Key Takeaways
- AI-generated summaries use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning models to automatically condense long documents into concise, meaningful insights.
- There are different types of AI summarization—extractive, abstractive, and hybrid—each designed to balance accuracy, readability, and contextual understanding.
- When applied strategically with human oversight, AI summarizers improve productivity, reduce information overload, and support faster, data-driven decision-making across industries.
In a world where the volume of digital information continues to grow exponentially, the ability to quickly understand and act on content has become essential. Long reports, lengthy research papers, exhaustive meeting transcripts and endless email threads can overwhelm even the most diligent readers. Artificial-intelligence-generated summaries have emerged as a powerful solution to this challenge, offering concise and coherent condensations of complex material. These summaries harness the power of AI and machine learning to automatically extract and synthesize the most important ideas from large volumes of text, enabling individuals and organisations to absorb key information faster and more efficiently than traditional manual reading allows.

At its core, AI-generated summarization is a type of automatic summarization that uses artificial intelligence algorithms to identify central themes, key facts and meaningful context within source content and present them in a reduced format.
Unlike simple keyword extraction, this process interprets meaning and relationships within the text, aiming to preserve the original intent and tone while stripping away redundancy. This technology is not limited to text alone; it can extend to audio, video and multimodal data, broadening its utility across sectors that rely on rapid content assimilation.
The rise of AI summarization comes at a time when businesses, researchers, educators and everyday users are inundated with more information than can realistically be processed manually.
By leveraging natural language processing, deep learning and advanced machine learning models, AI summarizers transform unwieldy documents into digestible overviews that help users make informed decisions without committing extensive time or resources. Whether it’s summarizing thousands of customer service chats, distilling insights from technical documentation, or providing quick overviews of news and articles, this technology is reshaping how information is consumed.
As AI summarization continues to improve, understanding how it works, where it excels, and where its limitations lie will be critical for anyone seeking to use or build applications around this technology. In the sections that follow, this article will explore the mechanisms behind AI summary generation, the key types of summarization methods, real-world use cases, and practical considerations that influence performance and reliability.
But, before we venture further, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About AppLabx
From developing a solid marketing plan to creating compelling content, optimizing for search engines, leveraging social media, and utilizing paid advertising, AppLabx offers a comprehensive suite of digital marketing services designed to drive growth and profitability for your business.
At AppLabx, we understand that no two businesses are alike. That’s why we take a personalized approach to every project, working closely with our clients to understand their unique needs and goals, and developing customized strategies to help them achieve success.
If you need a digital consultation, then send in an inquiry here.
Or, send an email to [email protected] to get started.
What are Artificial-Intelligence-Generated Summaries & How Do They Work
- What Are AI-Generated Summaries?
- The Purpose & Benefits of AI Summaries
- How AI Summary Generation Works
- Types of AI Summarization
- Use Cases & Real-World Examples
- Accuracy, Limitations & Considerations
- Best Practices for Using AI Summaries
- Future Trends in AI Summarisation
1. What Are AI-Generated Summaries?
Artificial-intelligence-generated summaries refer to condensed representations of longer texts, created autonomously by computer systems that use natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and deep learning models. These summaries aim to retain the most important insights from original content while eliminating superfluous information, allowing readers to grasp the essence of large data quickly without reading the entire material.
AI summarization is a form of automatic summarization, a field in computational linguistics and information retrieval focused on shortening documents algorithmically while preserving their central meaning. It can process a wide range of text content, from legal contracts and academic research to news articles, customer feedback, meeting transcripts, blogs, and reports.
The Core Definition and Scope
Automatic summarization involves reducing the volume of input text to a concise form that captures the key ideas and intent of the original content. This process leverages AI-powered techniques and models to analyze the meaning, structure, and significance of sentences within the source text and identify what information is essential to convey.
AI-generated summaries differ from traditional summaries in that they do not require human input for interpretation or rewriting. Instead, they use statistical patterns, semantic understanding, and, in advanced systems, generative modeling to create summaries that are either directly extracted or newly formulated.
How AI Summaries Are Categorized
AI-generated summaries can be broadly classified based on how they process and produce the summary content. The two main approaches are extractive and abstractive summarization. Some modern systems also combine both into a hybrid method.
Approaches to AI Summarization
| Method | Description | Example Output Style | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extractive Summarization | Selects and compiles important sentences or phrases from the original text without altering wording. | Direct sentences from text | Legal documents, research papers |
| Abstractive Summarization | Generates new condensed representations, paraphrasing original concepts. | Original summary phrased in new words | Conversational content, marketing briefs |
| Hybrid Summarization | Combines extractive selection with generative rewriting. | Mixture of extracted key points and rephrased insights | Complex documents requiring context clarity |
Extractive summarization functions like a highlighter, identifying the most relevant parts of a document and stitching them together into a summary. It excels at accuracy because it reproduces original text fragments, but may sometimes lack smooth flow.
Abstractive summarization goes further by understanding the semantic meaning and creating new sentences that convey the core information. This method produces summaries that are closer to how a human would explain the contents, though it can be more computationally demanding and sometimes less exact.
Practical Examples of AI-Generated Summaries
Example 1: News Article Summarization
Original content: A 1,500-word news article explaining regulatory changes in international trade.
- Extractive Output: A string of key sentences from the article that mention key markets, dates, and policy shifts.
- Abstractive Output: A concise paragraph summarizing the essence of the article: regulatory update, affected markets, and implications for stakeholders.
Example 2: Research Paper Synthesis
Use case: Scientists need a quick overview of multiple research documents.
- Multi-document summarization automatically merges insights from several studies to create a unified summary highlighting trends, findings, and gaps across documents.
Example 3: Meeting Transcripts
AI tools can condense a long meeting transcript into a short summary that highlights discussion points, decisions made, and follow-up action items. The output can be either extracted quotes or entirely reformulated sentences depending on the model used.
Types of Text Summarization in Practice
In the context of AI, summarization methods vary not just by output style but also by the scope and intent of the summary produced:
Generic vs. Query-Focused Summaries
| Summary Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Generic Summary | Provides an overall overview of the full text. | Summarizing a long report into main takeaways. |
| Query-Focused Summary | Tailors the summary to respond to a specific question or topic. | Extracting only sections relevant to a user’s query from a legal document. |
Generic summaries help provide broad insights, while query-focused summaries refine content to specific intent. Both are generated automatically based on the models and prompt instructions given to the AI.
AI Summarization Across Formats
Although the concept originated with text summarization, AI summarization technology has expanded into other content formats:
- Video summarization identifies key frames or segments that convey the most important parts of a video.
- Image collection summarization selects representative images from large galleries.
The Role of AI Models and Natural Language Processing
AI-generated summarization systems incorporate advanced NLP techniques, such as transformer architectures, to analyse syntax, semantics, and context. Models like GPT, BERT, BART and others are trained on vast text corpora to understand linguistic patterns and generate human-like summaries.
These models use deep neural networks to parse and transform text, enabling summaries that go beyond basic extraction and reflect nuance, meaning, and contextual relationships among concepts.
AI Summarization Examples in the Real World
AI summaries are now embedded in a variety of applications and platforms:
- Search engines provide AI-generated overviews of search results, delivering condensed summaries of topic clusters.
- Document management tools summarize contracts, research documents, technical manuals, and medical records.
- Customer support platforms generate summaries of chat histories to assist agents in quickly understanding customer issues.
2. The Purpose & Benefits of AI Summaries
AI-generated summaries are not merely a technological novelty; they serve fundamental roles in information management, productivity enhancement, decision support, and organisational efficiency. As the volume of digital information grows — accelerated by data generation that doubles frequently in many business contexts — AI summarisation has become a strategic tool for modern knowledge work. AI summaries help users understand complex content faster, reduce cognitive overload, and make data actionable across industries.
Purpose of AI Summaries
AI summaries have been adopted widely because they address several pervasive challenges in today’s information-driven environments:
Reduce Information Overload
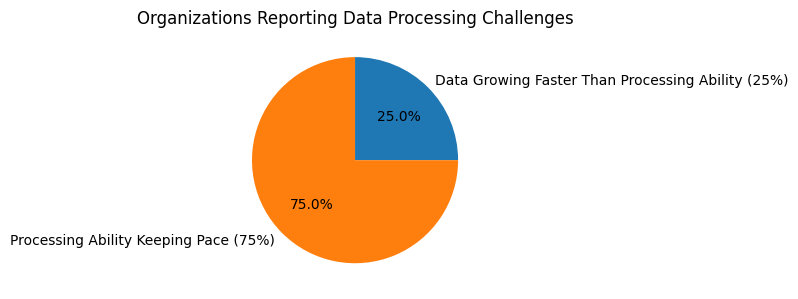
Organisations and individuals often face vast amounts of text – research reports, legal documents, news feeds, customer feedback, and communication logs. Traditional reading methods cannot scale to keep pace. AI summaries distil essential points from large content sets, enabling quick comprehension without manual reading. In one IDC-sponsored report, 25% of respondents said data volume is growing faster than their ability to process or manage it, underlining the need for AI-driven summarisation.
Accelerate Knowledge Work
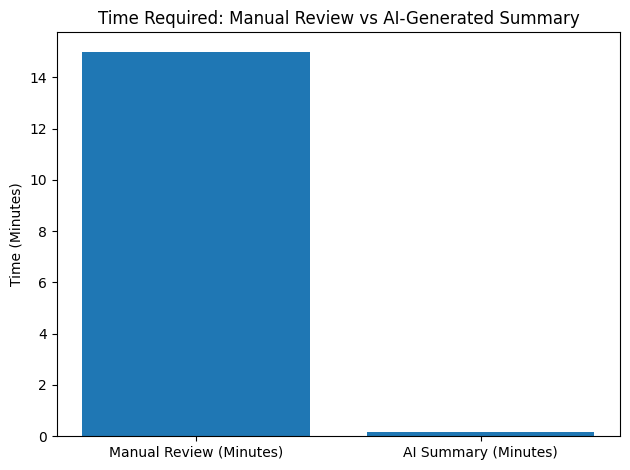
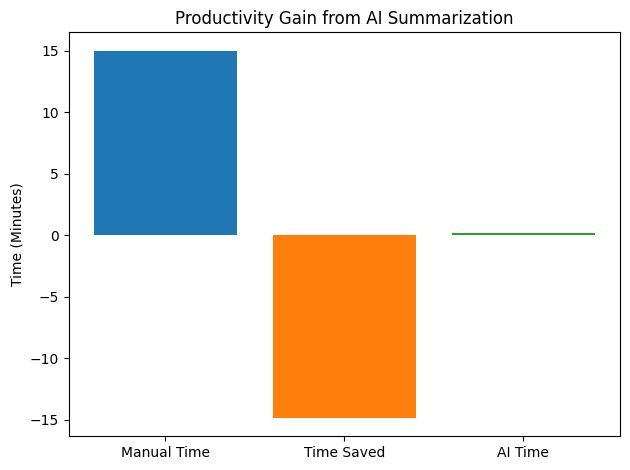
AI summaries enable professionals to access important insights in seconds rather than hours. For example, summarising a 3,000-word report might take a human reader 10–15 minutes, whereas an AI summariser can produce key points in under 10 seconds, dramatically accelerating workflows.
Support Rapid Decision-Making
Executives and teams need concise information to make strategic decisions. By highlighting key conclusions and data points, AI summaries reduce the time between information acquisition and action. In business settings, this supports agile decision cycles, especially in fast-moving environments such as financial markets or competitive positioning tasks.
Enable Scalability in Content Consumption
AI summarisation tools are designed to scale; they can process hundreds or thousands of documents without performance degradation. This capability is critical for areas such as legal contract review, market intelligence, regulatory compliance, and research aggregation, where manual processing would require substantial time and labour.
Benefits of AI Summaries
AI summarisation delivers measurable advantages across time, accuracy, usability, and organisational impact. These benefits extend from individual knowledge workers to enterprise-level workflows.
Time Efficiency and Productivity Gains
One of the most widely recognised benefits of AI summaries lies in time-savings. AI tools convert lengthy content into concise summaries almost instantly, freeing users to focus on higher-value tasks. This directly impacts individual productivity as well as organisational throughput. According to industry analysis, AI summarisation tools can reduce reading and comprehension time dramatically, enabling faster transitions from information intake to action.
A comparative overview demonstrates this benefit:
| Task | Manual Approach | AI Summary Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Reading a 3,000-word report | 10–15 minutes | 5–10 seconds |
| Reviewing multiple documents | Hours | Minutes or less |
| Summarising meeting transcripts | Manual note-taking | Automated extraction of key points |
This time savings compounds across teams and departments — particularly in high-volume environments like legal review, academic research, and customer support analytics.
Improved Accuracy and Consistency
AI summarisation tools apply consistent criteria to every document, reducing variability and subjective bias often seen in manual summarisation. This is especially valuable in compliance reporting, audit preparations, and regulatory submissions where accuracy and completeness matter. AI summaries ensure that key information is consistently represented, irrespective of the number of documents processed.
Enhanced Accessibility of Complex Information
AI summaries make complex or technical documents more accessible. This is beneficial in domains such as healthcare, research, engineering, and finance, where specialised terminology could otherwise hinder understanding. For instance, researchers can review complex literature quickly by focusing on distilled findings, while healthcare professionals can summarise patient data or clinical studies more efficiently.
Empowering Collaboration and Communication
By distilling long content into clear, actionable summaries, AI tools support better collaboration across teams. Summaries help ensure that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of material without requiring everyone to read full documents. This is particularly useful in project teams, cross-functional initiatives, and multi-location organisations where clear communication is essential.
For example, meeting summarisation can capture key points, decisions, and action items, enabling team members to stay aligned with less effort and reducing the risk of miscommunication.
Benefits Matrix: AI Summarisation Across Key Dimensions
The following matrix illustrates how AI summaries deliver value across different organisational functions:
| Dimension | Core Benefit | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Time & Effort | Reduces manual content processing time | Quickly summarising business reports |
| Accuracy & Consistency | Standardises information extraction | Compliance documentation and risk reporting |
| Comprehension | Distils complex content into digestible insights | Research review, technical literature |
| Collaboration | Supports shared understanding | Team meeting summaries and briefs |
| Decision Support | Highlights actionable insights | Executive dashboards and strategic planning |
| Scalability | Handles large volumes of content | Multi-document summarisation across archives |
This matrix underscores how AI summarisation not only addresses specific tasks but also integrates into wider organisational processes to support efficiency and strategic clarity.
Real-World Examples of AI Summarisation Benefits
Customer Feedback Analysis
Large e-commerce organisations often have thousands of customer reviews per product. AI review summarisation aggregates and highlights key themes from feedback, enabling quicker customer insights and better product positioning without manual review of every comment. This approach is increasingly adopted by leading brands to enhance shopper experience and drive conversions.
Customer Support Contact Centres
In customer service environments, summarisation reduces the need for agents to manually review long call transcripts. This speeds up ticket resolution, enhances quality assurance, and improves documentation accuracy, leading to faster service delivery and improved customer satisfaction.
Legal and Contract Review
Legal teams use AI summarisation to extract clauses, compliance requirements, or unusual language from extensive contracts. By automating this review process, organisations can shorten contract cycle times and reduce the risk of missing critical information.
Quantified Benefits: Industry Insights
While exact metrics vary by implementation, industry observations consistently show significant gains:
- AI summarisation can reduce reading and comprehension time from minutes to seconds for long documents.
- Organisations using AI summarisation report reductions in manual review effort and improved speed in decision cycles.
- Scaling summarisation across workflows supports consistent output quality, especially at higher data volumes where human effort would be prohibitively expensive.
3. How AI Summary Generation Works
Understanding how AI generates summaries involves unpacking the interaction of natural language processing, machine learning models, and algorithmic decision-making. AI summarization is not a single method but a combination of linguistic processing, relevance scoring, semantic understanding, and often deep generative models. This section breaks down these processes, explains core methodologies, and compares key techniques with examples.
Foundations: Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning
AI summarization depends fundamentally on Natural Language Processing (NLP), a subfield of artificial intelligence that enables machines to interpret, analyze, and generate human language. NLP combines linguistics and machine learning to convert unstructured text into structured, machine-understandable data. It enables tasks such as tokenization, semantic analysis, syntactic parsing, and context modeling. NLP frameworks allow computers to identify grammatical relationships, meanings, and discourse structure in text, which are essential for summarization.
At its core, summarization equates to reducing large bodies of text to their essential points while preserving overall meaning. AI summarization systems are typically trained on large datasets of texts and human-generated summaries. They learn patterns that map long inputs to short representations. Training data enables models to recognise which phrases and ideas are central and which are auxiliary.
Machine learning models used for summarization progressively moved from statistical and rule-based systems to neural approaches. Older methods relied on metrics like word frequency and sentence position to identify key content. Modern approaches use advanced neural networks capable of modelling linguistic patterns and learning semantic meaning, such as sequence-to-sequence architectures and transformer-based models.
Core Summarization Techniques
AI summarization operates through several distinct approaches. Each serves different objectives and requires varying levels of computational complexity and contextual understanding.
Extractive Summarization
Extractive summarization identifies sentences or phrases in the original text that are most relevant and stitches them together to form a summary. It examines linguistic and statistical signals such as sentence position, keyword frequency, and sentence similarity to determine relevance. Sentences with higher importance scores become part of the summary.
Key Characteristics:
- Preserves original wording without paraphrasing.
- Usually accurate because content isn’t rephrased, reducing risk of error.
- May produce summaries that are less smooth or cohesive in narrative flow.
Example: For a news article about regulatory changes, extractive summarization might select the paragraphs detailing the date of policy changes, affected sectors, and projected impacts, presenting them verbatim as summary content.
Abstractive Summarization
Abstractive summarization generates entirely new sentences that convey the core meaning of the source content rather than selecting text verbatim. It resembles how humans summarise text — reading, understanding, and rearticulating ideas in novel wording. Key to this technique is semantic understanding and the ability to generate fluent language.
Key Characteristics:
- Produces summaries with improved readability and logical flow.
- Requires models capable of deep semantic understanding.
- Can sometimes introduce slight factual inaccuracies (hallucinations) due to generative processes if not well trained.
Example: Summarising a research report, an abstractive model might articulate: “The study concludes that AI adoption increases productivity but requires human oversight to avoid error,” even if this exact sentence doesn’t appear in the original content.
Hybrid Summarization
Hybrid approaches combine extractive and abstractive techniques to enhance both accuracy and readability. An extractive phase first identifies the most relevant segments; a subsequent abstractive step rephrases or refines those segments into a more coherent summary.
AI Architecture and Semantic Processing
Modern summarization leverages large language models (LLMs) — transformer-based deep learning systems trained on vast text corpora. These models convert text into numerical representations (tokens) and learn patterns of language relationships. The transformer architecture uses mechanisms like self-attention to understand context by assessing the influence of each token across the entire text sequence.
Transformer-Based Workflow:
| Stage | Function |
|---|---|
| Tokenization | Converts text into discrete units that models can process. |
| Embedding | Maps tokens to numerical vectors representing meaning and positional context. |
| Attention Layers | Models relationships between all tokens in parallel, identifying contextually relevant features. |
| Decoder/Output Generation | Generates the summary based on the learned representation of the input text. |
In transformer models, each token’s representation evolves through multiple attention layers, enabling the model to capture subtle linguistic nuances and long-range dependencies in the text — elements critical to producing accurate and contextually appropriate summaries.
Comparative Summary of Techniques
| Technique | Core Mechanism | Typical Strengths | Typical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extractive | Selects sentences from original text | High fidelity to source content | May lack narrative fluency |
| Abstractive | Generates new sentences based on meaning | Produces fluent, human-like text | Computationally intensive; potential hallucinations |
| Hybrid | Combines extraction with generation | Balances accuracy and readability | More complex processing pipeline |
Sequential Process of AI Summary Generation
The summarization process typically follows a structured pipeline:
Text Preprocessing
Text is cleaned, tokenised, and normalised. Tokenisation splits text into constituent elements that models can process. Preprocessing may include eliminating extraneous characters and standardising formats.
Content Representation
AI models transform text tokens into vectors that encode semantic meaning. Embeddings position these vectors in a multi-dimensional space where semantic similarity can be quantified.
Relevance Scoring and Context Modeling
Extractive methods score sentences based on relevance metrics such as term frequency, semantic similarity, and lexical features. Neural models use attention mechanisms to determine which parts of the text contribute most to meaning.
Generation or Selection
Depending on the technique, the system either selects high-scoring sentences (extractive) or generates new text conditioned on its semantic understanding (abstractive or hybrid).
How AI Models Learn to Summarise
Training summarization models often involves supervised learning on large datasets where the input document is paired with human-generated summaries. Through training, models learn associations between input text patterns and summary outputs. High-performance models such as GPT and other LLMs are pre-trained on vast text corpora and fine-tuned for summarization tasks, enabling a combination of language generation and semantic compression.
Illustrative Example of the AI Summary Workflow
Consider an academic paper summarisation task:
- Input: Full research paper text (e.g., 5,000 words).
- Extraction Stage (Hybrid): Key sections like objectives, methodology, and conclusions are identified and extracted.
- Semantic Encoding: Tokens representing extracted content are processed through attention layers to generate vector representations.
- Summary Generation: An abstractive model produces a concise 200-word summary that paraphrases key ideas in natural language.
This approach retains accuracy by focusing on important segments while improving readability through generation.
Evaluation Metrics for AI Summaries
AI summarization quality is quantified using metrics such as ROUGE scores, which compare overlap between model summaries and reference summaries. Higher ROUGE scores indicate that the generated summary effectively captures essential text elements found in human references.
In summary, AI summary generation is a layered process that blends linguistic understanding, relevance assessment, and machine learning. By combining NLP techniques with transformer architectures and hybrid strategies, modern AI systems offer fast, coherent, and contextually meaningful summaries across diverse applications.
4. Types of AI Summarization
AI summarization encompasses several specialised methods designed to condense information effectively. Each type has unique strengths and use-cases depending on the complexity of the source content, the need for context, and the desired output fidelity. The main categories include extractive, abstractive, query-focused, multi-document, and hybrid summarization. Understanding these helps organisations choose the best strategy for tasks from news aggregation to research synthesis and customised query responses.
Extractive Summarization
Extractive summarization selects the most relevant sentences or phrases directly from the source text without changing the original wording. Think of it as highlighting key parts of a document to build a summary that retains the exact wording of the input. This method is widely used because it ensures high factual accuracy, preserves original meaning, and avoids potential language generation errors.
How It Works
Algorithms score and rank sentences based on linguistic features such as:
- Word frequency
- Sentence position
- Sentence similarity
- Keyword relevance
Sentences with the highest relevance scores are then concatenated to form the summary.
Use-Cases and Examples
Legal document review often relies on extractive summaries to ensure that key clauses and statements are directly pulled from the text, maintaining legal precision. Similarly, in academic research, extractive methods help identify significant findings for quick scanning.
Abstractive Summarization
Abstractive summarization goes beyond extraction by understanding the meaning of the input text and generating a new summary in the model’s own words. This technique resembles human summarisation — rephrasing and synthesising core ideas into a fluent narrative. Unlike extraction, abstractive summarisation may use vocabulary that was not present in the original document.
Key Features
- Generates new sentences to explain meaning
- Produces more natural and concise summaries
- Generally requires deep learning models such as transformer architectures
Although more computationally expensive, abstractive methods often produce smoother and more readable outputs, particularly useful for conversational or creative content where fluid language matters.
Example Application
Customer review summarisation on e-commerce platforms often uses abstractive models to synthesise sentiment, key themes, and product attributes into concise overviews that read naturally to consumers.
Query-Focused Summarization
Query-focused summarization tailors summaries to a specific user query or information need rather than producing a generic overview of the entire text. This method extracts or generates content that directly answers a targeted question, making it ideal for research assistants, question-answering systems, and personalised content delivery.
Distinctive Elements
- Understands user intent through query analysis
- Focuses on relevant segments from one or more documents
- Produces summaries that respond directly to information requests
Example
A medical professional seeking information on “treatment outcomes for condition X” could receive a focused summary that highlights just the findings relevant to that query from a large research corpus, rather than a generic summary of each study.
Multi-Document Summarization
Multi-document summarization processes a collection of related documents and synthesises a unified overview. This type is essential when information about the same topic exists across many sources, such as news articles, research papers, or customer feedback threads.
Challenges and Capabilities
Multi-document summarization must:
- Consolidate overlapping information
- Maintain coherence across diverse sources
- Resolve conflicting perspectives
It often uses both extractive and abstractive techniques together to balance accuracy with readability.
Example
News aggregation services automatically summarise multiple reports on breaking events into a single narrative, capturing varying viewpoints and key developments without requiring users to read every individual source.
Hybrid Summarization
Hybrid summarization blends extractive and abstractive methods to leverage the strengths of both. An extractive stage first identifies the most relevant content, which is then refined and rewritten during an abstractive generation stage to improve fluency and readability.
Advantages
- Preserves critical content from extraction
- Enhances summary coherence through abstraction
- Reduces the risk of factual hallucination compared to fully abstractive models
Example Workflow
- Extract sentences with the highest relevance scores
- Condense and rewrite them in a new narrative using a generative model
This approach is often used in summarising long reports or multi-topic documents, where both accuracy and readability are priorities.
Comparative Overview of AI Summarization Types
The following matrix outlines differences in purpose, methodology, and typical use scenarios for each major summarization type:
| Summarization Type | Primary Output Style | Best For | Typical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extractive | Verbatim sentences from source | High accuracy needs, legal/technical content | May lack narrative flow |
| Abstractive | Newly generated summary text | Consumer-friendly summaries, reports | Higher computational cost |
| Query-Focused | Targeted response to specific query | Research & personalised insights | Dependent on query accuracy |
| Multi-Document | Consolidated summary from many sources | News aggregation, research synthesis | Complexity in conflicting data |
| Hybrid | Extractive base refined by abstraction | Balanced accuracy & fluency | More complex pipeline |
AI Summarization in Practice
Across industries, AI summarization methods are increasingly integrated into workflows because they reduce reading time, improve information access, and support decision-making. For example, summarisation systems are embedded in business intelligence platforms, document management software, and customer support tools, helping professionals process large content volumes more efficiently.
By understanding the differences between summarization types — especially extractive, abstractive, and hybrid approaches — organisations can implement solutions that align with their data complexity, accuracy requirements, and user experience goals.
5. Use Cases & Real-World Examples
AI-generated summarization is one of the most widely adopted artificial intelligence technologies in practical settings. It is used across industries to turn long text, dialogue, and even multimedia content into concise, actionable insights. Below is a comprehensive examination of how AI summarization is applied in real-world environments, supported by verified examples, practical applications, and structured comparison tables.
Business & Enterprise Applications
AI summarization is increasingly integrated into enterprise workflows to enhance productivity, improve decision-making, and streamline operations.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) & Sales
Many CRM platforms now use AI to summarise customer interactions:
- Embedded summarization tools like Salesforce’s Einstein Conversation Insights generate call summaries and highlight key customer information to improve follow-ups and team collaboration. The generated summaries help sales teams understand call outcomes and next-step actions without listening to full recordings.
Contact Center & Support Operations
In high-volume helpdesk environments, AI summaries help staff handle information overload:
- Contact centre tools (e.g., Dialpad’s AI Recaps) automatically summarise call and meeting transcripts, helping agents capture action items and understanding outcomes without reading full transcripts.
- By summarising dialogue analytics, supervisors can identify common customer concerns and trends in support interactions, improving coaching and service quality.
Human Resources & Compliance
HR departments use AI summarization to expedite documentation processes:
- Summarizing candidate resumes across large applicant pools to identify key qualifications and match candidates with roles more efficiently.
- Reviewing updated policies and compliance documents to highlight changes and implications.
Content & Knowledge Management
AI summarization plays a significant role in transforming how organisations handle large text collections, research briefs, and knowledge base repositories.
Knowledge Base Automation
Modern helpdesk and self-service systems integrate summarization to:
- Automatically condense long procedural documents into concise answers tailored to user queries, reducing manual search time.
- Enhance tagging and classification so related content surfaces more easily in searches, improving knowledge retrieval.
Research & Literature Reviews
Researchers and academics benefit from automated summarization that rapidly condenses long papers:
- AI tools can process thousands of academic articles and synthesise the main contributions, enabling scholars to manage vast literature volumes efficiently.
Document Management
AI summarization assists in quickly understanding business reports, technical documentation, and compliance files:
| Application | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Contract summarization | AI extracts core clauses from legal contracts | Reduces time lawyers spend on initial review |
| Technical manuals | Summarising complex instructions into simplified overviews | Improves usability and training |
| Policy brief summarization | Condenses updates into digestible highlights | Supports rapid organisational compliance |
Media, Marketing & Publisher Platforms
AI summaries improve how information is consumed by end users and support content delivery strategies.
Consumer Reviews & E-Commerce
- Platforms like the Apple App Store have started using AI-generated review summaries that condense user feedback into paragraph-length highlights to help consumers assess key sentiments quickly.
News Aggregation & Media Outlets
Multi-document summarization techniques are used to:
- Aggregate news articles on a common topic into a single overview, reducing the time readers spend following developments across sources.
Marketing Content Creation
AI summarization helps content creators repurpose long-form pieces:
- Marketers can generate concise content previews (e.g., summarised blog excerpts) for newsletters or social media, improving engagement by delivering essential points quickly.
Productivity & Personal Use Cases
AI summarization is not limited to enterprise and media; it is embedded in many personal productivity tools.
| Tool Type | Typical Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Browser integration | Summarise articles or web pages instantly | Firefox’s “shake to summarize” feature provides instant webpage summaries on mobile browsers. |
| Email and message summaries | Summarise long email threads | AI assistants digest threads for quick comprehension. |
| Daily brief generation | Consolidates schedule, emails, and alerts | Smartphone platforms like Galaxy AI provide daily summaries of events and important updates. |
Healthcare & Clinical Documentation
AI summarization is transforming healthcare workflows by reducing administrative burden:
- Automated medical scribes transcribe consultations and summarise interactions, freeing clinicians to focus on patient care rather than documentation. Many clinicians using ambient AI tools report significant time savings and a better focus on patient interaction.
Cross-Industry Summarization Use Case Matrix
| Sector | Primary Use | Key Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|
| Sales & CRM | Summarising customer interactions | Faster deal tracking and follow-ups |
| Customer Support | Call/Transcript summarization | Improved resolution speed |
| HR/Compliance | Policy and resume summarization | Efficiency in review processes |
| Knowledge Management | Document knowledge extraction | Enhanced information retrieval |
| Media & Publishing | Condensed content delivery | User engagement and retention |
| Academic & Research | Literature summarization | Faster review of research trends |
| Healthcare | Clinical note summarization | Reduced administrative workload |
| Productivity Tools | Personal content summaries | Time savings and ease of access |
Example Implementation Scenarios
AI as Assistant in Meetings: AI tools integrated into video conferencing platforms can generate summaries and action items immediately after meetings, saving time and improving team coordination without manual note-taking.
Dialogue Summarization for Support: In call centres with high volumes of interactions, AI summaries allow supervisors to spot trends in customer concerns without listening to hours of recordings, supporting better strategic decisions.
Knowledge Base Answer Tailoring: AI summarization enables knowledge bases to return brief, relevant summaries based on user queries, reducing the need for users to sift through long documents manually.
AI summarization is now a foundational capability of many productivity, support, and content platforms, delivering tangible efficiency gains by converting dense, unstructured data into actionable insights. Its continued adoption reflects its proven value in real-world environments across industries and scales of operation.
6. Accuracy, Limitations & Considerations
While AI-generated summaries offer significant advantages in processing and condensing large volumes of information, they are not infallible. Understanding the accuracy constraints, potential pitfalls, and practical considerations is essential for responsible use, especially in professional, research, and high-stakes environments. This section unpacks key accuracy issues, common limitations, and strategic considerations when deploying AI summarization technologies.
Accuracy: What AI Summaries Get Right and Where Errors Occur
AI summarization models are built to identify and condense the most salient information from source content, but accuracy varies by context, complexity, and data quality.
Language Model Strengths in Accuracy
AI summarizers, especially those based on large language models (LLMs), can reliably extract key ideas, reduce information load, and generate cohesive overviews from straightforward texts. They perform well for:
- Factual summaries of structured content
- Short to medium-length documents
- Topics with clear, direct language
Their ability to replicate the form and substance of original texts is enhanced when adequate training data and domain relevance exist.
Sources of Inaccuracy
AI summarization systems may produce inaccurate outputs due to several inherent limitations:
- Hallucination – AI may create statements that appear truthful but are not supported by the source text, due to prediction-based generation processes. This phenomenon is widely discussed in AI literature as a core risk of generative systems.
- Misinterpretation of complex language – Ambiguity, technical jargon, or nuanced argumentation can lead to incorrect simplification or misrepresentation of key ideas.
- Incomplete context comprehension – Very long documents or those with layered structure often exceed the model’s context window, leading to partial or fragmented summaries.
- Bias and training limitations – Language varieties, under-represented dialects, or culturally specific meanings may be inaccurately processed due to limitations in the model’s training corpus.
These accuracy shortcomings can have tangible consequences. For instance, overly simplified or hallucinated summaries of research findings might lead to misguided decisions or errors in interpretation, particularly in academic or clinical contexts.
Common Limitations of AI Summarization
AI summarization systems face fundamental constraints that stem from both technical limitations and the inherent nature of automated text processing.
Loss of Nuance and Depth
AI summaries tend to prioritize general themes and key facts but can oversimplify complex ideas, especially in texts involving layered reasoning, theoretical arguments, or subtle distinctions. In research articles or philosophical works, this can lead to summaries that miss crucial depth or context.
Example: In summarising a dense academic debate with multiple theoretical positions, an AI may collapse distinct arguments into a generic statement, obscuring the differences between views.
Lack of Domain Expertise
AI models do not inherently possess specialised expertise. They rely on patterns learned from training data rather than real world subject-matter insight. Thus, summaries of advanced scientific research, legal texts, or specialised engineering documentation may lack precision or miss critical domain-specific nuances.
Evaluation Limitations
Common automatic metrics used to assess summarization quality — such as ROUGE — focus on word overlap with reference summaries and do not directly measure factual correctness, coherence, or logical flow. Thus, high scores do not guarantee semantic accuracy or usability in complex decision contexts.
Accuracy Challenges in Real-World Scenarios
The nature of the text and the expected use of summaries influence accuracy outcomes. The table below outlines typical challenges across different summarization contexts.
| Domain / Use Case | Accuracy Challenge | Typical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| News & Media | Rapidly evolving topics may contain conflicting or emerging information | Summaries may be outdated or oversimplified |
| Academic Research | Technical language and multiple hypotheses | Nuance loss and misrepresentation of findings |
| Legal Documentation | Structured clauses with precise legal meaning | Relevant legal nuances may be excluded or misinterpreted |
| Technical Reports | Complex technical specifications and tables | Data in technical formats may be mis-extracted or overlooked |
| Multilingual Content | Language model training bias toward certain languages | Inconsistent performance across language varieties |
Hallucinations and Factual Errors in Summaries
Hallucination is a specific form of inaccuracy where the AI output contains fabricated information that is plausible but not grounded in the source text. In natural language generation, hallucinations are a central challenge because generated summaries may sound authoritative despite being incorrect.
There are documented cases where AI systems have produced invented citations, fabricated details, or inaccurate context chains in generated text. This risk amplifies in high-stakes environments such as legal analysis, clinical summaries, and academic synthesis.
Considerations for Deployment and Governance
Effective use of AI summarization requires awareness of its limitations and deliberate strategies to mitigate potential errors.
Human Review and Validation
Especially for critical decisions or high-impact use cases (e.g., legal, medical, research summaries), human review remains indispensable. AI should augment, not replace, expert judgement.
Guideline: Always validate AI summaries with domain experts or cross-reference with original documents before finalising decisions.
Contextual Evaluation Metrics
Relying solely on automated metrics such as ROUGE or n-gram overlap may mislead users about summary quality. A combination of human evaluation, domain-specific checks, and multiple metrics offers a more complete picture of accuracy and usefulness.
Bias and Fairness Considerations
Language models can reflect and amplify biases present in their training data. This means summary outputs could inadvertently marginalise minority perspectives, misinterpret dialects, or skew interpretations if not properly audited.
Ensuring fairness requires testing with diverse datasets, regular audits, and employing models trained with balanced corpora.
Best Practices Matrix for High-Quality AI Summarization
The following matrix outlines recommended practices by category to manage accuracy and limitations effectively:
| Category | Best Practice | Expected Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Data Quality | Use high-quality, well formatted input text | Improves relevance and reduces context errors |
| Human Oversight | Combine AI output with expert review | Minimises factual and interpretive mistakes |
| Evaluation | Use both automated metrics and human judgement | Ensures coherence, depth, and factual integrity |
| Domain Training | Fine-tune models with domain-specific corpora | Boosts accuracy for specialised contexts |
| Ethics & Bias | Monitor for representation bias and fairness | Reduces skewed or discriminatory summary outputs |
| Iterative Feedback | Collect user feedback and refine models | Enhances performance and reliability over time |
Strategic Implications
AI summarization tools are powerful, but dependable deployment depends on careful integration with human expertise and robust evaluation frameworks. Users should treat AI summaries as starting points or aids, not definitive answers, particularly in domains where accuracy and nuance matter most.
The evolution of AI summarization — including advances in evaluation methods, multimodal context understanding, and domain-specific tuning — will continue to reduce limitations, but real-world deployment always requires balanced oversight and critical validation.
By understanding these accuracy issues, limitations, and considerations, organisations and individuals can better leverage AI summarization while mitigating risks, improving summary reliability, and aligning outcomes with intended uses.
7. Best Practices for Using AI Summaries
Effectively using AI-generated summaries requires more than simply running content through an algorithm. To get high-quality, reliable, and usable outputs from summarisation tools, organisations and individuals must combine well-defined processes, strategic configurations, and thoughtful integration of human expertise. Below is a detailed, SEO-optimised examination of best practices that ensure accuracy, relevance, and practical utility in AI summarisation.
Defining Clear Objectives and Audience Needs
Before applying an AI summariser, it is essential to clarify the purpose of the summary and who will use it.
Purpose-Driven Summarisation
Different objectives require distinct summarisation approaches:
- Executive Briefs: Focus on key decisions, financial figures, risks, and outcomes.
- Academic Literature Overviews: Prioritise methodological detail, context, and conclusions.
- Customer Feedback Synthesis: Highlight trending issues, sentiment patterns, and actionable insights.
By defining the intent, you can tailor the summarisation to deliver exactly what the audience expects, rather than a generic overview of the text.
Audience-Specific Detail Levels
Summaries for broader audiences should emphasise clarity and brevity, while technical audiences may require detail and domain-specific terminology. For example, an AI summary of a legal contract for lawyers differs from a general summary for business managers — optimize output based on these needs.
Crafting Effective Input and Prompt Instructions
AI summarisation quality is highly dependent on how you present the content and the instructions you give.
Clear and Precise Prompts
Precise instructions guide the AI model to produce targeted outcomes. Prompts should instruct on:
- Format: bullet points, paragraphs, executive highlights.
- Focus Areas: e.g., risks, action items, key results.
- Output Length: approximate summary size or specific word count.
Well-structured prompts help align output with your goals and reduce unhelpful or overly broad summaries.
Chunking Long Documents
When summarising lengthy source material that exceeds model context limits, divide the text into logical sections. Apply summarisation iteratively and then merge section summaries into a unified summary. This Map/Reduce strategy helps maintain contextual integrity.
Integrating Human Oversight and Review
AI summaries should not be considered final products without human quality checks, especially in contexts requiring accuracy and nuance.
Accuracy Validation
Human review is critical for:
- Fact checking, especially in sensitive fields like healthcare, law, and academic research.
- Contextual validation to ensure the summary captures implied meaning rather than superficial text patterns.
- Correction of hallucinations — AI models can sometimes invent plausible but inaccurate information, a phenomenon well-documented with generative tools.
By combining AI and human oversight, organisations can leverage speed while safeguarding quality.
Choosing the Right Summarisation Configuration
Different content types may require specialised configurations or hybrid methods.
Extractive vs. Abstractive Balance
Use extractive summarisation when precision and fidelity to original wording matter — for example, in legal or technical documentation. Abstractive methods work well when readability and narrative flow are important, such as summarising blog content or customer feedback. In some enterprise implementations, combining both approaches enhances both accuracy and readability.
Multi-Modal Summarisation
For content involving mixed formats, such as video lectures with slides or webinars with transcripts, use multi-modal summarisation techniques. These approaches help integrate text, audio, and visual cues into a comprehensive summary.
Iterative Refinement Workflow
Develop workflows that include iteration and refinement as part of the summarisation process.
Review and Improve Outputs
After generating a preliminary summary:
- Conduct a second round of summarisation focusing on precision or clarity.
- Use feedback loops (adjust prompts, refine instructions) to improve the next iteration.
- Perform comparative analyses between automated summaries and human-drafted summaries to spot gaps.
This iterative approach ensures that the summary evolves toward higher quality and relevance with minimal manual intervention.
Evaluation and Quality Metrics
Tracking quality through evaluation frameworks helps maintain high summarisation standards.
Evaluation Checklist
Evaluate each summary against these criteria:
- Coverage: Does the summary capture key components of the original?
- Alignment: Does it correctly reflect the source content?
- Clarity: Is the information easily understandable?
- Conciseness: Does it avoid redundancy while retaining key messages?
Implementing such metrics as part of QA processes in teams or automated pipelines helps maintain consistency and quality across summarisation tasks.
Best Practices Matrix for AI Summarisation
| Practice Category | Key Actions | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose & Audience | Define audience needs, tailor detail level | Higher relevance & user satisfaction |
| Prompt Engineering | Clear objectives, instruct format & focus | More accurate and targeted output |
| Chunking Strategy | Divide long texts and summarise sequentially | Maintains context and coherence |
| Human Oversight | Review summaries for accuracy and nuance | Reduced errors and improved reliability |
| Tech Configuration | Select extractive/abstractive/hybrid | Optimal balance of precision and readability |
| Evaluation Metrics | Coverage, alignment, clarity checks | Continual quality improvement |
Practical Implementation Examples
Sales Enablement Content
Marketing and sales teams can use AI summarizers to extract key product features and customer success points from lengthy interviews and case studies. By training AI to align outputs with brand voice, these summaries can subsequently be used across sales decks and marketing collaterals, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Educational and Research Summaries
For academic content, chunking complex research papers into smaller sections, then summarising and consolidating them, preserves contextual meaning and mitigates loss of depth. This method is particularly effective for literature reviews and systematic analyses where nuance and accuracy are paramount.
By following these best practices — from carefully crafting prompts to combining AI with human expertise and establishing quality evaluation frameworks — you can significantly enhance the effectiveness, accuracy, and operational value of AI-generated summaries across diverse use cases. These strategies ensure AI summarisation is not just fast, but also meaningful, reliable, and aligned with organizational goals.
8. Future Trends in AI Summarisation
Longer-context summarisation for “book-length” inputs
- What’s changing
- Summarisation is moving from “single-article length” to long-document and even corpus-level summarisation as model context windows expand and long-context engineering improves.
- Research is also clarifying a key nuance: a larger context window does not automatically mean better long-document understanding; performance can degrade with very long prompts unless you use strong retrieval, structuring, or chunking strategies.
- Why it matters
- Enables practical summarisation of contracts, technical manuals, policy binders, multi-hour transcripts, and multi-quarter reporting packs without heavy manual pre-editing.
- Practical example
- A legal team summarises a 300-page vendor agreement by generating section summaries (definitions, liability, termination) and then producing an executive “risk brief” that highlights non-standard clauses and negotiation priorities.
Long-context reality check table
| Trend | Opportunity | Known challenge | Recommended pattern |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bigger context windows | Summarise longer inputs in one pass | Long inputs can still reduce model accuracy | Use structured prompting + section chunking + synthesis layer |
| Long-document summarisation research | Better methods tuned for long sequences | Evaluation and factuality remain hard | Combine semantic evaluation + human checks for high-stakes outputs |
Evaluation is shifting from word overlap to semantic and factual measures
- What’s changing
- Industry and research are steadily moving beyond ROUGE-style overlap scoring toward semantic metrics that better capture meaning, especially for abstractive summaries.
- Why it matters
- As summaries become more generative, you need evaluation that flags:
- Meaning drift (summary says the opposite)
- Missing critical details
- Unsupported claims
- As summaries become more generative, you need evaluation that flags:
- Practical example
- A product team validates release-note summaries using a semantic metric (to check meaning alignment) plus a factual checklist (to ensure version numbers and deprecations match the source).
Quality measurement matrix
| Output risk | Best-fit metric / check | What it catches | Where it’s most useful |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paraphrase changes meaning | Semantic similarity scoring (e.g., BERTScore) | Meaning drift despite different wording | Abstractive summaries, marketing briefs |
| Missed key points | Coverage rubric + human spot checks | Omitted constraints, caveats, exceptions | Legal, compliance, research |
| Unsupported statements | Source-grounding review | Hallucinated details | High-stakes decision support |
Hybrid pipelines will become the default in enterprise summarisation
- What’s changing
- Large organisations increasingly prefer hybrid summarisation pipelines that combine:
- Retrieval / extraction of key evidence
- Abstractive synthesis for readability
- Guardrails (format, scope, verification steps)
- Recent reviews of long-document summarisation note rising use of hybrid approaches alongside improved evaluation practices.
- Large organisations increasingly prefer hybrid summarisation pipelines that combine:
- Why it matters
- Hybrids reduce risk while keeping summaries usable:
- Better factual fidelity than pure abstractive
- Better readability than pure extractive
- Hybrids reduce risk while keeping summaries usable:
- Practical example
- A compliance team generates:
- An extractive “evidence pack” with exact clauses
- An abstractive “executive summary” that explains impact and required actions
- A compliance team generates:
Enterprise summarisation architecture snapshot
| Layer | Typical capability | Output artifact |
|---|---|---|
| Retrieval / extraction | Pull most relevant sections, tables, clauses | Evidence bullets and citations |
| Synthesis | Rewrite and compress into narrative | Exec summary, brief, action list |
| Validation | Checks for missing constraints and mismatches | QA checklist, exception flags |
On-device summarisation for privacy-first workflows
- What’s changing
- Summarisation is moving onto devices for certain use cases, improving privacy and responsiveness. A visible example is Firefox for iOS introducing “shake to summarise,” designed to generate page summaries with a quick gesture.
- Why it matters
- On-device summarisation can reduce exposure of sensitive content and improve latency, especially for personal browsing and lightweight workplace content.
- Practical example
- A clinician uses on-device summarisation for non-identifiable medical education articles during rounds, while patient-specific documentation stays within approved clinical systems.
On-device vs cloud summarisation decision table
| Criteria | On-device tends to win | Cloud tends to win |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy posture | Better for sensitive content and local-first workflows | Depends on vendor controls and policies |
| Model capability | Best for lighter summaries and constrained contexts | Better for heavy reasoning, long documents |
| Cost profile | Lower marginal cost at scale | Usage-based, scales with volume |
Regulation and transparency requirements will shape summarisation UX
- What’s changing
- Regulation is pushing clearer disclosure when users interact with AI or encounter AI-generated content. EU AI Act transparency obligations (Article 50) emphasize informing people when they are interacting with AI systems and addressing labeling for synthetic content.
- Why it matters
- Summarisation experiences will increasingly include:
- AI disclosure prompts
- “How this summary was made” notes
- Provenance indicators (what sources were used)
- Summarisation experiences will increasingly include:
- Practical example
- An internal knowledge base shows: “AI-generated summary” plus clickable evidence snippets from the original policy sections for auditability.
Market expansion will accelerate summarisation feature adoption
- What’s changing
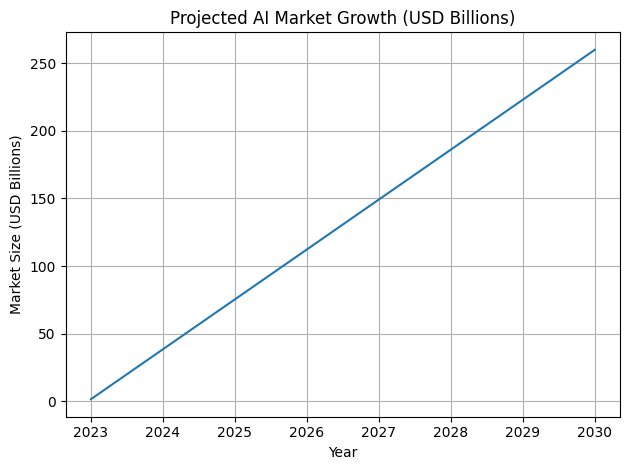
- Strong market growth projections point to continued investment in summarisation across productivity suites, browsers, and enterprise platforms:
- UNCTAD cites a projection of the AI market growing from $189B (2023) to $4.8T (2033).
- ABI Research estimates the AI software market at $122B (2024), reaching $467B (2030) at a 25% CAGR, with generative AI noted as the fastest-growing framework at 34.5% CAGR.
- IDC-linked reporting projects AI could contribute $19.9T cumulatively to the global economy through 2030, with a $4.9T contribution in 2030 (per the reported study).
- Strong market growth projections point to continued investment in summarisation across productivity suites, browsers, and enterprise platforms:
- Why it matters
- As AI investment rises, summarisation becomes a default capability in:
- Document tools
- Collaboration platforms
- Search experiences
- Vertical software (legal, healthcare, finance)
- As AI investment rises, summarisation becomes a default capability in:
Trend impact matrix
| Trend | What you’ll see in products | What it enables |
|---|---|---|
| Longer context + better long-doc methods | “Summarise this report” for very large files | Faster reviews of complex documents |
| Semantic evaluation + factual guardrails | Built-in “confidence” and verification steps | Safer summaries in high-stakes workflows |
| On-device summarisation | Local summarise buttons in browsers and apps | Privacy-first summarisation for everyday use |
| Transparency and labeling requirements | Clear AI disclosures and provenance indicators | Greater trust and compliance readiness |
What to watch next
- Summaries that are “interactive”: ask follow-ups like “expand risks only” or “show supporting paragraphs.”
- More reliable long-document handling via structured inputs and evidence-first pipelines, acknowledging that long context alone is not a silver bullet.
- Compliance-ready summarisation that bakes in transparency disclosures and content labeling by default.
Conclusion
Artificial-intelligence-generated summaries represent a significant evolution in how humans interact with, process, and understand large volumes of information. At their core, AI summaries leverage advanced machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) to condense lengthy content — whether text, audio, or video — into short, coherent, and meaningful representations of core ideas. This capability enables readers to rapidly grasp the most important insights without manually reviewing every detail of the original content, addressing one of the most persistent challenges of the digital age: information overload.
Across various sectors — from business intelligence and research to customer support and legal analysis — AI summarization tools have proven instrumental in accelerating workflows, enhancing decision-making, and supporting collaborative knowledge work. By analyzing linguistic patterns, semantic structures, and relevant context, these tools can extract, condense, and reframe key concepts in ways that are both efficient and useful for diverse audiences.
The mechanics behind AI summaries span extractive methods, which pull salient sentences directly from source material, to abstractive techniques, which generate entirely new language that captures meaning in a more natural and reader-friendly way. Hybrid solutions further combine these methods to balance fidelity with fluency. Over time, advances in large language models (LLMs) have significantly improved quality and versatility, enabling summarization not only of longer documents but also across multiple sources and data formats.
Understanding these approaches — and the underlying technologies of NLP and machine learning — is essential for assessing the capabilities and limitations of AI-generated summaries. While these systems dramatically reduce the time required to process information, they are not perfect; accuracy can vary based on input quality, domain complexity, and contextual nuance. This makes human oversight and thoughtful application crucial in professional and research environments.
Looking ahead, the future of AI summarization is poised for deeper integration into everyday tools and workflows. Innovations such as multi-modal summarization that integrates text with audio and video cues, interactive summarization where users can guide focus and length, and personalized summaries tailored to individual use cases are already emerging trends. Similarly, on-device capabilities — such as browser and mobile features that generate summaries in real time — illustrate how summarization is shifting from specialised software to mainstream productivity functionality.
Ultimately, AI-generated summaries are more than a convenience; they represent an essential adaptation to the pace and scale of information production in the modern world. When used strategically and responsibly, they empower professionals, students, and everyday users to work smarter, respond faster, and make more informed decisions. Whether deployed in enterprise systems, research platforms, or personal devices, AI summarizers are reshaping how people access meaning in a world increasingly defined by data.
If you are looking for a top-class digital marketer, then book a free consultation slot here.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your friends and business partners, and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the AppLabx Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to the AppLabx Blog.
People also ask
What are AI-generated summaries?
AI-generated summaries are concise versions of longer content created using artificial intelligence. They use natural language processing and machine learning to extract or generate key points from documents, articles, transcripts, or reports.
How do AI-generated summaries work?
AI summaries work by analyzing text with NLP models that identify important sentences, themes, and relationships. They either extract key parts of the original text or generate new condensed versions based on meaning.
What is the difference between extractive and abstractive summarization?
Extractive summarization selects exact sentences from the source text, while abstractive summarization rewrites the content in new words. Extractive focuses on accuracy, while abstractive focuses on readability and natural flow.
What is natural language processing in AI summarization?
Natural language processing, or NLP, enables AI systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It helps summarization models identify context, meaning, and important information within large text blocks.
Can AI-generated summaries replace human-written summaries?
AI summaries can save time and improve efficiency, but they may lack nuance or deep contextual understanding. Human review is recommended for high-stakes content like legal, medical, or academic materials.
Are AI summaries accurate?
AI summaries are generally accurate for straightforward content, but they can occasionally miss context or generate errors. Accuracy depends on model quality, input clarity, and the complexity of the source text.
What types of content can AI summarize?
AI can summarize articles, research papers, legal documents, meeting transcripts, emails, customer reviews, and even audio or video content when paired with transcription tools.
How do large language models help in summarization?
Large language models analyze patterns in massive text datasets. They understand context and semantics, enabling them to produce fluent, meaningful summaries rather than simply extracting sentences.
What are the benefits of AI text summarization?
AI summarization reduces reading time, improves productivity, minimizes information overload, and supports faster decision-making by highlighting key insights from lengthy documents.
Can AI summarize multiple documents at once?
Yes, multi-document summarization combines insights from several sources into one cohesive summary. This is useful for news aggregation, research synthesis, and large-scale data analysis.
Is AI summarization useful for businesses?
Businesses use AI summaries to streamline reporting, analyze customer feedback, summarize meetings, and review contracts, helping teams save time and improve operational efficiency.
How does AI handle long documents?
AI models process long documents using extended context windows or chunking techniques. They may summarize sections individually before combining them into a final comprehensive summary.
What are AI summary hallucinations?
Hallucinations occur when AI generates information not present in the source text. This can happen in abstractive models and requires human review for critical applications.
Can AI summaries be customized?
Yes, many tools allow users to control summary length, focus areas, tone, and format, enabling tailored outputs for executive briefs, academic overviews, or technical reports.
How is AI summarization evaluated?
AI summaries are often evaluated using metrics like ROUGE, which compares word overlap with reference summaries. Human evaluation is also important to assess clarity and factual accuracy.
Is AI summarization safe for sensitive data?
Safety depends on the platform used. Organizations should ensure compliance with data protection regulations and choose secure, enterprise-grade AI tools for confidential content.
What industries use AI-generated summaries?
Industries including healthcare, finance, legal, education, marketing, customer support, and research use AI summarization to process large volumes of information efficiently.
Can AI summarize audio and video content?
Yes, when combined with speech-to-text technology, AI can transcribe audio or video and generate summaries highlighting key points and action items.
What is real-time AI summarization?
Real-time summarization generates condensed insights from live meetings, webinars, or streaming data, helping users stay updated without reviewing full transcripts.
Does AI summarization improve productivity?
AI summarization significantly reduces the time spent reading lengthy documents, allowing professionals to focus on strategic tasks and decision-making.
What are hybrid AI summarization models?
Hybrid models combine extractive and abstractive techniques, first selecting key content and then rewriting it for clarity, balancing accuracy with readability.
How does AI reduce information overload?
By condensing large amounts of text into clear summaries, AI helps users quickly understand essential insights without processing unnecessary details.
Can AI summarize research papers accurately?
AI can summarize research papers effectively, but technical nuance may sometimes be simplified. Researchers should review summaries for completeness and precision.
What is query-focused summarization?
Query-focused summarization generates summaries tailored to a specific question or topic, extracting only the most relevant information from the source material.
How do transformer models support summarization?
Transformer models use attention mechanisms to understand relationships between words in context, enabling more coherent and context-aware summaries.
Are AI-generated summaries SEO-friendly?
AI summaries can be SEO-friendly if they include relevant keywords and maintain clarity. However, human optimization may still be needed for best search performance.
What are the limitations of AI summarization?
Limitations include potential hallucinations, loss of nuance, difficulty with complex language, and dependence on input quality and model training data.
Can AI summaries help with meeting notes?
Yes, AI can automatically summarize meeting transcripts, extract action items, and highlight decisions, reducing manual note-taking efforts.
How does AI summarization support decision-making?
By presenting concise insights from detailed reports or data, AI summaries help leaders quickly assess information and make informed decisions.
What is the future of AI-generated summaries?
Future advancements include multi-modal summarization, improved accuracy, larger context windows, and more personalized, interactive summary generation.
Sources
Genesys
ShareFile
Enago
Wikipedia
IBM
DigitalOcean
Obot.ai
Box
Slack
Microsoft
AWS
Microsoft Learn
CASMI Northwestern
Socialnomics
PayPal
Zoom
Dialpad
Monday.com
SciSpace
The Verge
Narrato
Medium
arXiv
Galileo
Clarifai
TitanCorp
AlleyCorp Nord




































