquiry here.
Or, send an email to [email protected] to get started.
What are Evolving Consumer Behaviors & How To Market To Them
- Explain Consumer Behaviour Fundamentals
- Identify Key Trends in Evolving Consumer Behaviours
- Explore Behavioural Patterns and Models
- Explain Why Consumer Behaviours Evolve
- Strategies for Marketing to Evolving Consumer Behaviours
- Practical Examples and Case Studies
1. Explain Consumer Behaviour Fundamentals
Understanding consumer behaviour is essential for building effective marketing strategies. It enables businesses to anticipate customer needs, tailor messaging, improve engagement, and increase conversions. This section explores the core concepts, influencing factors, behavioural models, and real-world applications of consumer behaviour in modern marketing.
Definition and Scope of Consumer Behaviour
• Consumer behaviour refers to the psychological, emotional, and behavioural processes individuals or groups go through before, during, and after making purchasing decisions
• It includes every touchpoint — from awareness and evaluation to buying, post-purchase engagement, and advocacy
• Behavioural insights help businesses create relevant messaging, identify pain points, and optimize the customer journey
Example: A consumer exploring smartphones may start with online research, check YouTube reviews, visit in-store for a trial, compare prices across platforms, and finally decide based on a brand’s sustainability values
Key Factors Influencing Consumer Behaviour
Consumer decisions are shaped by a mix of internal and external factors. These elements impact how individuals perceive needs, gather information, and make purchase decisions.
Internal Factors
• Motivation – Personal needs (basic to aspirational) that trigger buying decisions
• Perception – How consumers interpret brand messaging, ads, and product claims
• Attitudes and Beliefs – Pre-existing opinions or emotional reactions to a brand
• Lifestyle and Personality – Choices based on interests, income, hobbies, and self-identity
External Factors
• Cultural Influences – Social norms, traditions, and regional buying behaviour
• Social Groups and Reference Points – Influence from family, friends, influencers, and peers
• Economic Conditions – Income levels, inflation, and perceived value for money
• Technological Advancements – Availability of mobile apps, virtual assistants, and AI-powered recommendations
The Impact of Digital Transformation on Behaviour
The shift to digital environments has redefined how consumers behave. From hyper-personalization to voice search, digital transformation plays a central role.
• Consumers now expect 24/7 access to information across all devices
• Social media and online reviews shape first impressions
• AI tools suggest products based on browsing and purchase history
• E-commerce platforms offer 1-click buying, increasing impulsive purchases
Matrix: Digital Impact on Consumer Behaviour
| Digital Element | Consumer Expectation | Marketing Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Accessibility | Instant access anywhere | Mobile-first website and content design |
| Personalization Algorithms | Relevant product recommendations | AI-driven marketing and email segmentation |
| Social Proof (Reviews, UGC) | Validation from peers | Influencer marketing and review generation |
| Omnichannel Touchpoints | Seamless transitions between platforms | Unified brand experience across channels |
| Voice Search Integration | Conversational queries and quick answers | Optimization for long-tail and voice search |
Types of Consumer Buying Behaviour
Consumer behaviour varies depending on the complexity of the purchase decision and the level of involvement.
| Buying Behaviour Type | Characteristics | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Complex Buying Behaviour | High involvement, high price, infrequent purchase | Buying a new car or house |
| Dissonance-Reducing | High involvement, limited differences in brands | Choosing a life insurance plan |
| Habitual Buying | Low involvement, repeated purchases, convenience | Buying groceries or toiletries |
| Variety-Seeking | Low involvement, frequent brand switching | Trying new snack or beverage |
Models of Consumer Decision-Making
Marketers use behavioural models to map how a customer interacts with a brand throughout the decision-making process.
AIDA Model (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action)
• Grabs attention with visuals or messaging
• Builds interest through value-driven content
• Stimulates desire by aligning with needs
• Encourages action with strong CTAs
Buyer Decision Process
• Need Recognition – Realizing a need or problem
• Information Search – Researching solutions
• Evaluation of Alternatives – Comparing products
• Purchase Decision – Making the final selection
• Post-Purchase Behaviour – Satisfaction, reviews, and loyalty
Chart: Consumer Decision Process Funnel
This funnel demonstrates the narrowing stages of decision-making:
- Awareness Stage → Large audience, triggered by problem recognition
- Consideration Stage → Narrowed options based on information
- Evaluation Stage → Detailed comparison and assessment
- Purchase Stage → Decision execution
- Post-Purchase → Reflection, satisfaction, loyalty, or dissonance
Real-World Example: Netflix’s Use of Behavioural Data
Netflix uses advanced behavioural analytics to shape user experience:
• Tracks what users watch, re-watch, pause, and skip
• Uses this data to deliver personalized recommendations
• Introduces new series with predictive models based on similar viewer preferences
• Result: High engagement and long-term subscriber retention
Conclusion: Why Understanding Fundamentals Is Critical
Grasping the foundations of consumer behaviour is crucial for any brand seeking long-term customer connection. By analyzing what drives purchase decisions, identifying behavioural triggers, and aligning marketing strategies accordingly, companies can influence consumer choice, build loyalty, and increase lifetime value. The next step is understanding how these behaviours are evolving and what adaptive marketing tactics are necessary to keep pace.
2. Identify Key Trends in Evolving Consumer Behaviours
Consumer behaviours are constantly shaped by technological advancements, cultural values, socio-economic shifts, and digital innovation. As brands compete for attention in a saturated, real-time marketplace, understanding the key trends influencing buyer decisions has become essential for effective marketing. Below are the most impactful trends reshaping how consumers discover, evaluate, and engage with brands.
Digital-First and Omnichannel Expectations
Consumers today operate across multiple digital platforms, expecting a seamless and unified experience across all touchpoints.
• Engage with brands on websites, mobile apps, social media, and in-store simultaneously
• Expect frictionless movement between online and offline channels
• Prefer brands that deliver consistent messaging and service across platforms
Example: Apple ensures a consistent experience across its website, retail stores, customer support, and mobile apps, reinforcing brand trust
Matrix: Omnichannel Behaviour vs. Expectations
| Consumer Activity | Channel Used | Brand Expectation |
|---|---|---|
| Research product | Website, YouTube, Blogs | Detailed, mobile-friendly content |
| Make a purchase | E-commerce, App, In-store | Fast, easy checkout and return options |
| Ask for support | Chatbot, Social Media, Email | Immediate, consistent assistance |
| Leave reviews/share content | Instagram, TikTok, Reddit | Recognition and brand interaction |
Personalization and Hyper-Relevance
Modern consumers expect brands to understand their needs, preferences, and behaviours, delivering tailored experiences in real time.
• Desire for customized recommendations, emails, and offers based on past interactions
• Prefer dynamic content that reflects personal interests, location, or lifecycle stage
• Respond more positively to contextual messaging that reflects intent and urgency
Example: Netflix uses viewing history to personalize content recommendations, increasing engagement and user satisfaction
Table: Personalization Elements and Their Marketing Impact
| Personalization Feature | Behaviour Triggered | Marketing Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Product Recommendations | Browsing and purchase history | Increased average order value |
| Dynamic Email Campaigns | Lifecycle or recent activity | Higher open and click-through rates |
| Location-Based Offers | Real-time location tracking | Immediate action and in-store visits |
| Personalized Content Feeds | Engagement history | Longer session durations |
Values-Driven and Ethical Consumerism
Consumers are aligning their purchasing behaviours with social, environmental, and ethical values.
• Actively support brands that demonstrate transparency, sustainability, and ethical sourcing
• Willing to pay more for environmentally friendly or socially responsible products
• Avoid brands associated with exploitation, greenwashing, or lack of accountability
Example: Patagonia’s dedication to environmental activism and sustainable materials has cultivated a loyal customer base
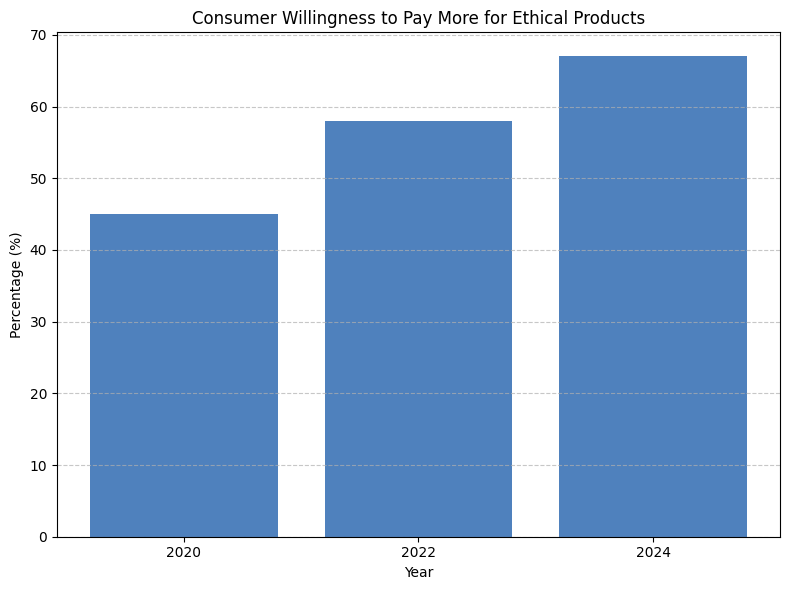
Chart: Consumer Willingness to Pay More for Ethical Products
A vertical bar chart showing rising percentages by year (e.g., 2020: 45%, 2022: 58%, 2024: 67%) highlighting the increasing number of consumers willing to spend more on ethical brands
Influencer-Led and Peer-Driven Decision Making
The role of social media influencers, online reviews, and peer content has significantly grown in shaping purchasing choices.
• Consumers trust peer reviews and influencer endorsements more than traditional advertising
• Micro-influencers are seen as more authentic and relatable than celebrity endorsements
• Communities like Reddit and TikTok are becoming powerful decision-making platforms
Example: Glossier built its brand primarily through user-generated content and micro-influencer engagement, bypassing traditional advertising
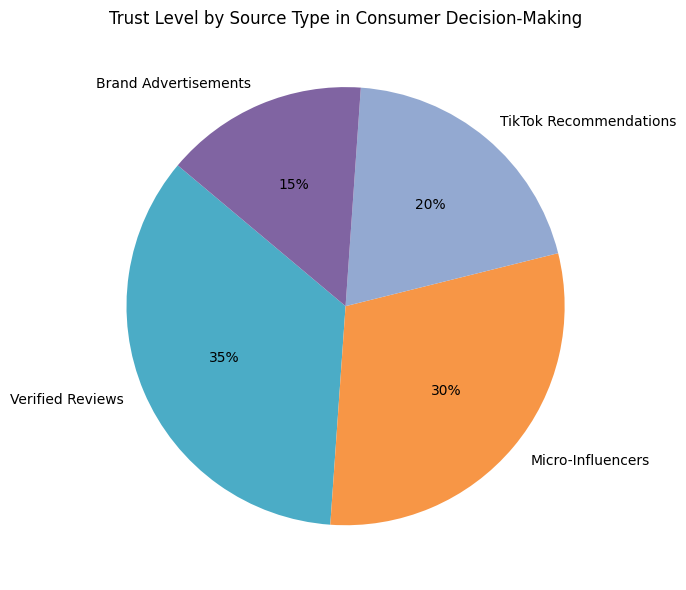
Matrix: Peer Influence Channels vs. Trust Impact
| Source Type | Trust Level (High/Medium/Low) | Influence on Decision |
|---|---|---|
| Verified Reviews | High | Strong trust and purchase driver |
| Micro-Influencers | High | Authentic product discovery |
| TikTok Recommendations | Medium-High | Trend-based, viral engagement |
| Brand Advertisements | Medium-Low | Limited influence without proof |
Instant Gratification and Convenience Culture
The rise of on-demand services and fast delivery has trained consumers to expect immediacy in product access and brand interaction.
• Preference for brands that offer same-day or next-day delivery
• Expect fast-loading websites, mobile apps, and customer support
• Low tolerance for friction or delay in digital experiences
Example: Amazon Prime’s promise of fast, free shipping has reset consumer expectations across all retail categories
Table: Convenience Features and Their Influence on Behaviour
| Feature | Consumer Expectation | Resulting Behaviour |
|---|---|---|
| One-Click Checkout | Speed and simplicity | Increased cart completion rate |
| 24/7 Customer Support | Instant assistance | Higher satisfaction and retention |
| Same-Day Delivery | Fast product access | Repeat purchases and loyalty |
| Auto-Replenishment Services | Effortless subscription management | Reduced churn and higher CLV |
Sustainability and Minimalist Purchasing
Conscious consumerism is driving more intentional and less impulsive purchases, focusing on long-term value over short-term gains.
• Preference for quality, durable products over cheap, disposable items
• Increasing interest in second-hand markets and product lifecycle extensions
• Conscious effort to reduce waste and carbon footprint through fewer, smarter purchases
Example: IKEA’s buy-back and resell program encourages eco-friendly reuse, appealing to environmentally aware customers
Shift Toward Experience over Ownership
Younger generations in particular are placing more value on experiences than on material goods.
• Prefer spending on travel, events, learning, and self-improvement over luxury goods
• Seek memorable brand interactions and community engagement rather than just product utility
• Expect experiential elements in marketing, such as AR, VR, or gamification
Example: Airbnb markets not just stays but curated local experiences, resonating with millennials and Gen Z
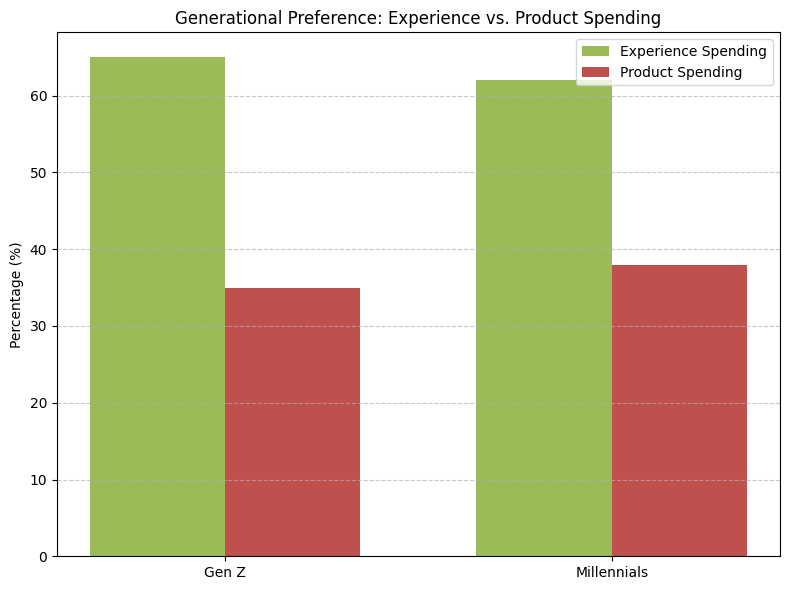
Chart: Generational Preference for Experience vs. Product Spending
A side-by-side bar chart comparing Gen Z and Millennials’ spending allocation: Experience (65%) vs. Products (35%)
Privacy Awareness and Data Control
With rising concerns around data security and digital surveillance, consumers are becoming more cautious about sharing personal information.
• Expect transparency on how their data is collected, used, and stored
• Prefer opt-in models, anonymized tracking, and clear privacy settings
• Support brands that prioritize ethical data practices and trust-building communication
Example: Apple’s privacy-first initiatives such as App Tracking Transparency have elevated consumer control and set new expectations
Conclusion: Anticipating and Acting on Key Behavioural Trends
These key trends underscore a broader transformation in consumer mindset—marked by higher expectations, greater awareness, and deeper engagement. Businesses that recognize these behavioural shifts and adapt with precision will not only remain relevant but also build resilient, future-ready brands. By embedding these trends into strategic planning, marketers can create campaigns and experiences that meet the evolving needs of today’s empowered consumer.
3. Explore Behavioural Patterns and Models
Understanding behavioural patterns and decision-making models is essential for developing marketing strategies that influence how consumers interact with brands. These models provide a framework for interpreting customer actions, motivations, and preferences throughout the buying journey. This section explores key behavioural models, customer journey phases, and practical frameworks, supported by tables and real-world examples.
Types of Consumer Behavioural Patterns
Different purchase situations trigger distinct patterns in consumer behaviour. Marketers must identify these to personalize engagement effectively.
• Complex Buying Behaviour
– High involvement, significant price, or personal relevance
– Example: Purchasing a car, real estate, or luxury watch
– Consumers seek extensive information, compare multiple options, and evaluate brand reputation
• Dissonance-Reducing Behaviour
– High involvement, but low perceived brand differences
– Example: Buying a fire extinguisher or home insurance
– Marketers must reinforce confidence and reduce buyer remorse
• Habitual Buying Behaviour
– Low involvement, recurring purchases of familiar products
– Example: Buying toothpaste or milk
– Success relies on brand visibility, convenience, and price
• Variety-Seeking Buying Behaviour
– Low involvement but high brand switching
– Example: Trying new snack brands or mobile apps
– Encourages marketers to use trial campaigns or new packaging
Table: Behavioural Patterns by Decision Type
| Behaviour Type | Involvement Level | Brand Comparison | Marketing Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complex Buying | High | Extensive | Informative content and reassurance |
| Dissonance-Reducing | High | Minimal | Post-purchase confidence, guarantees |
| Habitual Buying | Low | Minimal | Availability and branding |
| Variety-Seeking | Low | High | Novelty and attention-grabbing design |
The Five-Stage Buyer Decision Process
A widely adopted behavioural model maps the consumer journey in five key stages. Each stage presents an opportunity for tailored marketing.
• Need Recognition
– Triggered by internal or external stimuli (problem awareness or aspiration)
– Example: A user’s phone slows down, prompting them to seek an upgrade
• Information Search
– Consumers seek relevant options via search engines, reviews, or influencers
– Channels: Google, YouTube, Reddit, forums
• Evaluation of Alternatives
– Side-by-side comparisons of features, pricing, and social proof
– Decision often influenced by user reviews, return policies, and peer recommendations
• Purchase Decision
– Final choice made; influenced by urgency, promotions, or brand trust
– Tactics: Limited-time discounts, free shipping, checkout ease
• Post-Purchase Behaviour
– Satisfaction leads to loyalty, reviews, or word-of-mouth
– Dissonance may cause returns or negative feedback
Funnel Chart: Five-Stage Decision-Making Process
- Top Funnel: Awareness/Need Recognition (broad audience)
- Mid Funnel: Consideration and Evaluation (narrowed down options)
- Bottom Funnel: Decision and Post-Purchase (focused action or loyalty/attrition)
Behavioural Economics and Cognitive Biases
Consumer decisions are not always rational. Behavioural economics explains the irrational factors influencing buying.
• Anchoring Bias
– Relying heavily on the first piece of information seen
– Example: A discounted product appears more valuable when the original price is highlighted
• Loss Aversion
– People prefer avoiding losses over acquiring gains
– Tactic: “Don’t miss out,” limited-time offers
• Social Proof
– Following the actions of others as validation
– Example: “10,000+ customers already bought this”
• Scarcity Effect
– Perceiving products as more desirable when in limited supply
– Strategy: Countdown timers, low stock notifications
The AIDA Model (Attention – Interest – Desire – Action)
AIDA remains a foundational marketing funnel to convert attention into action.
• Attention
– Eye-catching ads, visual branding, or viral headlines
– Example: Spotify billboards or Apple’s product launches
• Interest
– Relevant content that addresses specific needs or problems
– Tools: Blogs, product demos, influencer videos
• Desire
– Emotional connection or perceived benefit
– Example: Nike ads linking products with performance excellence
• Action
– A compelling CTA leading to a purchase, signup, or download
– Methods: “Buy Now,” “Get Started,” or “Try Free for 30 Days”
Matrix: AIDA Model Across Marketing Channels
| Stage | Content Type | Channel Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Attention | Display ads, viral videos | YouTube, TikTok, Out-of-Home |
| Interest | Blog posts, tutorials | Google Search, LinkedIn |
| Desire | Testimonials, case studies | Social media, email marketing |
| Action | CTA buttons, checkout prompts | Website, app, landing pages |
Consumer Behavioural Segmentation
Consumers can also be segmented based on behavioural attributes. This allows brands to customize offers and communication for better outcomes.
• Usage Rate
– Light, medium, or heavy users
– Example: Loyalty programs for frequent customers
• Purchase Occasion
– Regular, seasonal, or special occasion buyers
– Example: Valentine’s Day marketing for gifting brands
• Customer Loyalty
– Loyalists vs. switchers
– Strategy: Rewards, early access, exclusive deals
• Benefits Sought
– Price-sensitive vs. quality-seekers
– Tailor campaigns by highlighting either affordability or premium features
Table: Behaviour-Based Segmentation Tactics
| Segmentation Type | Consumer Trait | Marketing Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Usage Rate | High-usage buyers | Personalized offers, loyalty points |
| Purchase Occasion | Gift buyers | Occasion-based campaigns and bundles |
| Loyalty Level | Brand loyalists | VIP programs, early access, exclusivity |
| Benefits Sought | Value seekers | Discounts, product comparisons |
Example: Amazon’s Behaviour-Driven Strategy
Amazon integrates multiple behavioural models to optimize conversions:
• Tracks browsing and purchase history to recommend relevant products
• Applies urgency (“Only 3 left in stock”) and social proof (“Bestseller”)
• Sends post-purchase emails to drive reviews or upsells
• Customizes the homepage experience by user persona
Conclusion: Why Behavioural Models Matter
Behavioural patterns and models offer critical insights into the consumer psyche, allowing marketers to move from generic targeting to strategic precision. Understanding not only what consumers do, but why they do it, helps businesses craft tailored experiences that meet expectations and build lasting loyalty. Whether through decision funnels, cognitive insights, or behavioural segmentation, these tools empower brands to navigate evolving behaviours with clarity and confidence.
4. Explain Why Consumer Behaviours Evolve
Consumer behaviours do not remain static. They shift over time, influenced by changes in technology, culture, economic realities, and personal experiences. These evolving behaviours reflect how consumers adapt to new environments, information sources, and societal pressures. Understanding the reasons behind these changes allows businesses to stay aligned with consumer needs, maintain brand relevance, and unlock long-term loyalty.
Technological Advancements and Digital Acceleration
The rapid pace of technological innovation has fundamentally reshaped consumer expectations and behaviours.
• Increased Access to Information
– Consumers can research, compare, and review products instantly through smartphones and digital platforms
– Example: Shoppers use barcode scanning apps in-store to compare prices online before purchasing
• Rise of Mobile and On-Demand Experiences
– Mobile apps, e-commerce platforms, and food delivery services promote immediacy and convenience
– Behavioural shift: Expectation for real-time support, 24/7 availability, and fast delivery
• Personalization Through AI and Algorithms
– Streaming platforms like Netflix or e-commerce sites like Amazon personalize recommendations
– Result: Consumers now expect tailored experiences from all brands
Table: Technology’s Influence on Consumer Behaviour
| Technological Driver | Behavioural Shift | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile-first platforms | Increased app usage and shorter attention spans | In-app purchases and mobile UX priority |
| Search engines & AI | On-demand information and comparison shopping | Real-time pricing decisions |
| Voice assistants | Conversational search behaviours | “Alexa, reorder detergent” |
| AR/VR experiences | Immersive exploration before purchase | Virtual furniture previews |
Cultural, Social, and Generational Shifts
Changing values, social norms, and generational preferences contribute significantly to evolving consumer choices.
• Generational Influence
– Gen Z and Millennials prioritize sustainability, diversity, and brand authenticity
– Boomers often prefer traditional touchpoints and value-driven messaging
• Social Justice and Conscious Consumerism
– Growing demand for brands that take a stand on ethics, inclusion, and sustainability
– Example: A fashion brand showcasing supply chain transparency to appeal to value-driven consumers
• Influencer and Peer Validation Culture
– Social media has made peer opinions more influential than corporate advertising
– Behavioural shift: Consumers trust user-generated content over branded content
Matrix: Generational Consumer Priorities
| Generation | Key Values | Purchase Influencers | Preferred Channels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gen Z | Authenticity, activism | Social media, influencer content | TikTok, Instagram, YouTube |
| Millennials | Experience, convenience | Reviews, loyalty programs | Instagram, Email, YouTube |
| Gen X | Reliability, value | Brand reputation, practical features | Facebook, Email |
| Boomers | Quality, service | Word of mouth, traditional ads | Television, Print, Email |
Economic Pressures and Global Events
Global and regional economic conditions often reshape consumer confidence, purchasing power, and spending habits.
• Recession or Inflation
– Shifts behaviour towards price sensitivity, prioritizing value-for-money and discount-seeking
– Example: Surge in private-label product sales during economic downturns
• Pandemic and Health Crises
– Triggered a major rise in e-commerce, telemedicine, and digital payments
– Accelerated behaviour: Avoidance of physical stores and increased use of delivery platforms
• Job Market Trends and Financial Security
– Consumers with financial uncertainty delay high-value purchases or seek long-term utility over luxury
Chart: Economic Impact on Purchase Priorities
A bar chart can demonstrate percentage shifts in key spending categories during and after economic disruptions (e.g., travel, luxury, essentials, health)
Sustainability and Ethical Consumption
With increased awareness of environmental issues and global inequality, consumers are adopting more mindful purchasing behaviours.
• Eco-Conscious Choices
– Rise in demand for recyclable packaging, organic materials, and low-emission logistics
– Example: Growth of refillable product brands in cosmetics and household cleaning
• Transparency and Accountability
– Consumers favour brands that are open about sourcing, labour practices, and environmental impact
– Behavioural shift: Boycotting unethical brands or supporting purpose-driven businesses
• Long-Term Thinking over Instant Gratification
– Buyers are placing more value on durability, minimalism, and reduced waste
Table: Sustainability Impact on Behaviour
| Sustainability Element | Behavioural Response | Brand Example |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic-free packaging | Preference for eco-brands | Lush, The Body Shop |
| Fair-trade sourcing | Willingness to pay premium for ethics | Ben & Jerry’s, Patagonia |
| Carbon-neutral logistics | Added trust and brand preference | IKEA, Allbirds |
| Ethical supply chains | Influences repeat purchase decisions | Everlane, Veja |
Digital Communities and Social Proof
The rise of digital communities and interactive platforms has changed how trust is built and decisions are validated.
• Real-Time Feedback Loops
– Consumers seek instant feedback from peers and experts before committing to a product
– Behavioural shift: Delay in impulse buying, more structured decision processes
• Influencer Authority Over Traditional Ads
– Micro and macro influencers shape brand perception and product adoption
– Example: TikTok trends can lead to viral product sell-outs within hours
• Community-Driven Brand Loyalty
– Niche online communities around specific interests drive stronger brand identity and customer retention
Matrix: Social Influence Behavioural Drivers
| Social Influence Factor | Consumer Impact | Marketing Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| Influencers | Higher credibility than ads | Collaborations and endorsements |
| User-Generated Content | Builds trust and relatability | Campaigns showcasing real user stories |
| Online Reviews | Impact purchase conversion significantly | Reputation management and review strategy |
| Communities (Reddit, Discord) | Foster brand evangelism | Engagement through niche networks |
Data Privacy Awareness and Control
As data breaches and targeted ads become common, consumers are more protective of their personal information.
• Demand for Transparency
– Consumers want to know how their data is used and protected
– Behavioural response: Avoiding brands with vague data policies
• Opt-In Engagement Only
– Preference for value-exchange in marketing, such as giving an email in return for a discount or ebook
• Regulatory Influence
– Laws like GDPR and CCPA increase awareness and shape consumer expectations
Example: Apple’s App Tracking Transparency feature sparked a decline in third-party tracking, forcing brands to pivot to first-party data strategies
Conclusion: The Drivers Behind Consumer Behaviour Evolution
Consumer behaviours evolve due to a complex interplay of technology, values, economic realities, global trends, and generational differences. Businesses must regularly reassess their audience understanding and shift strategies accordingly. By identifying and responding to the underlying forces behind behavioural change, brands can remain resilient, connect meaningfully with audiences, and maintain a competitive edge in a dynamic market landscape.
5. Strategies for Marketing to Evolving Consumer Behaviours
In an era where consumer preferences are constantly shifting, businesses must adapt their marketing strategies to remain relevant, competitive, and connected to their audiences. Traditional approaches no longer suffice as digital technologies, global influences, social trends, and ethical considerations reshape how people make decisions. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of effective, modern strategies for marketing to evolving consumer behaviours.
Leverage Behavioural Data and Consumer Insights
Modern marketing requires a deep, data-driven understanding of consumer motivations, preferences, and decision-making patterns.
• Collect first-party data through website analytics, surveys, loyalty programs, and purchase history
• Use CRM tools and AI-powered platforms to segment audiences based on behaviour, location, and preferences
• Monitor click paths, bounce rates, and cart abandonment to refine messaging and user experience
• Apply predictive analytics to anticipate future behaviours and trends
Matrix: Data-Driven Tools vs. Marketing Outcomes
| Tool Type | Application Area | Outcome Achieved |
|---|---|---|
| CRM Systems (e.g., HubSpot, Salesforce) | Lead tracking and segmentation | Personalized customer journeys |
| Predictive Analytics | Forecasting purchase likelihood | Targeted promotions and upselling |
| Web Analytics (e.g., GA4) | Behavioural tracking | UX improvements and funnel optimization |
| Social Listening Tools | Real-time sentiment analysis | Responsive content and PR crisis control |
Create Highly Personalized and Contextual Marketing
Consumers today expect messaging tailored to their individual needs, preferences, and behaviours.
• Segment audiences by demographic, psychographic, and behavioural data
• Use dynamic content and AI-based recommendations in emails and product pages
• Implement adaptive landing pages that change based on referral source or device type
• Send cart abandonment emails or personalised SMS based on real-time behaviour
Example: Spotify’s “Wrapped” campaign uses listener data to generate individual year-in-review stories, fostering deep engagement and shareability
Adopt an Omnichannel Marketing Strategy
Consumers now engage across multiple touchpoints — websites, social media, apps, email, and in-store — and expect a seamless brand experience throughout.
• Integrate marketing across all channels to ensure consistent messaging and brand tone
• Use marketing automation tools to synchronize communications (e.g., pushing a social media ad after email engagement)
• Optimize UX across devices to ensure smooth transitions between platforms
Chart: Omnichannel vs. Single-Channel Conversion Rates
Bar chart showing how omnichannel users have 2–3x higher lifetime value and conversion rates compared to single-channel users
Develop Authentic, Purpose-Driven Brand Messaging
Value-driven consumers now support brands that reflect their ethics and contribute to causes they care about.
• Communicate transparency in sourcing, sustainability, and social responsibility
• Align brand purpose with cultural values and environmental goals
• Showcase real impact through storytelling, partnerships, and community programs
Example: Patagonia markets its environmental activism as part of its core identity, fostering strong emotional loyalty from eco-conscious consumers
Table: Brand Purpose Alignment and Consumer Impact
| Brand Action | Consumer Response | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Public environmental stance | Increases loyalty among Gen Z and Millennials | Patagonia donating to climate groups |
| Ethical sourcing transparency | Higher trust and long-term repeat purchases | Everlane’s “Radical Transparency” |
| Diversity in advertising | Improves brand perception and inclusiveness | Nike’s inclusive campaigns |
Utilize Influencer and Social Proof Marketing
Modern consumers rely heavily on peer validation and influencer endorsements when making decisions.
• Partner with micro and macro influencers whose values align with your brand
• Encourage user-generated content and customer testimonials
• Showcase product reviews, case studies, and community engagement
Example: Fenty Beauty’s influencer-driven strategy resulted in high brand awareness and rapid global adoption among diverse audiences
Matrix: Influencer Types and Marketing Goals
| Influencer Tier | Follower Range | Ideal Use Case | ROI Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nano | <10K | Niche product awareness | High engagement, low cost |
| Micro | 10K–100K | Authentic product endorsement | Moderate reach, strong conversions |
| Macro | 100K–1M | Broad brand awareness | High visibility, medium engagement |
| Mega | 1M+ | Mass product launches | Expensive, high brand exposure |
Incorporate Agile and Adaptive Marketing Tactics
Evolving behaviours demand flexible, real-time strategies that can be continuously refined.
• Use A/B testing to refine campaign messaging, visuals, and calls-to-action
• Implement short feedback loops to quickly act on customer responses
• Create modular content assets that can be repurposed across different formats and platforms
• Monitor trends in real-time through Google Trends, TikTok, and Reddit
Example: Oreo’s famous “You Can Still Dunk in the Dark” tweet during the Super Bowl blackout showcased agile marketing at its best
Design Experiences Around Emotional Drivers
Emotions play a critical role in influencing behaviour. Emotional connections drive customer satisfaction and advocacy.
• Use storytelling to connect with values, aspirations, and real-life challenges
• Highlight emotional outcomes in product messaging (e.g., “peace of mind,” “belonging,” “freedom”)
• Leverage video marketing to trigger emotional resonance
Chart: Emotional vs. Rational Messaging Impact on Engagement
Line chart showing campaigns with emotional appeal yielding significantly higher shareability and long-term brand recall than rational-only campaigns
Enhance Customer Experience Across the Journey
Consumer loyalty is no longer built solely on product quality but also on experience consistency and satisfaction.
• Map out and optimize the customer journey from awareness to post-purchase
• Implement proactive customer support via chatbots, social DMs, and email automation
• Gather real-time feedback to refine every interaction touchpoint
Table: Customer Journey Optimization Strategy
| Journey Stage | Consumer Expectation | Marketing Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Relevant messaging and clarity | SEO, social media ads, brand storytelling |
| Consideration | Easy comparison and education | Product demos, reviews, webinars |
| Purchase | Smooth checkout and transparent pricing | Cart optimization, mobile UX |
| Post-Purchase | Continued support and value | Email onboarding, loyalty programs |
| Advocacy | Recognition and empowerment | Referral programs, UGC promotion |
Conclusion: Actionable Marketing That Aligns With Evolving Behaviours
To succeed in today’s dynamic landscape, brands must move beyond static, one-size-fits-all approaches. Evolving consumer behaviours call for marketing strategies that are data-informed, emotionally resonant, omnichannel, personalized, and purpose-driven. By continuously aligning their efforts with what consumers value, brands can build stronger relationships, drive consistent engagement, and thrive in an increasingly competitive and change-driven environment.
6. Practical Examples and Case Studies
To effectively understand how evolving consumer behaviours influence marketing outcomes, it’s essential to examine how leading brands have adapted their strategies in real-world scenarios. These practical case studies illustrate the power of behavioural insight-driven marketing, showcasing both successes and failures. The following examples provide actionable lessons for marketers seeking to align with dynamic customer expectations.
Amazon: Hyper-Personalization Through Data Analytics
Amazon is a prime example of how behavioural tracking and predictive analytics can enhance customer engagement and drive conversions.
• Uses real-time browsing, purchase, and search data to deliver dynamic, personalized recommendations
• Employs machine learning algorithms to adjust product suggestions, promotions, and delivery preferences
• Features “frequently bought together” bundles based on behaviour correlations
Marketing Outcomes
• Over 35% of Amazon’s sales are driven by its recommendation engine
• Higher average order value through upselling and cross-selling tactics
Matrix: Amazon’s Personalization Techniques vs. Results
| Personalization Strategy | Behavioural Basis | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Product Recommendations | Browsing and purchase history | Higher engagement and conversion |
| Email Alerts | Abandoned cart and wishlist data | Recovered sales and customer retention |
| Predictive Reordering Prompts | Repeat purchase cycles | Customer convenience and loyalty |
Nike: Emotional Branding and Inclusivity in Messaging
Nike’s marketing strategy has evolved by connecting with consumers on an emotional and cultural level, particularly through social justice themes and community engagement.
• “You Can’t Stop Us” campaign emphasized unity during global crises
• Collaborated with athletes and activists to highlight stories of resilience and inclusivity
• Implemented personalized training content and Nike Run Club to connect fitness data with brand experiences
Marketing Outcomes
• Substantial increase in brand sentiment and social media engagement
• Sales rose by over 10% after launching inclusive campaigns in 2020–2021
Chart: Nike’s Campaign Impact on Consumer Sentiment
Bar chart showing positive brand sentiment before and after major emotional branding campaigns (e.g., Colin Kaepernick partnership)
Starbucks: Behaviour-Driven Loyalty and App Integration
Starbucks has continuously adapted to changing consumer preferences by integrating digital convenience and reward-based engagement.
• Introduced the Starbucks Rewards mobile app to facilitate payments, ordering, and personalized offers
• Tracks behaviour such as purchase frequency, location, and product preferences
• Uses gamification (stars and milestones) to increase user activity
Marketing Outcomes
• Over 60% of transactions in the U.S. are now digital
• The Starbucks Rewards program accounts for nearly 30 million members globally
Table: Starbucks App Features vs. Behavioural Goals
| Feature | Target Behaviour | Resulting Action |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Offers | Encourage repeat purchases | Daily visits and upsells |
| Mobile Ordering | Reduce in-store wait times | Higher app engagement and convenience |
| Reward System (Stars) | Drive loyalty through gamification | Increased retention and basket size |
Spotify: User-Centric Content Experience
Spotify leverages listening history, mood analysis, and time-of-day usage patterns to curate highly personalized experiences.
• Spotify Wrapped offers a year-in-review for each user, turning data into social content
• Daily Mixes and Discover Weekly playlists cater to individual listening behaviours
• Offers contextual playlists such as “Morning Drive” or “Focus Time” based on usage history
Marketing Outcomes
• Millions of shares of Spotify Wrapped on social platforms every year
• Higher user engagement and retention due to personalization
Matrix: Spotify’s Behaviour-Driven Features
| Feature Type | Consumer Insight Used | Emotional/Functional Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Spotify Wrapped | Yearly listening data | Shareability, brand loyalty |
| Discover Weekly | Genre and artist preferences | Continuous engagement |
| Contextual Playlists | Listening time and mood analysis | Relevance and convenience |
Sephora: Omnichannel Beauty Experience
Sephora has excelled in creating a seamless omnichannel experience by aligning in-store and digital journeys with consumer behaviour insights.
• Uses virtual try-on technology and mobile apps to enhance product discovery
• Loyalty program tracks both online and in-store purchases
• Offers beauty quizzes to deliver product recommendations based on preferences and past purchases
Marketing Outcomes
• High conversion rates from app users who engage with virtual try-on features
• Increased customer lifetime value through seamless loyalty integration
Table: Sephora’s Omnichannel Strategy Breakdown
| Channel Integration | Behavioural Strategy | Marketing Impact |
|---|---|---|
| App + In-Store Sync | Unified purchase history | Seamless personalization and rewards |
| Virtual Try-On | Reduce return rate, increase confidence | Boosted product trial and conversions |
| Loyalty Program | Recognize consistent shoppers | Improved retention and advocacy |
Failed Example: Kodak’s Resistance to Behavioural Shifts
Kodak’s decline is often cited as a cautionary tale for ignoring evolving consumer behaviour and technological innovation.
• Failed to embrace digital photography despite holding early patents
• Continued investing in film while consumers shifted to digital and smartphones
• Misread the behavioural trend of instant sharing and convenience
Marketing Consequences
• Lost market leadership to competitors like Canon and Sony
• Filed for bankruptcy in 2012 despite being once synonymous with photography
Chart: Kodak’s Market Share Decline vs. Consumer Adoption of Digital Photography
Line graph illustrating Kodak’s shrinking market share alongside the rise of digital camera adoption (1995–2010)
Conclusion: Actionable Lessons from Market Leaders
These practical examples reveal a consistent theme — brands that anticipate, track, and respond to evolving consumer behaviours outperform those that remain static. Whether it’s personalization, emotional engagement, omnichannel experience, or agility in response to change, successful marketing today is rooted in behavioural intelligence. Businesses must continuously analyze what drives their customers and adjust their strategies accordingly to remain relevant, competitive, and loved.
Conclusion
As consumer expectations evolve in tandem with advancements in technology, cultural shifts, and socio-economic dynamics, the way individuals engage with brands is undergoing a profound transformation. Today’s consumers are no longer passive recipients of advertising messages. Instead, they are empowered, informed, and more intentional in their buying behaviours. From prioritizing convenience and personalization to valuing transparency and ethical alignment, their decision-making journey is influenced by a complex web of emotional, digital, and societal factors.
Understanding evolving consumer behaviours is not merely a marketing trend—it is a strategic imperative. Businesses that recognize the fluid nature of consumer preferences and proactively adapt their marketing strategies are far better positioned to thrive in today’s competitive landscape. Traditional marketing funnels have been replaced by dynamic, non-linear customer journeys, where personalization, social validation, digital convenience, and emotional relevance determine success or failure.
To remain relevant and resonate with modern audiences, marketers must embrace a multifaceted strategy:
• Leverage behavioural data and analytics to understand customers at a granular level
• Design omnichannel experiences that provide consistency and flexibility across every platform
• Personalize content and communication in real time to match individual preferences and behaviours
• Foster trust and loyalty through authentic, purpose-driven messaging and socially responsible practices
• Utilize social proof, influencer collaboration, and user-generated content to build credibility and engagement
• Continuously test, learn, and adapt using agile marketing frameworks that evolve with shifting trends
Real-world case studies from brands like Amazon, Spotify, Nike, Starbucks, and Sephora demonstrate how behavioural intelligence can drive measurable impact. These companies show that aligning with evolving behaviours does more than improve engagement—it builds loyalty, enhances brand equity, and drives sustainable growth. In contrast, examples such as Kodak’s decline highlight the risks of failing to adapt to new consumer realities.
Ultimately, marketing to evolving consumer behaviours requires a deep understanding of human psychology, data-driven precision, technological fluency, and cultural sensitivity. It demands a shift from transactional thinking to relationship-building, from static campaigns to adaptive ecosystems. Brands that recognize this and invest in evolving alongside their customers will not only survive the next wave of change—but lead it.
If you are looking for a top-class digital marketer, then book a free consultation slot here.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your friends and business partners, and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the AppLabx Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to the AppLabx Blog.
People also ask
What are evolving consumer behaviors?
Evolving consumer behaviors refer to changing patterns in how people research, choose, and purchase products based on new technologies, values, and expectations.
Why is understanding consumer behavior important in marketing?
Understanding consumer behavior helps marketers create strategies that resonate with customers, improve targeting, and increase engagement and conversion.
What causes consumer behaviors to change over time?
Consumer behaviors evolve due to digital innovation, economic conditions, generational shifts, social trends, and access to real-time information.
How has technology influenced modern consumer behavior?
Technology enables consumers to research, compare, and purchase faster while expecting personalized, convenient, and seamless experiences across channels.
What role does social media play in shaping consumer decisions?
Social media influences consumers through peer reviews, influencer endorsements, and real-time brand interactions that shape trust and awareness.
How can businesses adapt to evolving consumer expectations?
Businesses must leverage data, personalize experiences, embrace omnichannel marketing, and align with customer values to stay competitive.
What is behavioral segmentation in marketing?
Behavioral segmentation involves dividing audiences based on their actions, such as purchasing habits, brand loyalty, or product usage.
How does personalization impact consumer behavior?
Personalized content and offers increase customer satisfaction, relevance, and conversion rates by aligning with specific needs and interests.
What is the difference between traditional and modern consumers?
Traditional consumers followed linear buying paths, while modern consumers are digital-first, value-driven, and influenced by real-time information.
Why do Gen Z consumers behave differently from other generations?
Gen Z values authenticity, digital convenience, and ethical alignment, making them more likely to support brands with transparent, purpose-driven messaging.
How can companies use data to understand evolving behaviors?
Companies can analyze browsing patterns, purchase history, and engagement metrics to identify preferences and predict future actions.
What is the role of emotional marketing in consumer engagement?
Emotional marketing builds stronger connections by tapping into feelings, values, and aspirations that drive deeper brand loyalty.
How do consumers respond to brand purpose and ethics?
Consumers increasingly support brands that take a stand on sustainability, social justice, and transparent business practices.
What are the key trends in consumer behavior in 2024 and beyond?
Trends include personalization, conscious consumerism, mobile-first behavior, influencer trust, and omnichannel engagement.
How can brands remain relevant in changing consumer landscapes?
Brands must continuously evolve their strategies by listening to customer feedback, monitoring trends, and adapting messaging and offerings.
What is the consumer decision-making process?
It involves five stages: need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior.
How does omnichannel marketing support evolving consumer needs?
Omnichannel marketing ensures seamless experiences across platforms, allowing customers to interact with brands where and how they prefer.
What are some common behavioral models used in marketing?
Popular models include AIDA, the Buyer Decision Process, and Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs for understanding motivations.
Why is mobile optimization crucial for reaching modern consumers?
Most consumers browse and shop on mobile devices, so a fast, user-friendly mobile experience boosts retention and conversions.
How does user-generated content influence consumer behavior?
User-generated content builds trust, provides authentic validation, and encourages community engagement around a brand.
What is the impact of online reviews on buying decisions?
Online reviews serve as social proof, significantly influencing trust and purchase intent among potential customers.
How can businesses track evolving consumer preferences?
Use tools like web analytics, heatmaps, social listening platforms, and CRM data to monitor and analyze changing behaviours.
What role do influencers play in consumer purchasing?
Influencers guide purchase decisions through relatable content, product recommendations, and perceived authenticity.
Why is loyalty program customization important today?
Tailored loyalty programs increase engagement and retention by aligning rewards with individual consumer behaviour and interests.
How can brands reduce consumer churn in dynamic markets?
By offering ongoing value, maintaining relevance, and building strong emotional connections, brands can retain evolving customers.
What are some examples of brands adapting to consumer behavior?
Brands like Amazon, Nike, Spotify, and Sephora personalize experiences, use real-time data, and align with ethical values successfully.
What mistakes do brands make when ignoring behavior changes?
They risk reduced engagement, declining sales, and loss of trust by staying rigid, tone-deaf, or misaligned with audience expectations.
How do cultural shifts influence buying behaviour?
Cultural shifts shape values, lifestyle choices, and social norms, influencing how and why people buy certain products or services.
What is the role of sustainability in consumer decisions?
Sustainability influences buying behaviour as more consumers seek environmentally responsible and ethically sourced products.
How should marketers future-proof their strategies for behaviour changes?
They should invest in agility, monitor trends, embrace innovation, and focus on building long-term, value-aligned customer relationships.





























